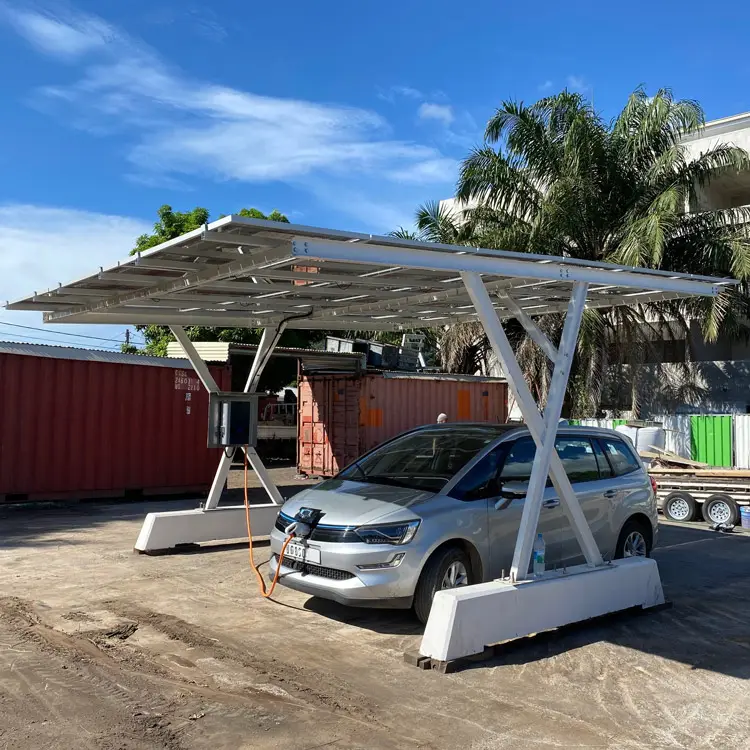
How much to install ev charger at home ?

How much to install ev charger at home ?
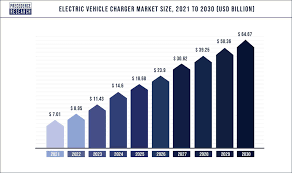
Installing a home EV charger can cost anywhere from $350 to over $8,000, depending on the type of charger, power needs, installation difficulty, and geographic location. A typical 7–11 kW AC charger setup costs most households between $500 and $1,500. Home charging becomes a smooth overnight routine with this investment, but high-power DC units or electrical upgrades may result in higher costs. We break down each cost layer below to assist you in creating an efficient budget.
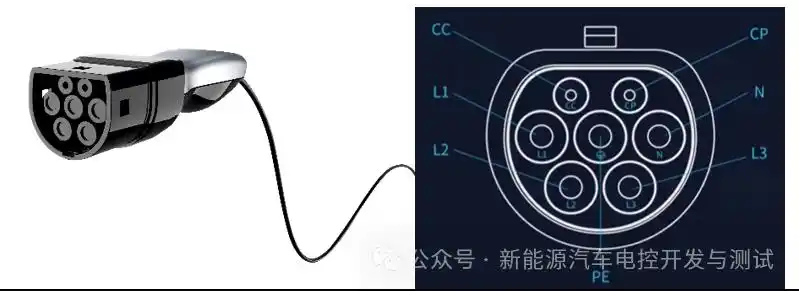
Charger Hardware: Portable vs. Stationary Solutions
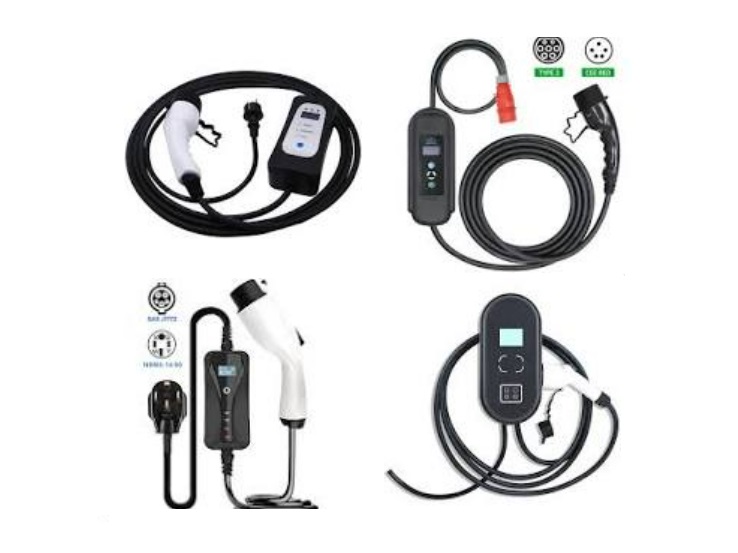
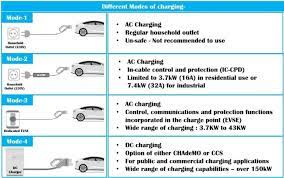
An affordable starting point is provided by portable chargers. These “granny cables” range in price from $12 to $420 (¥90 to 3,000) and fit into regular outlets. While smart versions with LCD screens, like the Baseus Tesla-compatible 3.5 kW cord ($92/¥659), add features like weather resistance and charge scheduling, basic 16A/3.5 kW models, such as universal cables for BYD or Geely, start at $12 (¥90). However, their dependence on current outlets and slow speeds (15–25 km/h) make them impractical for everyday use.
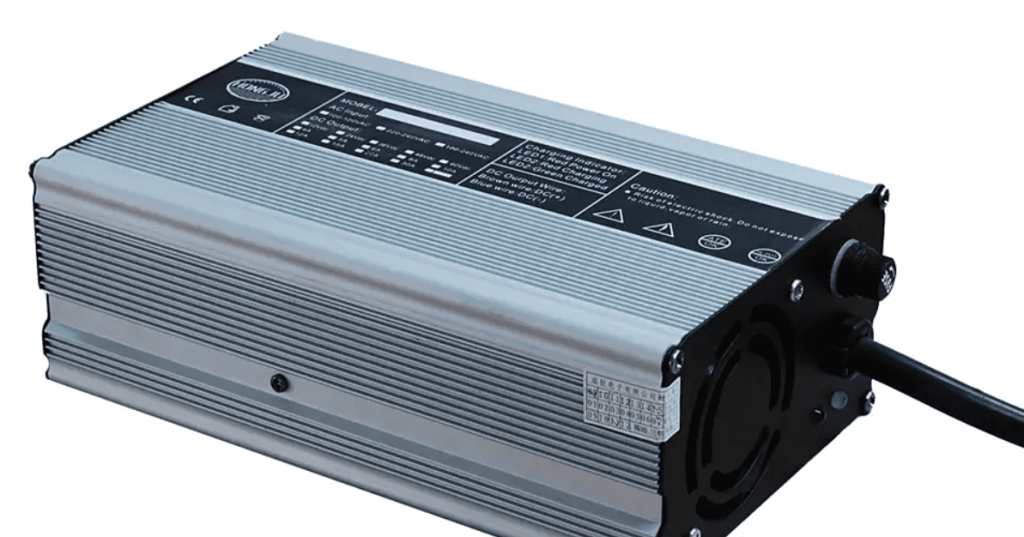
Stationary AC chargers are the most popular for dedicated home charging. The standard 7 kW unit costs between $200 and 850 (¥1,500 and 6,000). Basic models from brands like Delixi cost $141 (¥1,009), while Xiaomi’s Wi-Fi-enabled charger costs $420 (¥2,999). As demonstrated by Bull’s 11 kW model, upgrading to 11 kW three-phase power allows for faster charging (60–70 km/h), but it also increases hardware costs to $580–1,200 (¥4,000–8,500). Notably, automakers like Tesla and BYD frequently reduce this cost by giving away free chargers with car purchases.
Installation: Labor, Materials, and Hidden Complexities
Installation fees hinge on your electrical infrastructure and parking layout. Simple setups—with the charger near the electrical panel—cost $150–$300 (¥1,000–2,000) for labor. This covers mounting the unit, connecting wiring, and safety testing. However, challenges arise when:
- Long cable runs exceed 30 meters, adding $0.65–$1.30/meter (¥45–90/m) for copper cabling. A 50-meter extension can inflate costs by $325 (¥2,250).
- Complex routing through concrete walls or underground conduits requires drilling, trenching, or protective tubing, increasing labor to $500+ (¥3,500).
- Electrical panel upgrades become necessary for older homes with insufficient capacity. Adding a 40A circuit breaker costs $70–$140 (¥500–1,000), but full panel replacement surges to $700–$2,800+ (¥5,000–20,000).
High-Power DC Chargers: Speed at a Premium
Although they are uncommon in homes, 20–80 kW DC fast chargers allow for “gas-station-like” speeds. The premium, which ranges from $1,100 to $2,300 (¥9,800 to 16,800) for hardware alone, excluding installation, is demonstrated by NIO’s 20 kW unit. Industrial-grade components such as liquid-cooled cables and 380V transformers are required for deployment, which raises the overall cost to $14,000–$27,500 (¥100,000–200,000). These systems work well for luxury estates or fleet operators, but they are rarely cost-effective for average households.
Permits, Subsidies, and Ongoing Costs
Regulatory compliance often includes:
- Permit fees: $15–$150 (¥100–1,000) for local grid approvals.
- Grid application: Utilities may mandate dedicated EV meters, costing $42–$140 (¥300–1,000).
Government subsidies dramatically offset costs. China’s regional programs reimburse 30–50% of hardware expenses (up to $420/¥3,000 per charger), while cities like Shanghai offer additional tax credits. The U.S. federal tax credit covers 30% of installation (up to $1,000). Always verify local programs—some require using approved installers or specific charger models.
Maintenance adds $70–$140/year (¥500–1,000) for software updates, connector replacements, and safety inspections.
Real-World Cost Scenarios
- Minimalist Setup: Using a free Tesla charger with 10-meter installation: $220 (¥1,500).
- Typical 7 kW AC Installation: Xiaomi charger + 25-meter cabling + labor: $770 (¥5,500).
- Premium 11 kW System: Bull charger + panel upgrade + 40-meter trenching: $2,240+ (¥16,000).
Smart Strategies to Reduce Expenses
- Leverage manufacturer deals: 76% of automakers (e.g., BYD, NIO) bundle free chargers with new EVs.
- Time installations strategically: Off-peak electrician rates (winter months) save 10–15%.
- Group installations: Coordinate with neighbors to share trenching or transformer costs.
- DIY where safe: Self-install wiring conduits (if permitted), but hire pros for electrical connections.
Conclusion: Balancing Convenience and Cost
Since electricity is 70% less expensive per kilometer than gasoline, home EV charging offers unparalleled convenience and long-term savings. A 7–11 kW AC charger, with net costs of $350–$1,400 (¥2,500–10,000) after subsidies, is the best option for most people. For safety and compliance, give certified installers priority, and always get grid approvals before making hardware purchases. “A well-planned system pays for itself in 18 months via fuel savings—but cutting corners risks fires or $2,800 rework bills,” observes one installer from Guangzhou. You can turn your garage into a productive and affordable refueling station by being aware of these factors.