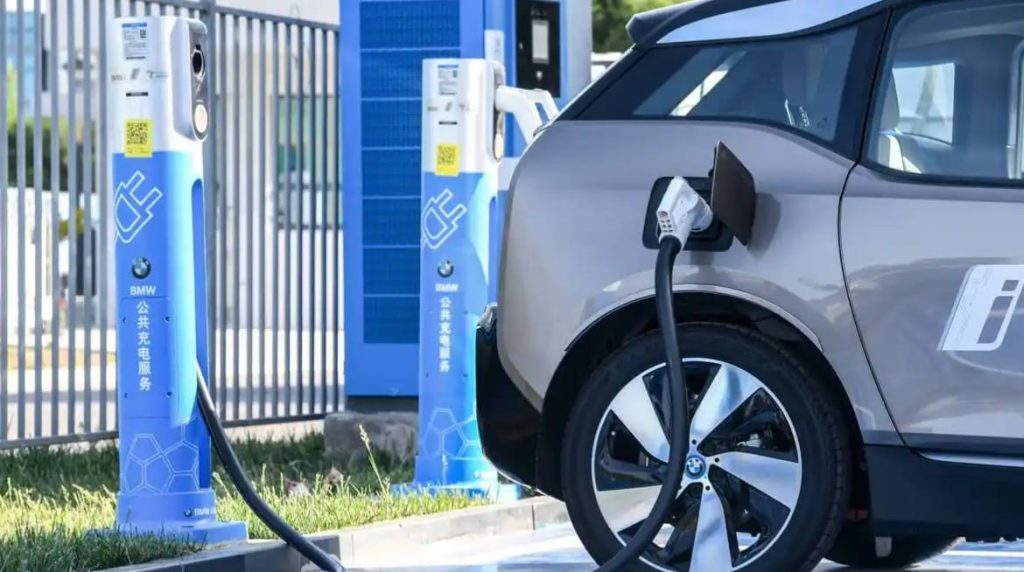How to use ev charging stations?

How to use ev charging stations? Planning, physical connection, payment activation, monitoring, and safe disconnection are the five essential steps involved in using an electric vehicle (EV) charging station, with significant regional variations. Being aware of these subtleties as a global manufacturer guarantees that your goods satisfy the demands of regional consumers. We deconstruct the procedure for the main markets below, combining safety procedures and technical standards.
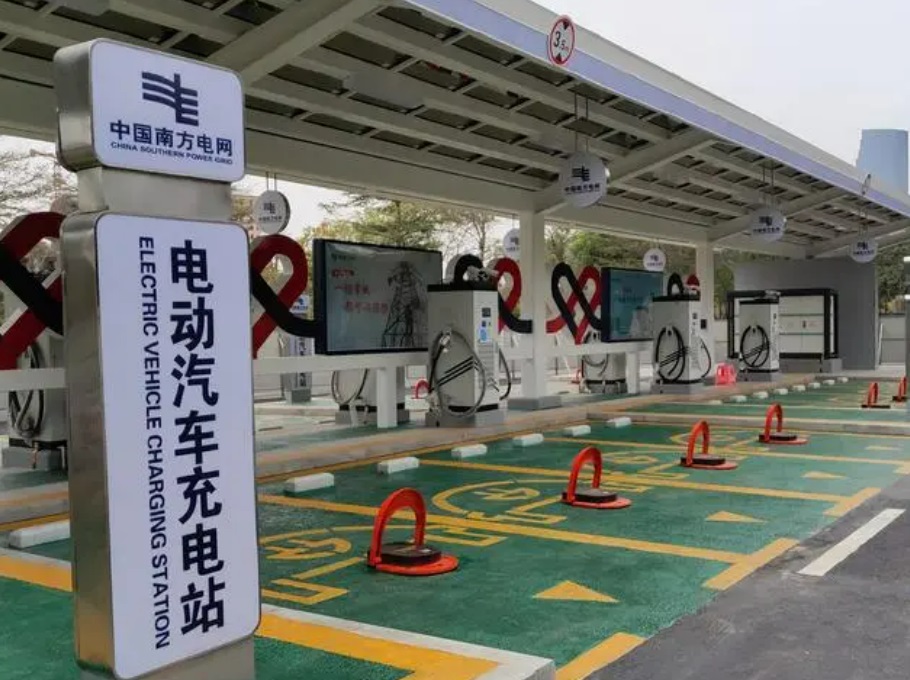
Step 1: Pre-Charging Planning and Station Selection
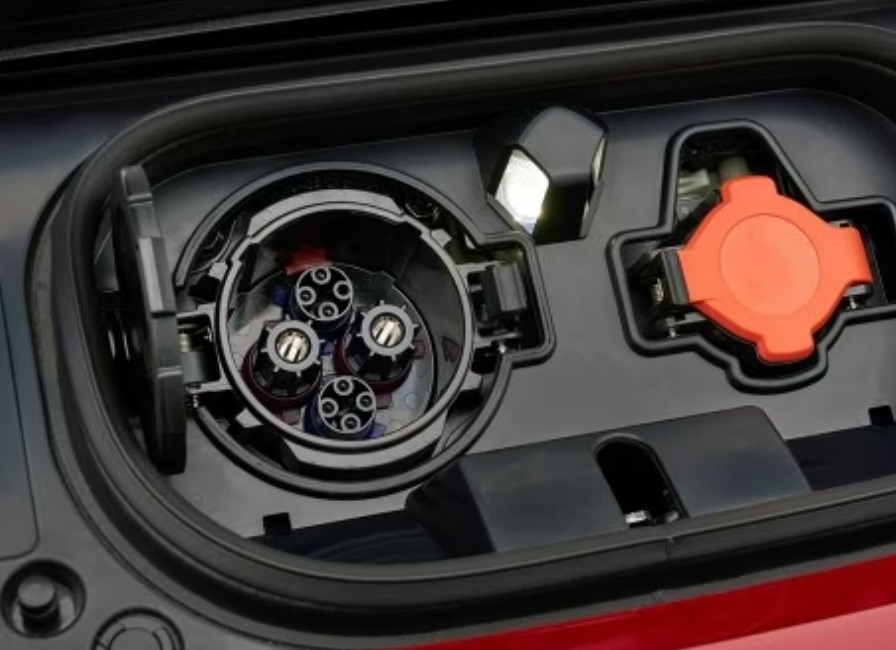
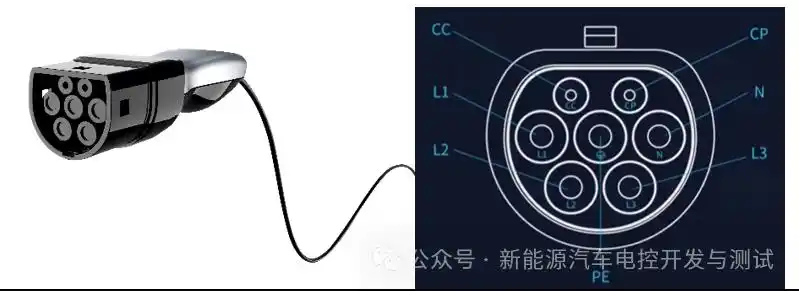
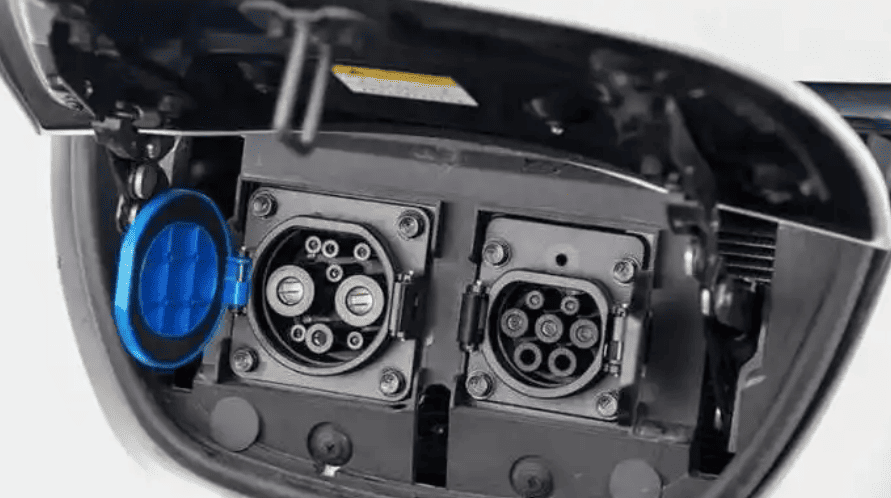
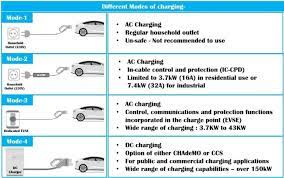
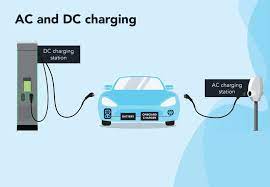
Before heading to a charging station, compatibility checks and route planning are essential. Start by confirming your vehicle’s charging port type: North American models typically use CCS Combo 1 or Tesla’s proprietary connector; European EVs require Type 2 (Mennekes); Japanese cars often support CHAdeMO or Type 2. Mismatched ports will halt your charging session.
Next, assess your power needs. A DC fast charger (50–350 kW) adds 100–300 km of range per hour but costs more and stresses batteries. AC slow chargers (7–22 kW) are gentler and cheaper but take 4–8 hours for a full charge. Use apps like PlugShare (global), ChargePoint (US), or e-Mobility Power (Japan) to find stations with:
- Real-time availability
- Supported plug types
- Payment methods (e.g., contactless cards, app-only)
- Amenities (restrooms, cafes) during long charges
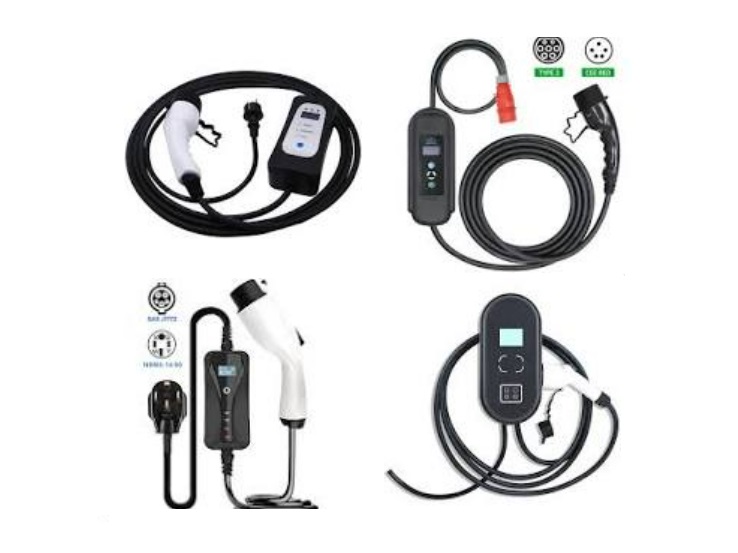
Pro Tip for Manufacturers: Design chargers with dual cables (e.g., CCS + CHAdeMO in Japan) to broaden compatibility.
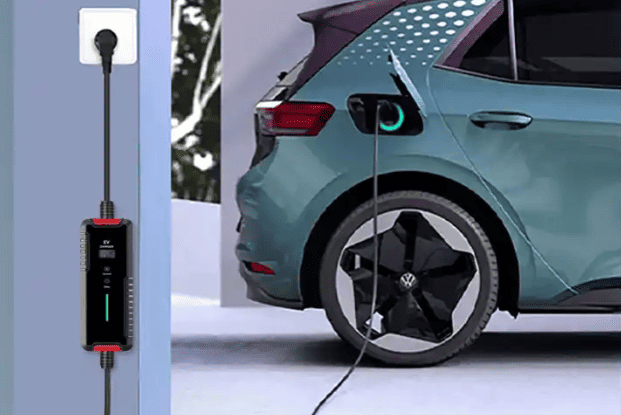
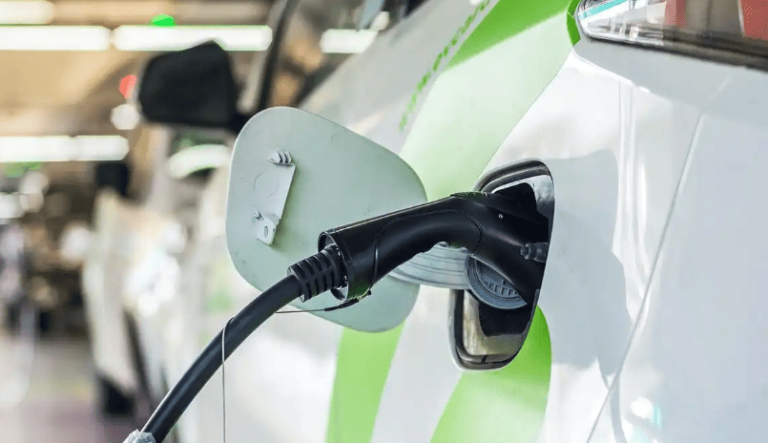
Step 2: Physical Connection – Universal Steps with Regional Tweaks
Once parked, follow these hardware-handling protocols:
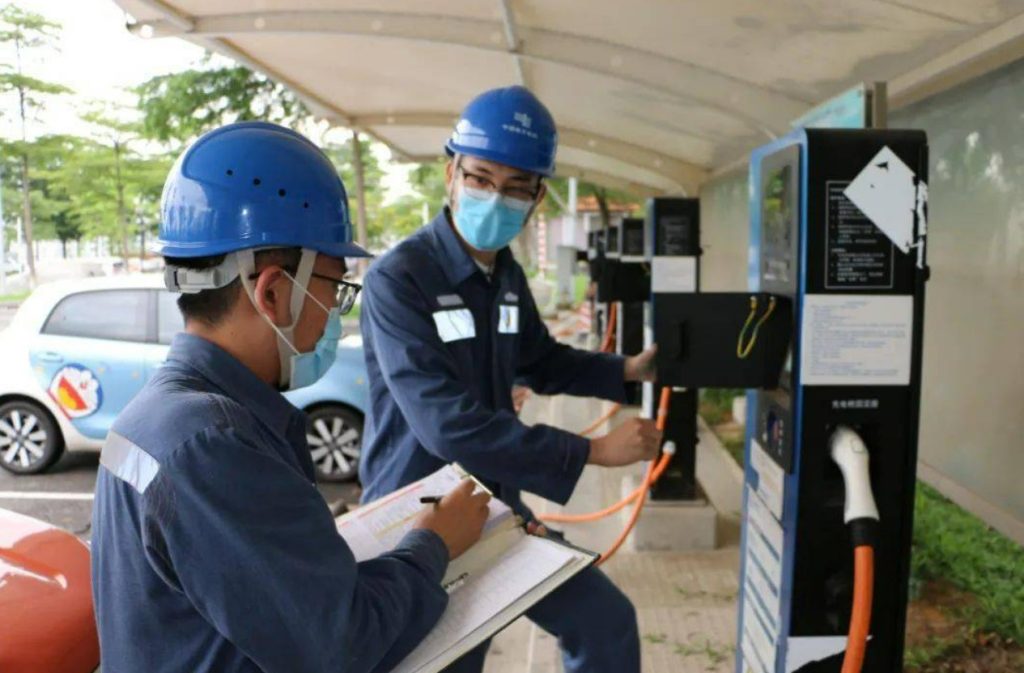
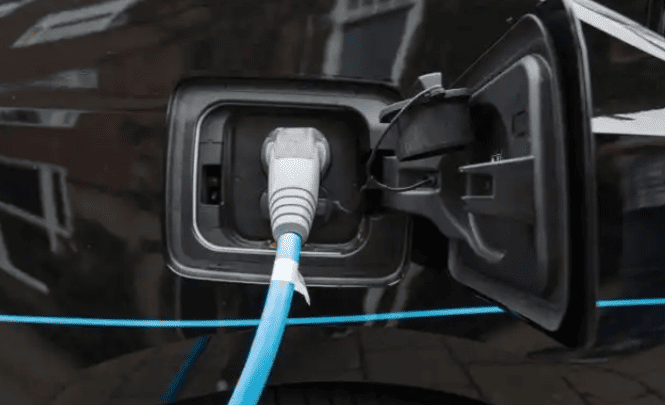
- Position your vehicle: Align the charging port within 1–2 meters of the charger. Engage the parking brake and power off the vehicle (mandatory in South Korea).
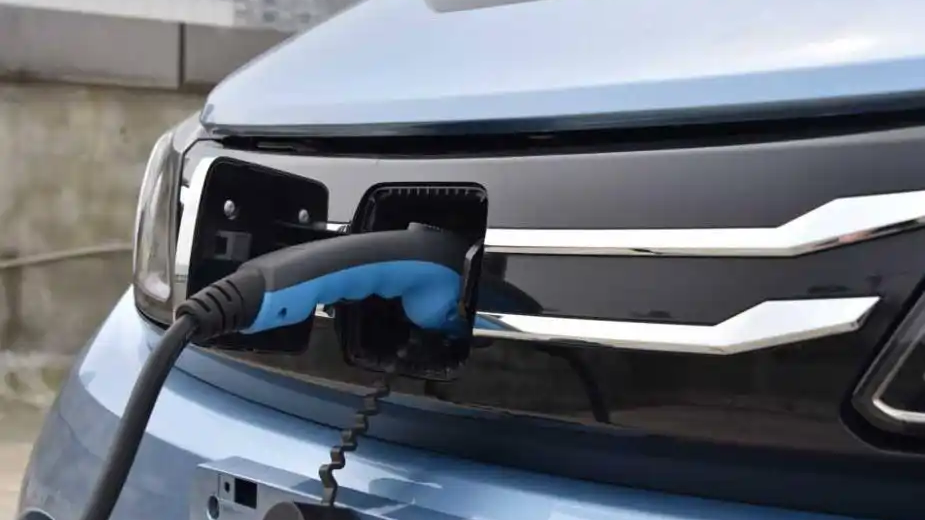
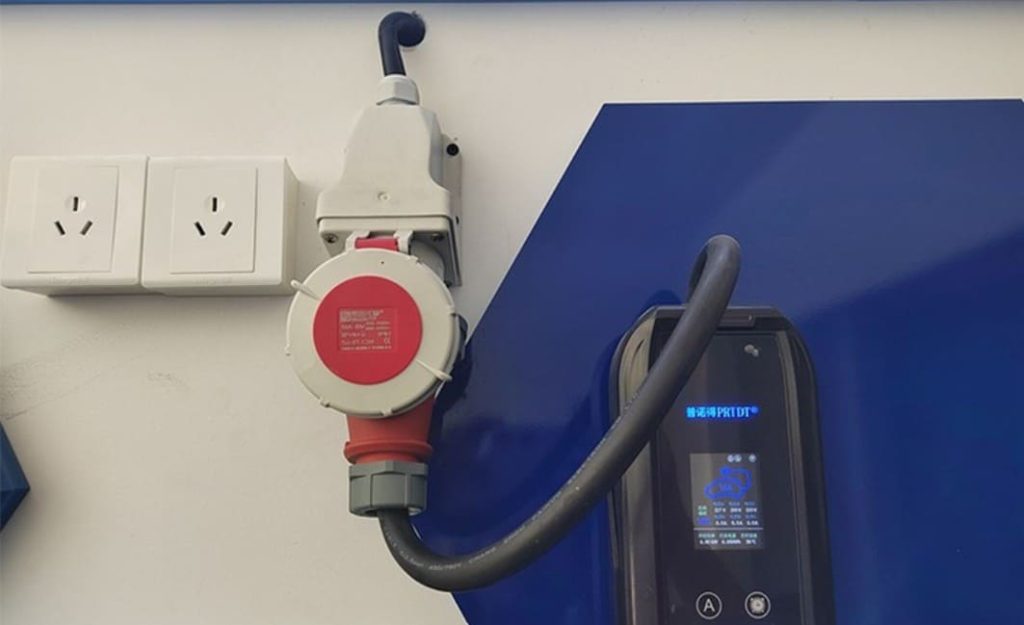
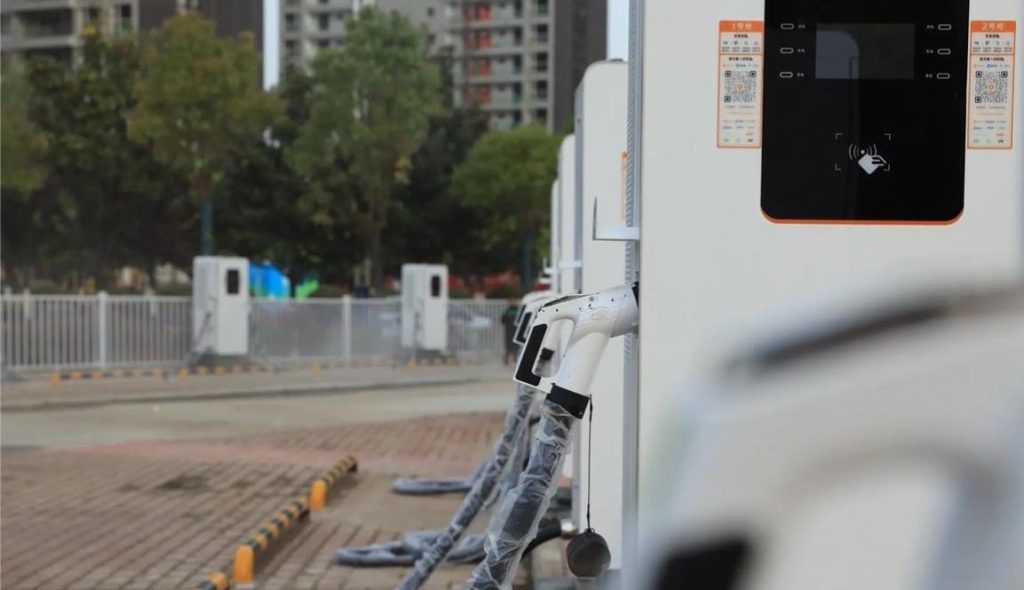
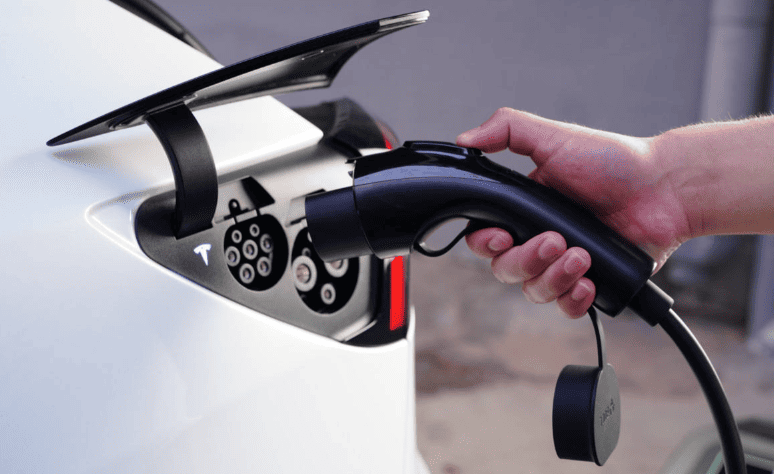
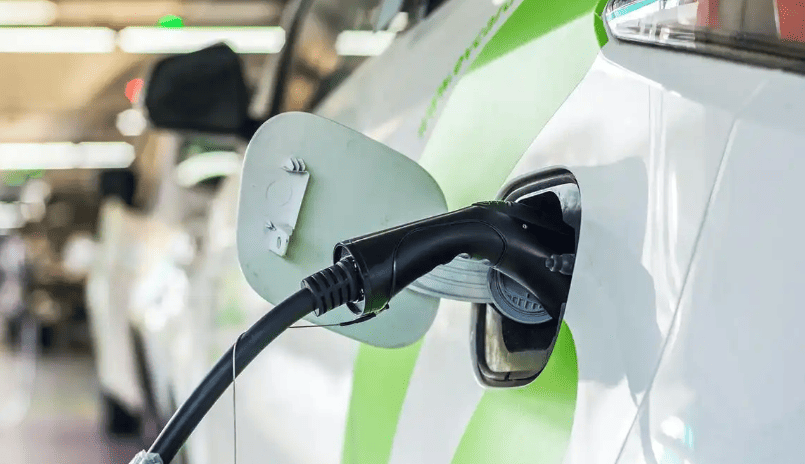
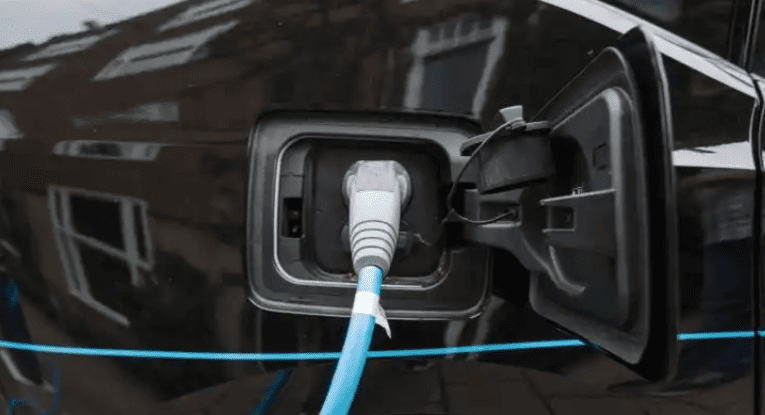
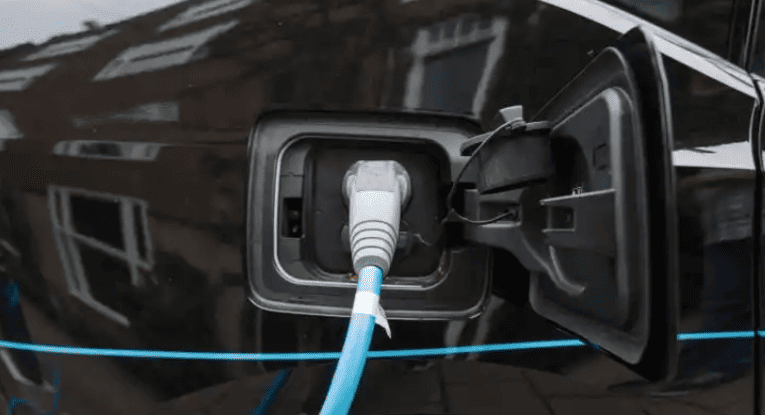
- Unlock the charging port: Use your key fob, dashboard button, or manual release lever (location varies—Tesla’s is near the taillight; Hyundai’s is behind a front grille).
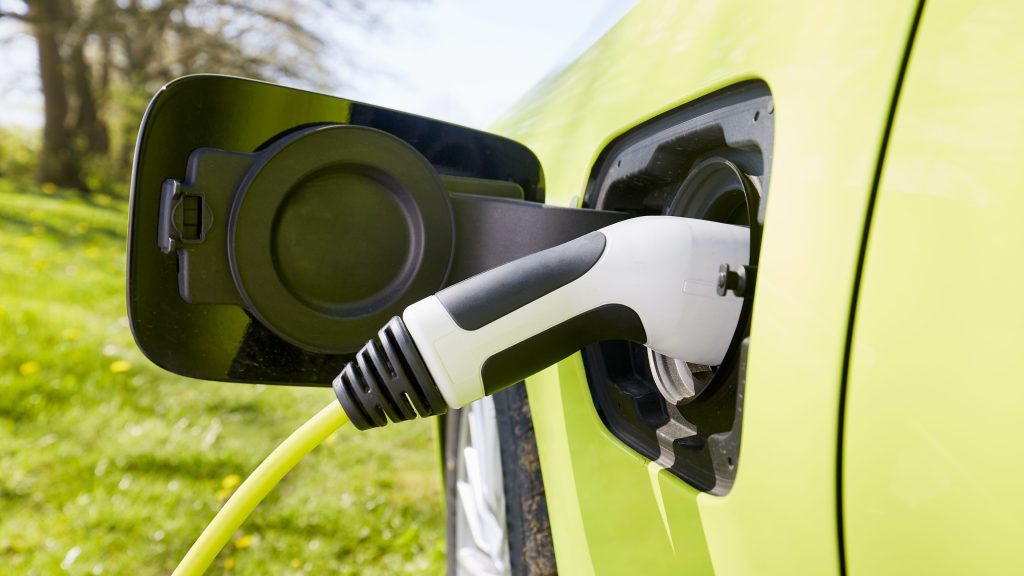
- Inspect and connect:
- Wipe debris/moisture from the plug and port (critical in humid climates like Thailand).
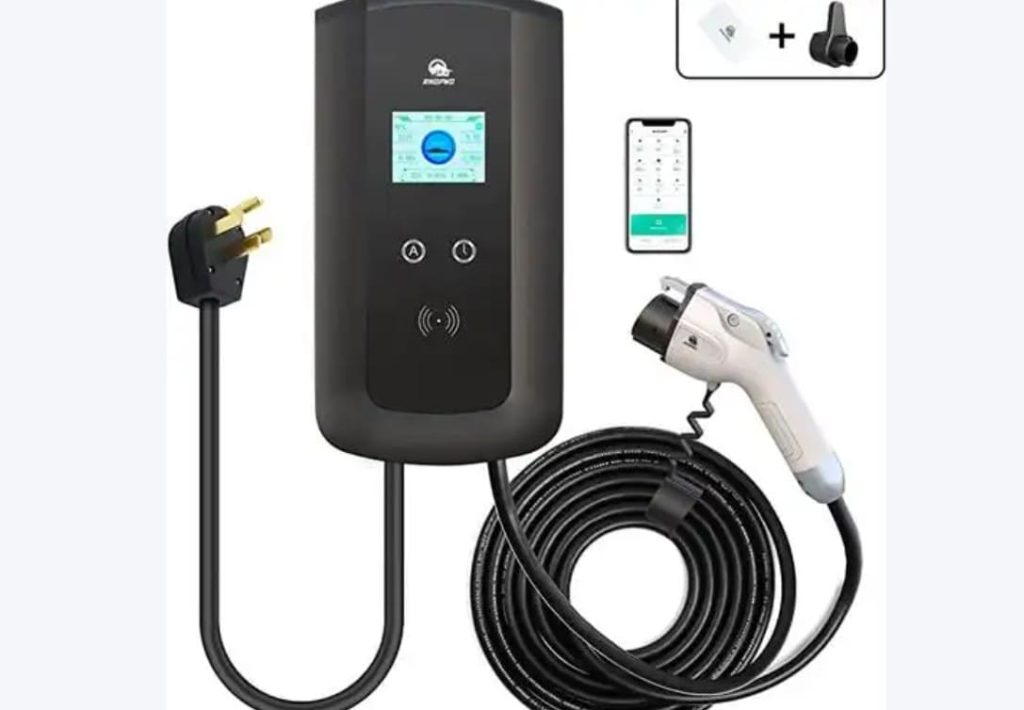
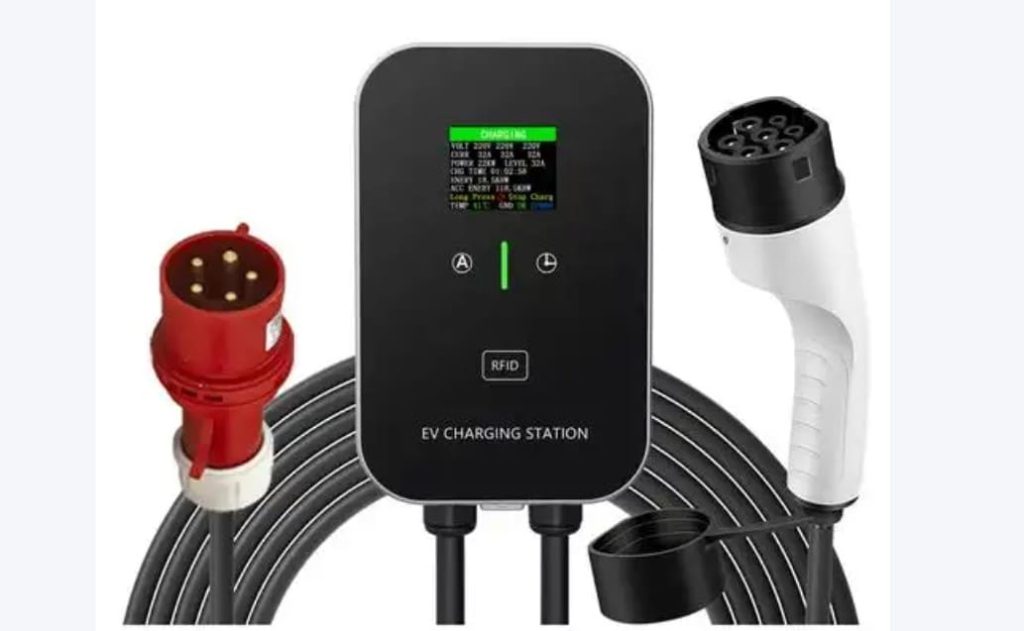
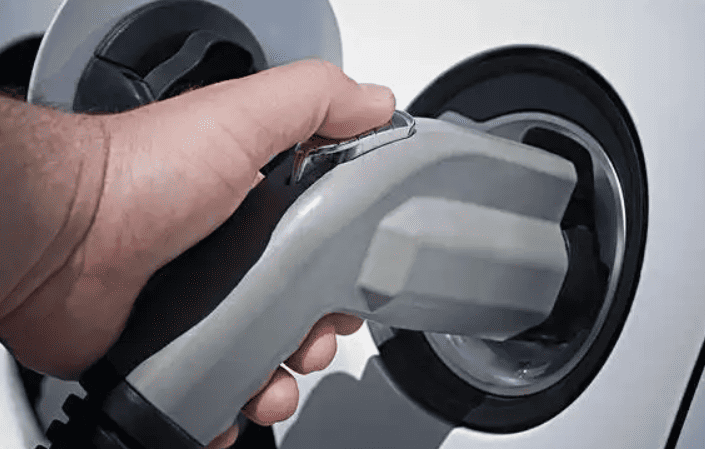
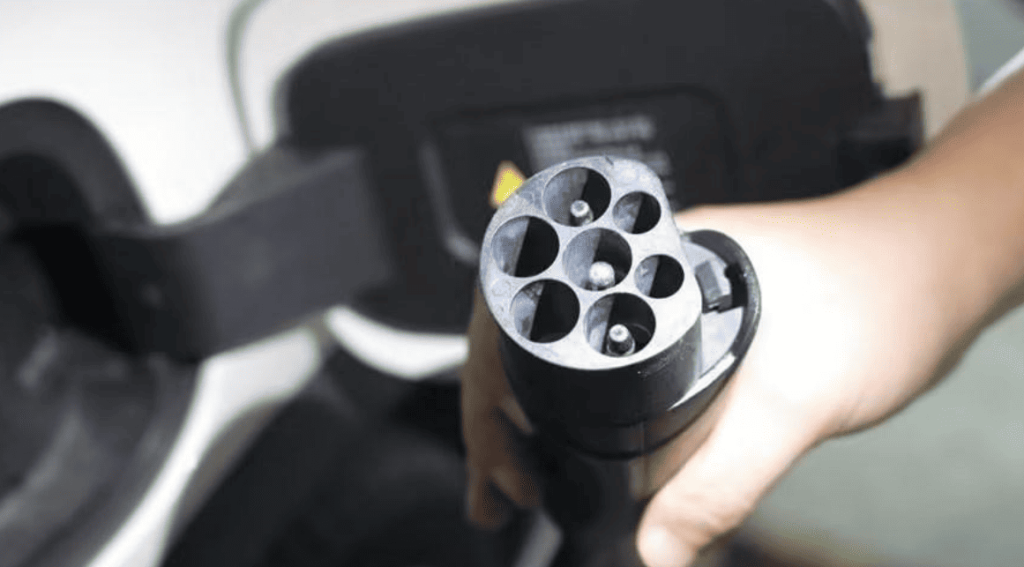
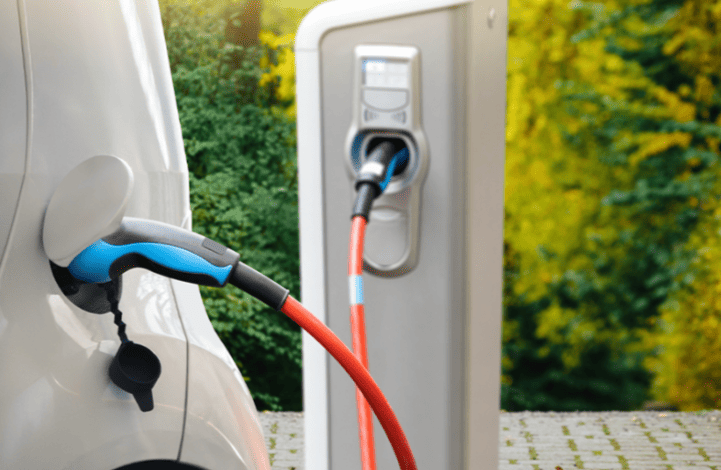
- For DC fast chargers: Grip the thick, heavy gun (9-pin connector), press the unlock button, and insert firmly until you hear an audible click.
- For AC slow chargers: Use the lighter 7-pin plug; no button press needed.
Regional Variations:
- Europe: Type 2 plugs often require rotating a locking ring after insertion.
- Japan: CHAdeMO connectors have a distinct latch lever—push down before inserting.
- Safety Note: Never force a plug. If resistance exceeds 5 kg of pressure, abort and check compatibility.
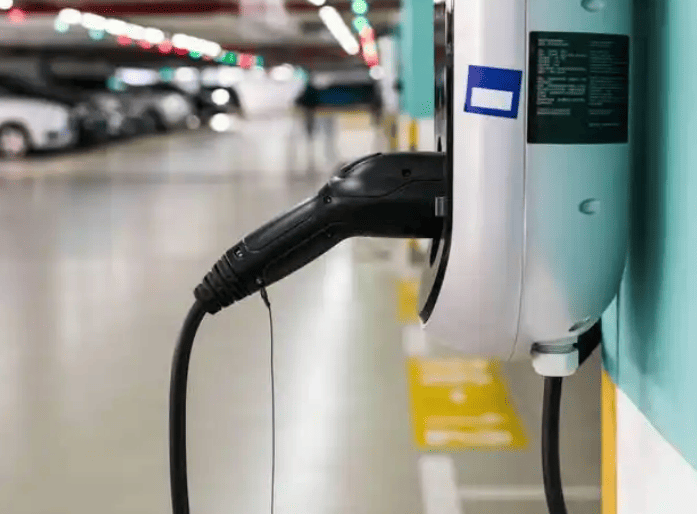
Step 3: Initiating Charging – The Payment Divide
This step varies dramatically by market due to payment infrastructure and regulations:
North America: App/Card Dominance
- App activation (e.g., Electrify America):
- Scan the QR code on the charger → Log in to your account → Select payment method → Tap “Start Charging”.
- Speed tip: Pre-load apps like EVgo with payment details to skip setup delays.
- Credit card swipe: Insert a chip card or tap via Apple Pay. Requires PCI-DSS-compliant readers.
- Tesla Superchargers: Automatic billing via car recognition—no app needed.
Europe: Contactless and “Plug & Charge”
- RFID cards (e.g., Plugsurfing): Tap against the reader → Charging starts instantly.
- Contactless debit/credit cards: Mandatory for >50 kW chargers per EU’s AFIR regulation.
- Automated systems: Cars with ISO 15118 support (e.g., Porsche Taycan) authenticate and bill automatically upon plug-in.
Asia-Pacific: Mobile-First Solutions
- Japan: Use Suica/Pasmo transport cards (tap to pay) or operator-specific apps like JCN.
- South Korea: QR code scanning via KakaoPay/T Map apps is government-mandated.
- China: WeChat/Alipay dominate—scan, pay, and charge in 10 seconds.
Manufacturer Insight: Integrate multi-language interfaces and dual payment modules (QR + NFC) for Asian exports.
Step 4: Monitoring and Safety During Charging
Once charging begins:
- Verify activation:
- Dashboard indicators: “Charging” light (green on Nissan Leaf) or screen display (e.g., Tesla’s charging animation).
- Charger screen: Shows real-time kW, voltage, cost, and estimated completion.
- Safety protocols:
- Never unplug mid-charge: DC fast chargers deliver 400–800V—premature disconnection risks arcing.
- Weather precautions: Use covered stations in rain/snow; avoid charging in temperatures >40°C (reduces efficiency).
- Fire prevention: Park 3+ meters from combustibles; report overheating smells immediately.
- Optimize charging:
- For battery health, set limits to 80% via your car’s app (exception: long trips).
- Off-peak discounts: Schedule charging at night in California (post-11 PM) or Germany (10 PM–6 AM) for 30–50% savings.
Step 5: Ending the Session and Disconnection
Stopping safely prevents damage and billing errors:
- Halt charging:
- App control: Tap “Stop Charging” in your operator’s app.
- Physical action: Press the red button on the charger (EU/Japan) or swipe your RFID card.
- Wait 10–30 seconds: Allows capacitors to discharge (prevents sparking).
- Unplug correctly:
- Press the gun’s unlock button firmly → Pull straight out (no twisting).
- Stuck plug?: Try remotely unlocking via your car’s app (e.g., Tesla’s “Unlock Charge Port” feature).
- Final checks:
- Close the charge port cover (prevents dirt/water ingress).
- Verify payment completion: App notifications or bank SMS (US/EU); printed receipts (Japan).
Critical Regional Notes:
- Germany: “Plug & Charge” systems auto-stop when full; no user action needed.
- Australia: Double-check EFTPOS terminal approval before leaving remote sites.
- Emergency: If a gun jams, call the charger’s helpline (e.g., ChargePoint: +1-888-758-4389).
Manufacturer Checklist: Designing User-Centric Chargers
- Hardware:
- Include dual-cable setups (CCS + CHAdeMO) for Asia-Pacific.
- Weatherproof to IP65 (rain) and IK10 (vandalism) ratings.
- Software:
- Support OCPP 1.6 for third-party app integration.
- Enable load balancing to prevent grid overloads.
- Safety:
- Auto-shutoff at 95% battery to prevent overcharging.
- Thermal sensors to halt charging if ports overheat.
- Compliance:
- UL certification (North America), CE (EU), KC (Korea).
The Future: Autonomous Charging
By 2026, robot-assisted charging will emerge (e.g., Tesla’s Snake Bot), where cars self-park and plugs autonomously connect. Manufacturers should prioritize machine-readable port designs and 5G vehicle-to-grid (V2G) communication.
“The best charger is invisible—it just works. That’s the goal.”
— Senior Engineer, IONITY Munich Hub
Final Tip for Drivers: Practice at home/work first. Use slower, forgiving AC chargers before tackling complex DC stations. With global standards converging, charging will soon be as simple as fueling gas—but cleaner and cheaper.