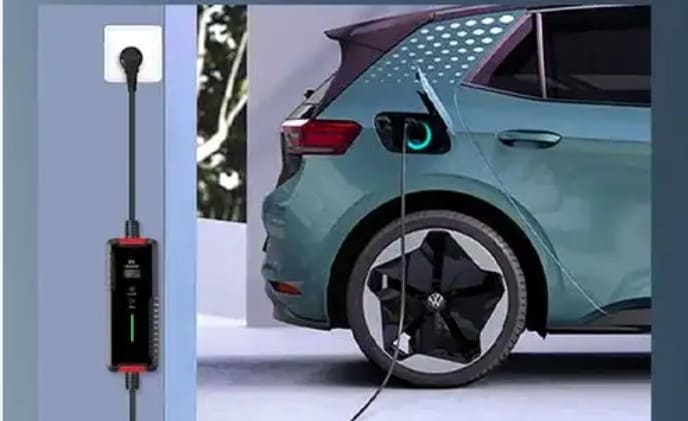
Where to install ev charger at home?

Installing an EV Charger at Home: Guidelines and Considerations
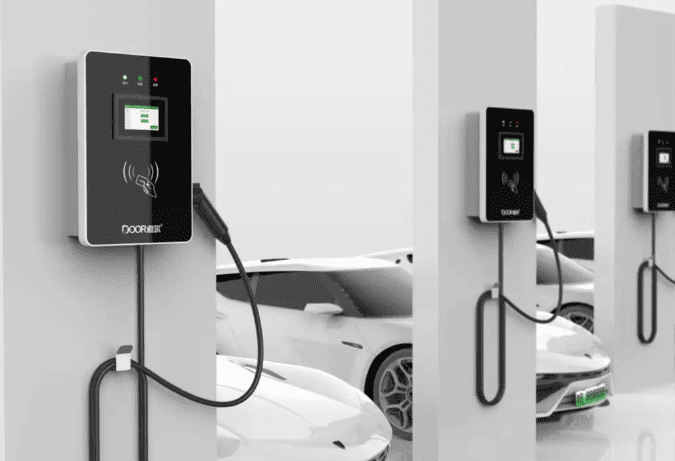
An EV charger at home should be installed in a fixed parking space, preferably a privately owned one. The basic requirements for installing a home charging station include:
- Parking Space Ownership or Long-Term Usage Rights: Proof of ownership or a long-term lease agreement (typically at least one year) for the parking space is required.
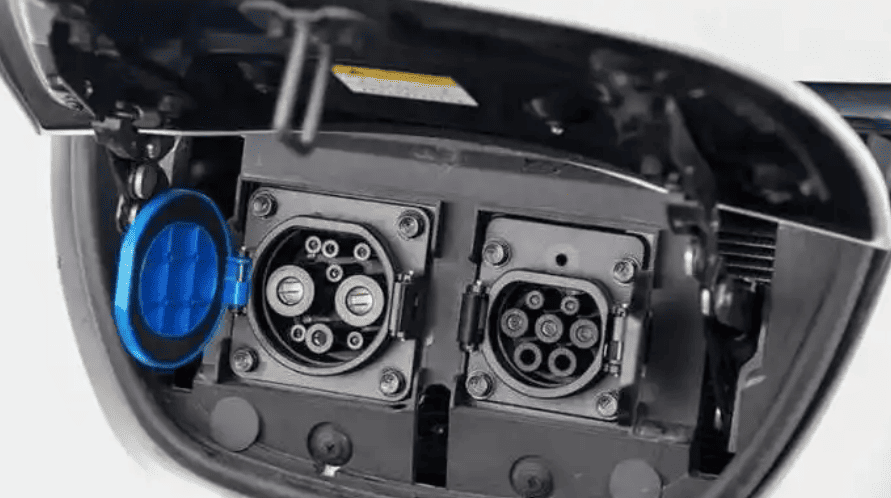
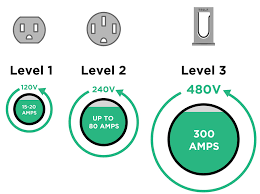
- Power Capacity Assessment: The residential power system must have sufficient capacity to support the additional charger. Older communities may require an electrical assessment. A 7kW charger typically requires a single-phase meter, while 11kW or higher requires a three-phase meter.
- Property Management Approval: Written consent from the property management is necessary.
- Vehicle Purchase Proof: Documentation such as the EV purchase invoice, vehicle registration, or license plate certificate must be provided.
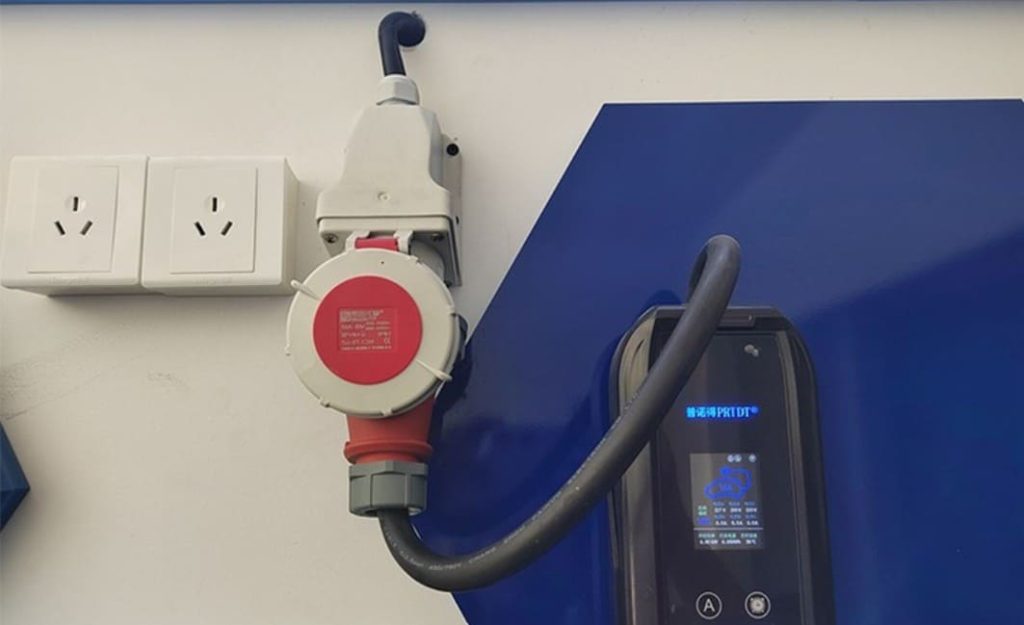
- Installation Location Requirements: The charger should avoid fire exits and public facilities, maintaining a safe distance from surrounding structures. For underground parking, waterproofing and moisture-proofing measures must be considered.
Steps to Install a Home Charging Station:
- Pre-Purchase Consultation: Before buying an EV, consult with property management about installation feasibility and assess whether a 220V or 380V meter is needed.
- Prepare Application Materials: These include a copy of your ID, proof of parking space ownership or lease agreement, property management approval, EV purchase documents, and the charger’s technical specifications (provided by the manufacturer).
- Submit an Electricity Application: Apply online via State Grid’s “Online State Grid” app or Southern Grid’s “Southern Grid Online” app, or visit a local power supply office in person.
- Charger Installation: After approval, the power company will arrange professional installation.
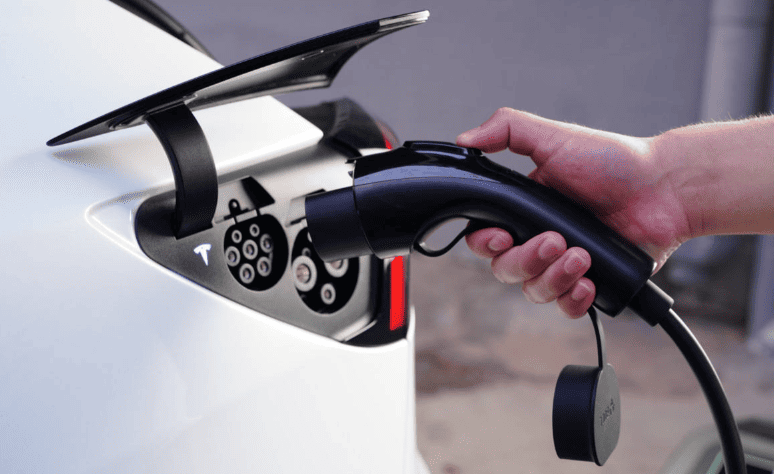
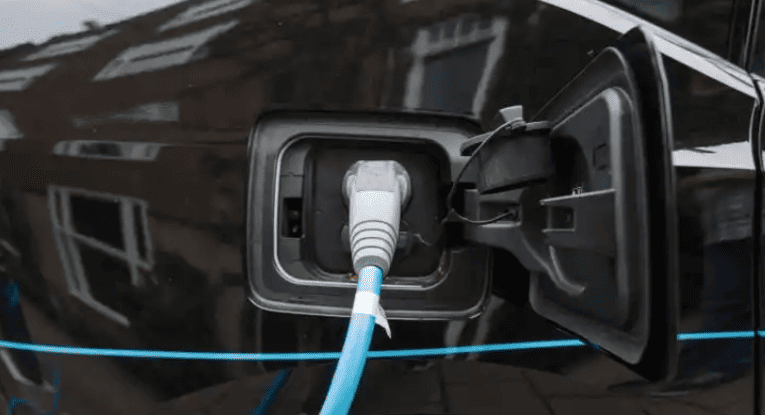
Can Electric Cars Be Charged at Home?
Currently, most EVs can be charged at home using a standard 220V outlet (slow charging). While slower, this method is gentler on the battery and suitable for overnight charging. However, safety precautions are essential.
Key Points for Home Charging:
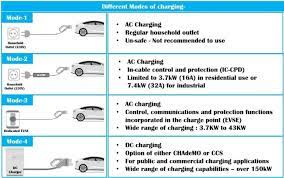
- Use a 16A Outlet: For higher power (3.5 kW), use a 16A outlet (like those for air conditioners). Standard 10A outlets (2.2 kW) are slower.
- Extension Cord Selection: If needed, use a 16A-rated, waterproof, and durable extension cord (2.5–4 sq. mm cross-section).
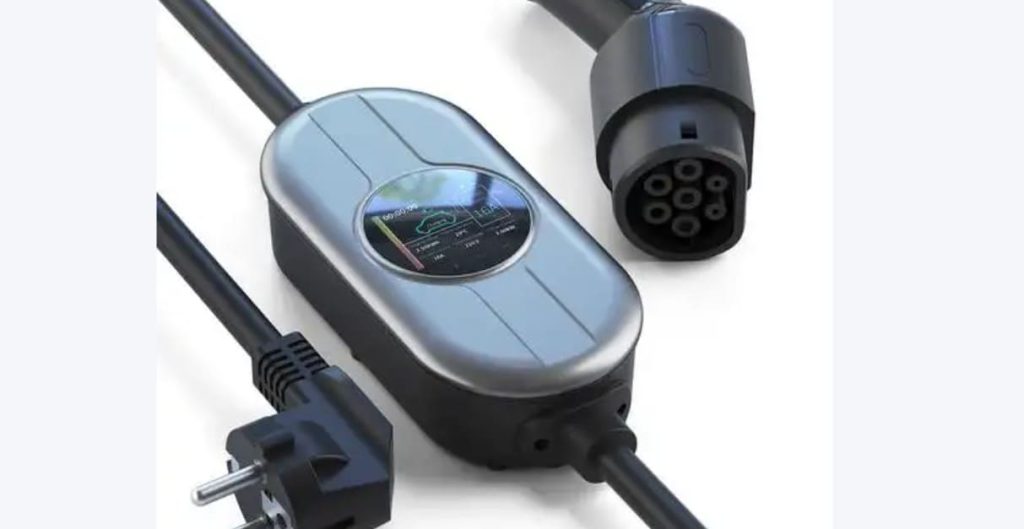
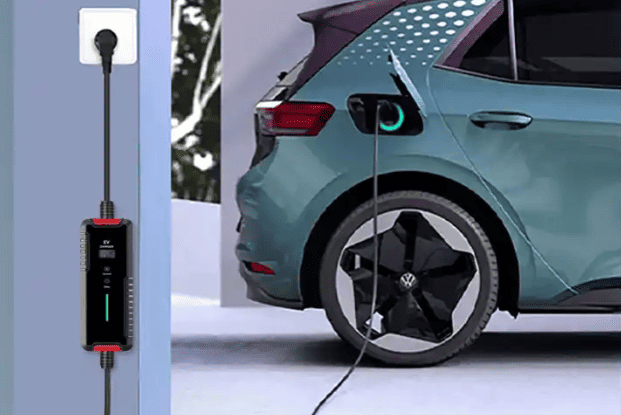
- Portable Charger Options: Factory-included chargers (e.g., 1.6 kW) are slow. For faster charging, consider third-party options like Prudent’s portable charger (3.5 kW on 16A outlets, 2.2 kW on 10A outlets).
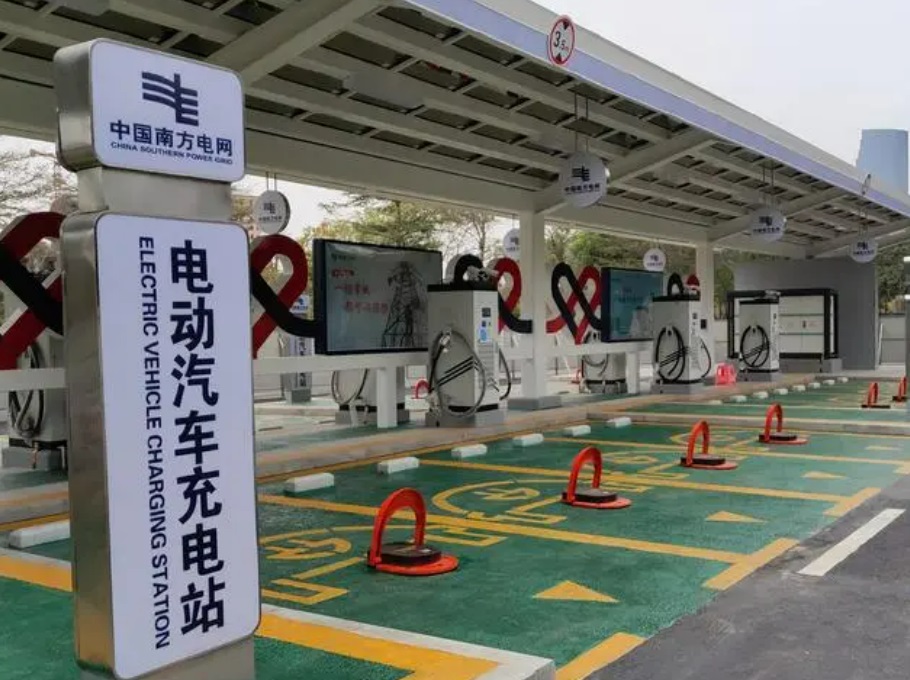
Alternative to Charging Stations:
A portable charger (e.g., Prudent’s dual-mode 7kW/11KW charger) can be a flexible solution, especially where fixed stations aren’t allowed. It works with both 16A and 10A outlets via adapters and is ideal for travel or multi-location use.
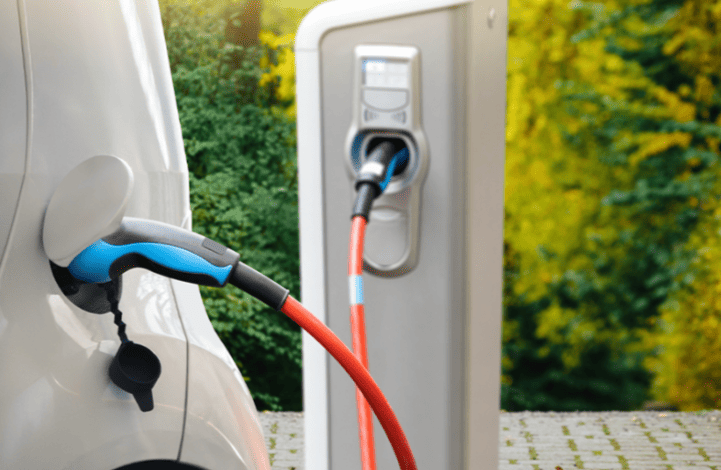
Comprehensive Guide to Home or EV Charger Installation
With the rise of EVs, home charger installation has become a priority. This guide breaks down the process:
I. Prerequisites
- Parking Space: Ownership or a lease of ≥1 year.
- Power Capacity: Older buildings may need upgrades (7kW = single-phase; 11kW+ = three-phase).
- Property Approval: Management must consent (legally, they cannot unreasonably refuse).
- EV Documentation: Purchase/registration proof.
- Location Safety: Avoid obstructions; waterproofing for underground spots.
II. Installation Steps
- Pre-Purchase Check: Confirm feasibility with property management.
- Gather Documents: ID, parking proof, property approval, EV docs, charger specs.
- Apply for Power: Online (via utility apps) or offline (local office). Specify “EV charging” for preferential rates.
- Site Inspection: Power company checks wiring paths and capacity within 1–3 days.
- Installation: Professionals install the meter and charger (2–4 hours).
- Inspection & Use: Final approval by power company and property management.
III. Key Considerations
- Overcoming Property Resistance: Provide safety certifications, propose clean wiring plans, or escalate complaints if needed.
- Meter-Charger Match: 7kW (single-phase) suits most homes; 11kW (three-phase) is faster but harder to approve.
- Cabling: Use 6 sq. mm copper for 7kW; 10 sq. mm for 11kW.
- Brand Choice: Opt for OEM or certified brands (e.g., Star Charge, Teld, Zhida). Costs: 2,000–5,000 RMB (+ installation).
- Maintenance: Regular checks for wear, avoid storms, monitor heat.
IV. FAQs
- If Property Refuses: Seek reasons, offer solutions (e.g., load-sharing), or complain to housing authorities.
- No Fixed Parking?: Explore shared community chargers or portable options.
- Costs: ~3,000–7,000 RMB total (charger + installation + cables). Some areas waive meter fees.
- Outdoor Installation: Use IP54-rated units with weather protection.
- Power Impact: 7kW equals 3 AC units; charge during off-peak or get a dedicated meter.
V. Usage Tips
- Off-Peak Charging: Save 50% by charging overnight (10 PM–8 AM).
- Battery Care: Charge to 80–90%; avoid dropping below 20%.
- Sharing Economy: Rent out your charger via apps like Star Charge.
- Smart Features: Use app-enabled chargers for remote monitoring.
- Maintenance: Biannual checks for cable wear and connector cleanliness.
Conclusion
While the process may seem daunting, systematic planning ensures success. Home charging offers unmatched convenience—plug in overnight, wake up to a full battery. As policies improve and property managers adapt, barriers are fading. Address charging needs before buying an EV to fully enjoy its benefits. Persistence pays off: collaborate with stakeholders, and don’t hesitate to seek official support. Embrace “charging freedom” and green mobility!
Read More: How to pack ev charger?