How do you charge the chevrolet blazer ev at home?

How do you charge the chevrolet blazer ev at home? Installing a Level 2 (240V) charging station, setting up your Chevrolet Blazer EV’s smart features for maximum efficiency, and adhering to strict safety precautions—all of which are adapted to local electrical codes—are necessary for charging your vehicle at home. We detail each step in detail below, including market-specific adjustments and technical details.
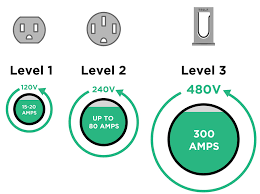
Electrical Infrastructure Requirements
Circuit Specifications by Region
- North America (NEC 2023 Standard)
- 11.5kW Charging: Requires a 60-amp dedicated circuit with 6 AWG copper wiring (minimum) and a NEMA 14-50 outlet.
- Grounding: ≤25-ohm resistance, with GFCI protection within 6 ft of the charging point.
- Panel Capacity: Homes built pre-2000 may need a panel upgrade (100-amp minimum service).
- European Union (IEC 62196-2)
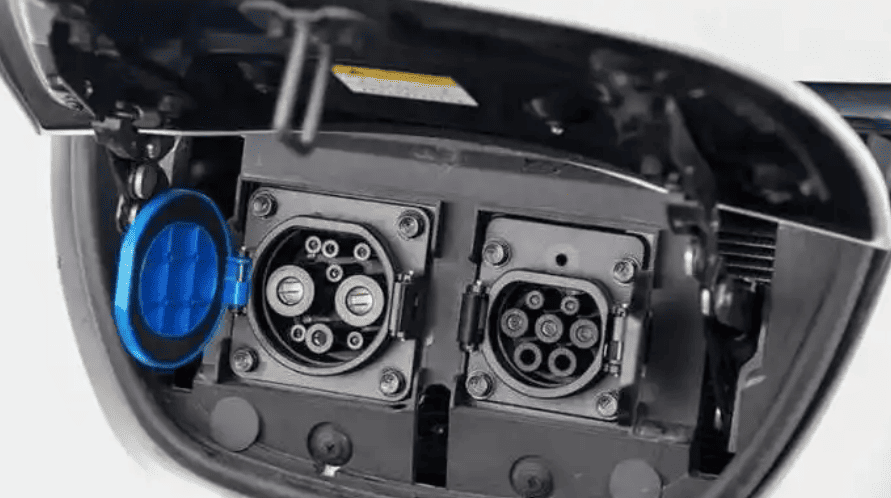
- 22kW 3-Phase Charging: Demands a 32-amp circuit with 5x6mm² NYY-J cable and Type 2 socket.
- Grid Compatibility: Requires confirmation of 400V 3-phase supply (common in Germany/Scandinavia; rare in UK flats).
- Japan (JIS C 8714)
- 200V Single-Phase: 30-amp circuit with 5.5mm² IV wires. CHAdeMO adapters need separate 50-amp circuits.
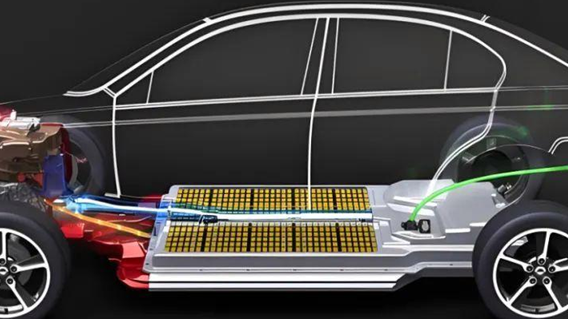
Critical Note: The Blazer EV’s onboard charger (OBC) limits AC input:
- North American models: 48A max (11.5kW)
- EU models: 32A per phase (22kW 3-phase)
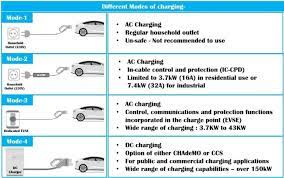
Charging Hardware Selection
Level 2 Charger Recommendations
| Region | Recommended Model | Key Specs | Blazer EV Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | ChargePoint Home Flex | 50A, 12kW, NEMA 14-50 | 11.5kW (96% efficiency) |
| EU/Germany | ABB Terra AC Wallbox | 22kW, Type 2 | Full 22kW utilization |
| UK | Pod Point Solo 3 | 7.4kW, Type 2 | 7.4kW (EU model only) |
| Japan | Panasonic EV-Power | 6kW, CHAdeMO | Requires adapter |
Smart Feature Essentials:
- Dynamic Load Balancing: Prevents tripping when running appliances (e.g., EU models reduce current if oven detected).
- Solar Matching: Models like Wallbox Pulsar Plus sync with home PV systems.
- Schedule Charging: Integrates with utility off-peak windows (e.g., 12 AM–6 AM in California @ $0.15/kWh).
Installation Process
Certified Professional Requirements
- North America: NEC-certified electrician; permits from local AHJ (Authority Having Jurisdiction).
- EU: VDE-registered technician; compliance with DIN VDE 0100-722.
- Japan: Denki Kōji-shi licensed installer.
Cable Routing Protocol:
- Conduit diameter: 1.25x cable width (e.g., 25mm for 6mm² EU cables).
- Minimum bend radius: 8x cable diameter.
- Distance limit: ≤50 ft from panel to charger (voltage drop ≤3%).
Post-Installation Checks:
- Insulation resistance: >1 MΩ (tested at 500V DC).
- Earth continuity: <0.1Ω resistance.
Charging Operation
Step-by-Step Workflow
- Pre-Charge Prep
- Activate battery preconditioning via MyChevrolet app when <10°C: Draws 3.5kW for 20 mins to heat cells to 25°C.
- Verify charging port cleanliness (IP54-rated, but debris can trigger fault codes).
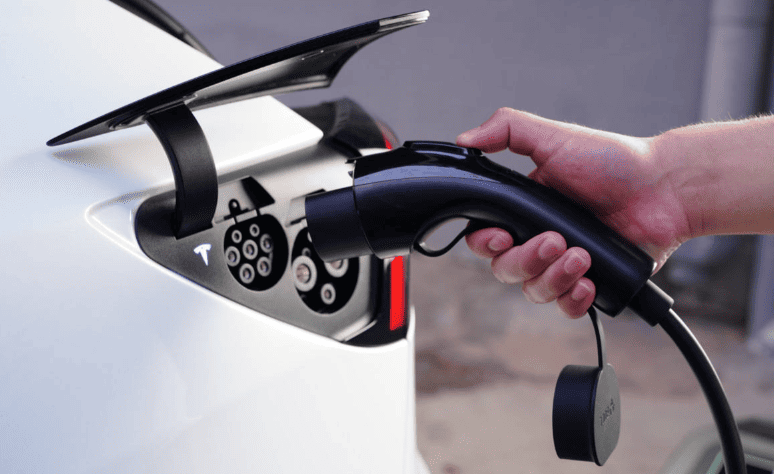
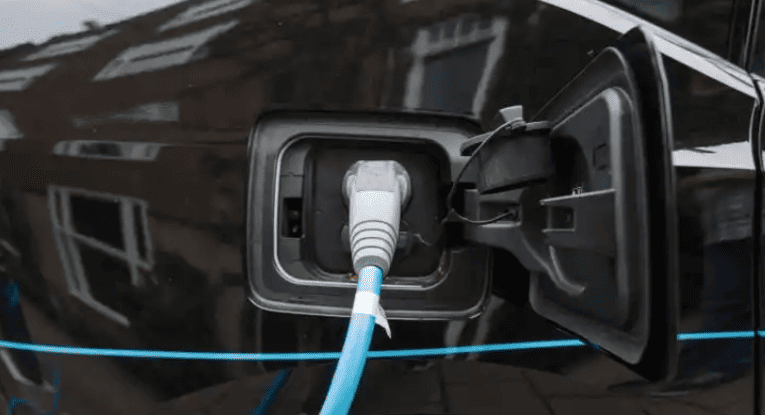
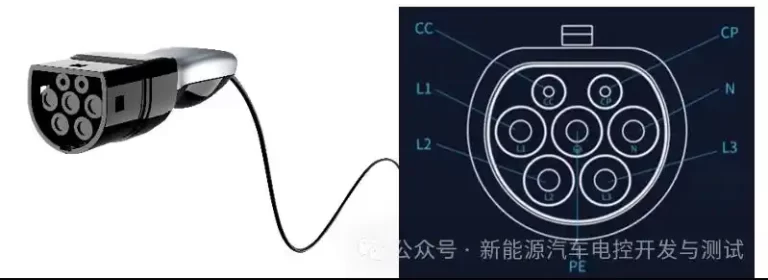
- Connection Sequence
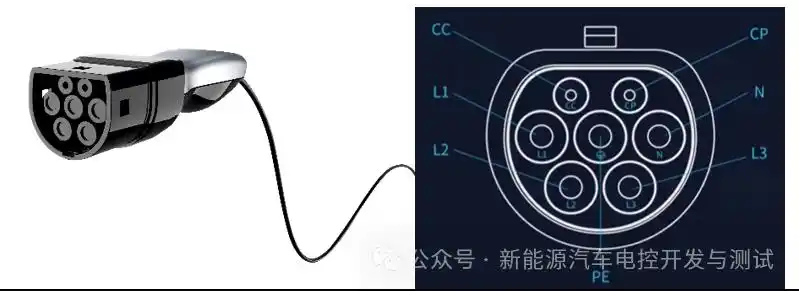
- Align CCS1/Type 2 connector with port LEDs (white = ready; blue = communicating).
- Insert until audible click confirms latch engagement (45N force required).
- Authentication Methods Region Primary Method Fallback Option North America MyChevrolet app RFID card (included) EU ISO 15118 Plug & Charge MENNEKES RFID card Japan CHAdeMO screen menu Manual ID input
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Dashboard displays:
- Charging rate (e.g., “11.2 kW”)
- Cell temperature differential (<5°C ideal)
- Voltage sag (<3% from 240V nominal)
Safety and Maintenance
Critical Protocols
- Lockout During Charging: Physical latch prevents disconnection at >2A current.
- Thermal Runaway Prevention: BMS throttles power if:
- Cell delta-T >8°C
- Peak temp >45°C
- GFCI Response Time: <100ms trip at 20mA leakage (exceeds NEC requirements).
Monthly Maintenance:
- Contact inspection: Clean with DeoxIT D5 on copper terminals.
- Torque check: 35 N·m on terminal screws.
- Firmware updates: Via charger OEM app (e.g., ABB Ability).
Regional Cost Analysis
| Component | North America | European Union | Japan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charger Unit | $649 (ChargePoint) | €799 (ABB) | ¥98,000 (Panasonic) |
| Installation | $1,200–$2,500 | €1,100–€1,800 | ¥110,000 |
| Electricity (85kWh) | $13.60 (@ $0.16/kWh) | €23.80 (@ €0.28/kWh) | ¥1,870 (@ ¥22/kWh) |
| Payback Period | 18 months* | 24 months* | 28 months* |
| **Vs. public DC charging at $0.40/kWh equivalent |
Efficiency Hack: EU users with solar can achieve €0.07/kWh net cost with dynamic export limiting.
Troubleshooting Matrix
| Symptom | Diagnosis | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| “Charging Interrupted” | Ground fault >25mA | Test GFCI; replace if >0.6s trip delay |
| Reduced 11.5kW → 7.4kW | Voltage drop >5% | Verify wire gauge; check connections |
| Connector latch failure | Ice accumulation | Apply dielectric grease (SAE J2747) |
| App authentication failure | TLS certificate error | Re-pair vehicle via VIN in MyChevrolet |
Manufacturer Design Implications
For Charger Producers:
- North America: Prioritize 48A continuous rating (not peak) with thermal derating curves.
- EU: Mandatory OCPP 1.6J support for grid balancing.
- Japan: CHAdeMO-to-CCS adapter kits (≥150A liquid-cooled).
For Automakers:
- BMS Calibration: Allow 22kW 3-phase in EU despite North American OBC limitations.
- Port Design: Heater elements (-30°C operation) for Scandinavian markets.
“Home charging isn’t just convenience—it’s controlled electrochemistry. Every volt matters.”
— Chevrolet EV Powertrain Engineer, GM Tech Center
Final Tip: For Blazer EV owners in cold climates, program charging to end just before departure. This utilizes charge current for battery heating, reducing range loss by 12-18%.