What ev charger does tesla use?
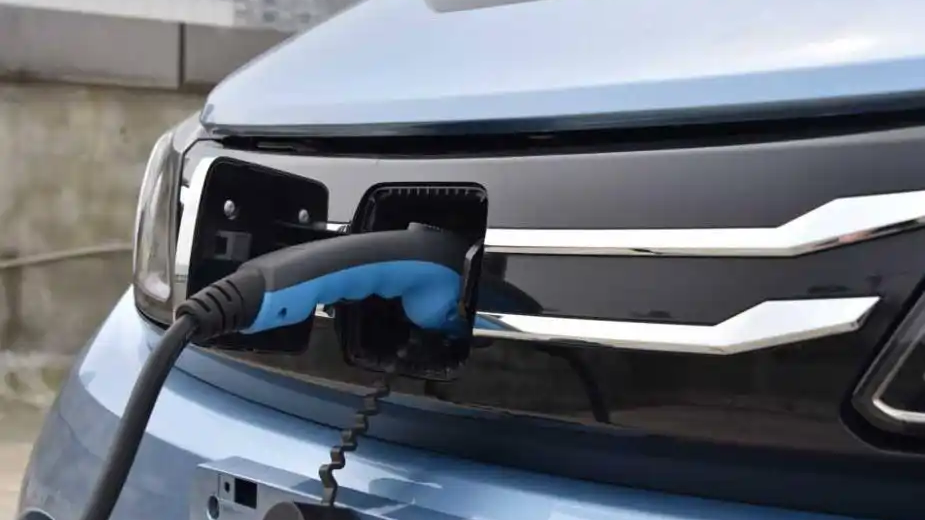
Tesla primarily uses two types of electric vehicle chargers: alternating current (AC) chargers and direct current (DC) chargers.
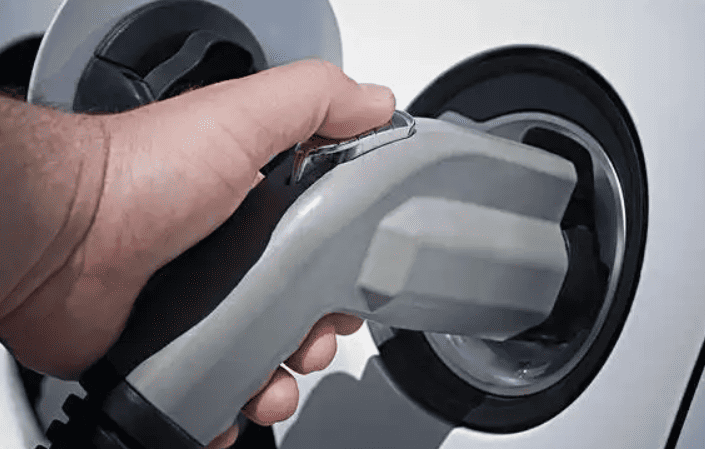
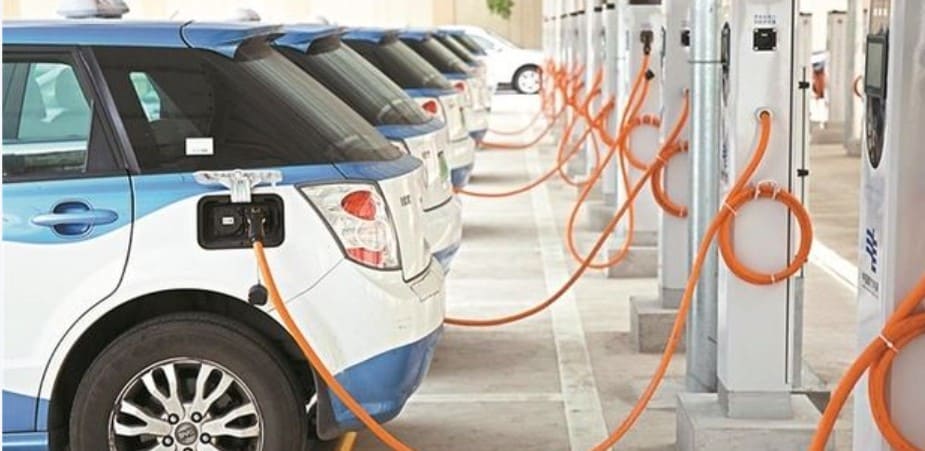
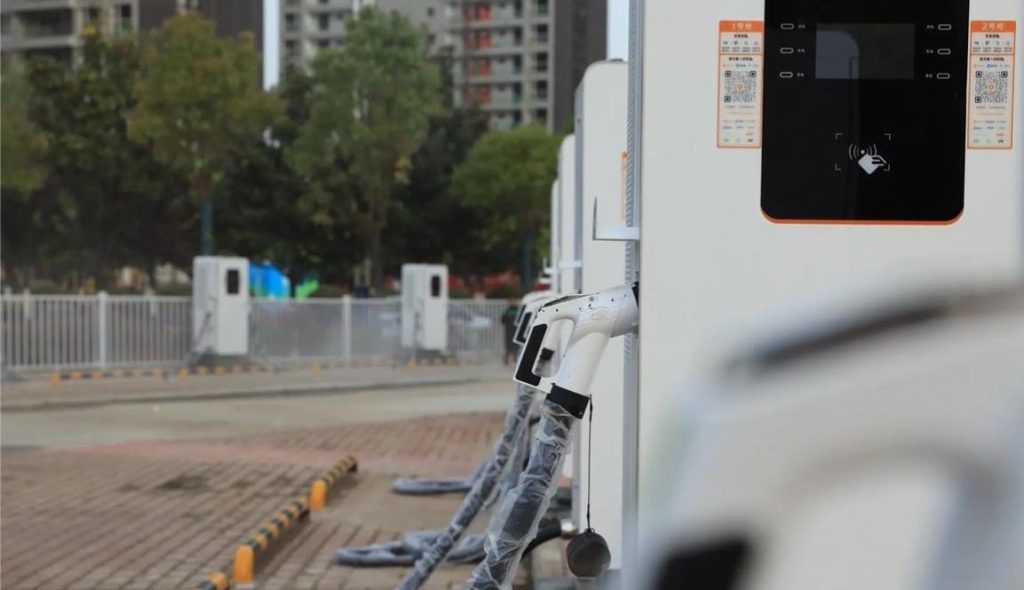
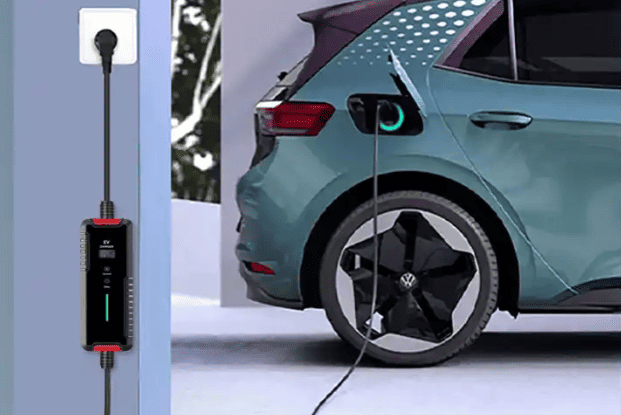
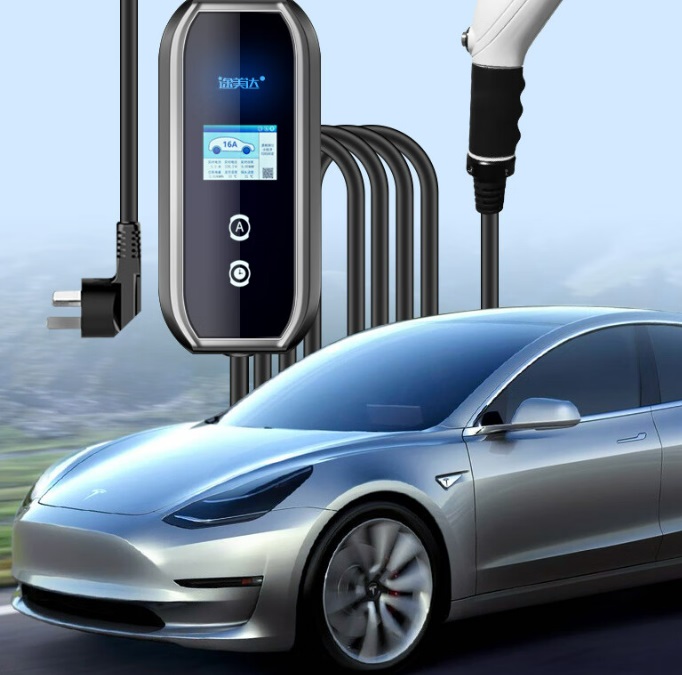
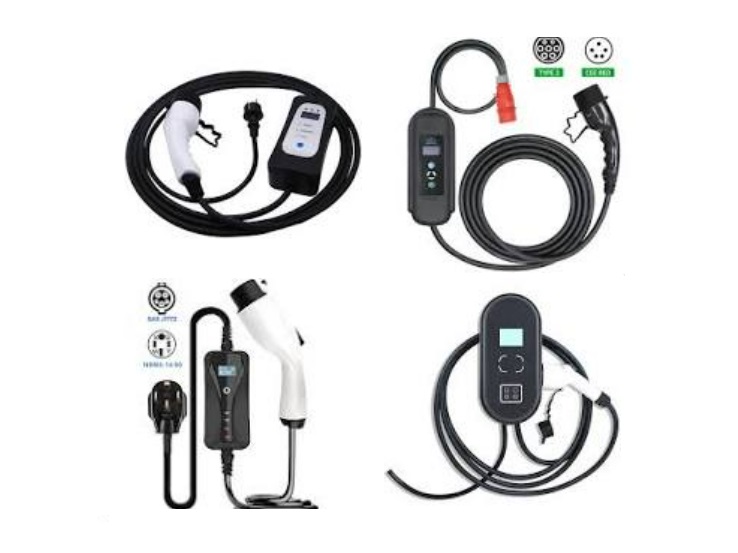
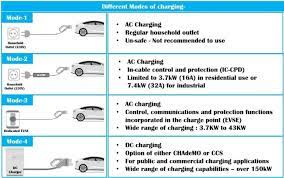
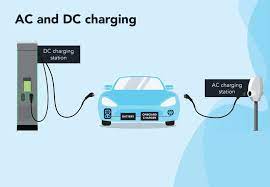
Tesla vehicles can be charged using both AC and DC power. AC chargers are typically used at home or public charging stations, while DC chargers are commonly found at fast-charging stations. AC chargers require connection to a 220V power source at home or public charging stations, where the onboard charger converts AC to DC to charge the battery, usually taking a longer time to complete the charging process. DC chargers, on the other hand, provide direct current directly, enabling rapid charging, making them suitable for long-distance travel or emergency situations.
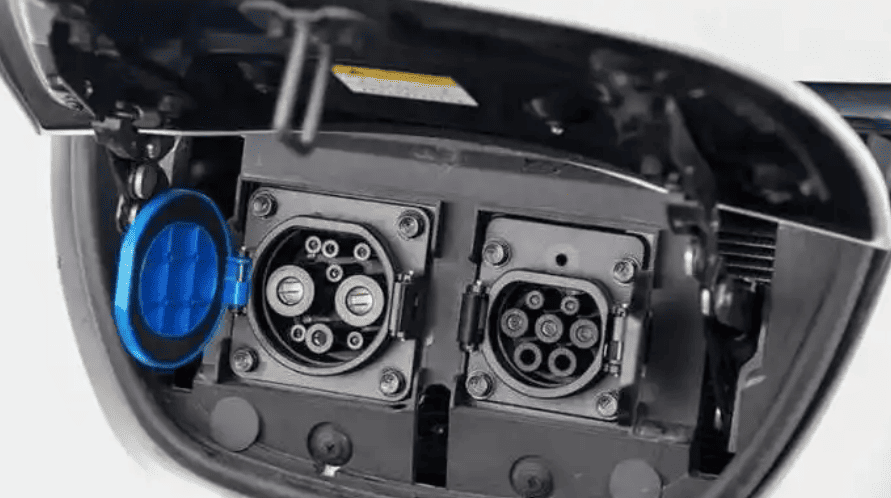
Tesla’s AC chargers can be connected to New National Standard (GB/T) charging equipment via an adapter. This adapter has one end that connects to Tesla’s charging port and the other end that connects to the GB/T charging connector. Additionally, Tesla offers a European-standard mobile connector, compatible with dedicated circuit sockets supplying 230V (single-phase) or 230V/400V (three-phase) 50Hz AC power, suitable for all Tesla vehicles designed for the European market.

Tesla EV Charging: Not Limited to Tesla Stations!
🌍 Globally, electric vehicle charging standards are not uniform. In North America, for example, L1 and L2 AC charging primarily use the SAE J1772 plug, also known as the “J-plug.” Tesla provides an adapter with each vehicle, allowing owners to charge using J-plug-compatible sockets or charging stations.
🔌 The Combined Charging System (CCS) resembles a household charging interface but includes two additional pins. This standard is adopted by most automakers in North America, including Volkswagen, Audi, BMW, Kia, Mercedes-Benz, and others.
🔌 CHAdeMO is a charging system developed by the Japanese company Tepco. Currently, in North America, only Nissan and Mitsubishi use this type of plug.
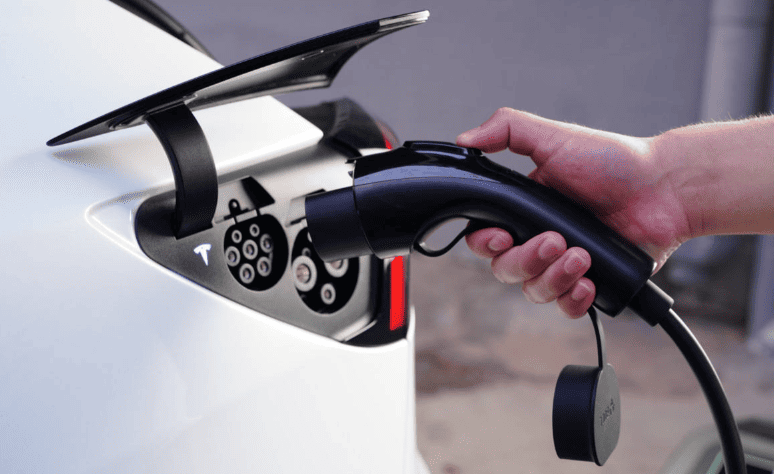
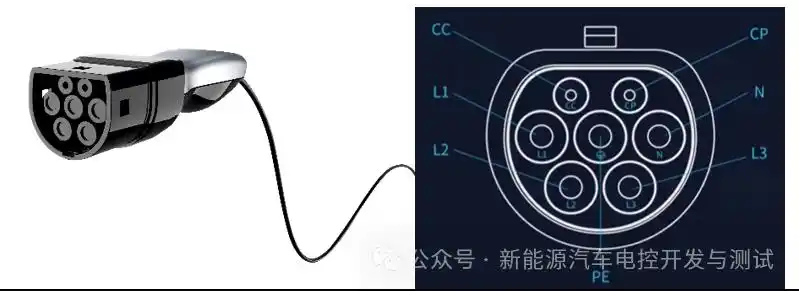
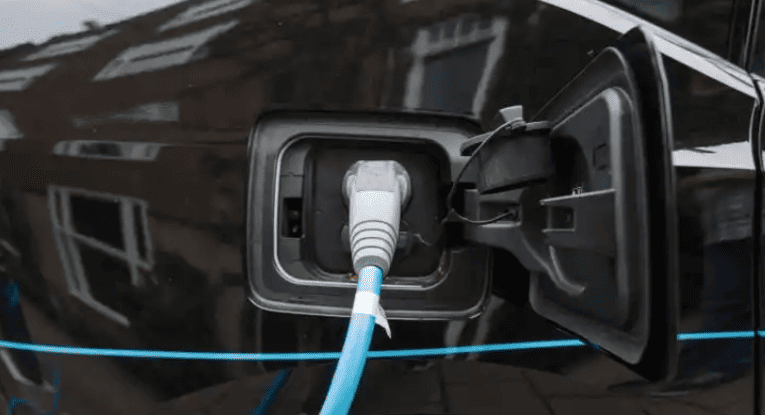
🔌 Tesla uses its proprietary plug for L1, L2, and L3 charging. Tesla’s Supercharger stations are exclusively for Tesla owners, but Tesla owners can use adapters to charge at other fast-charging stations.
🚗 If you drive a Tesla, the brand offers a dedicated charging system. However, Tesla also provides adapters, allowing you to charge at other fast-charging stations. For EVs of other brands, unless equipped with an adapter, they cannot directly use Tesla’s Superchargers or Wall Connectors.
In-Depth Analysis of North American EV Charging Standards: CCS vs. Tesla’s Technical Approach
Don’t miss this deep dive into North American EV plug standards, uncovering the secrets of Tesla and CCS. The charging process for electric vehicles relies on standardized plugs, and the variations across regions can be confusing. To help you better understand North American EV plug standards, this article provides a detailed breakdown, making it easy to grasp the key differences.
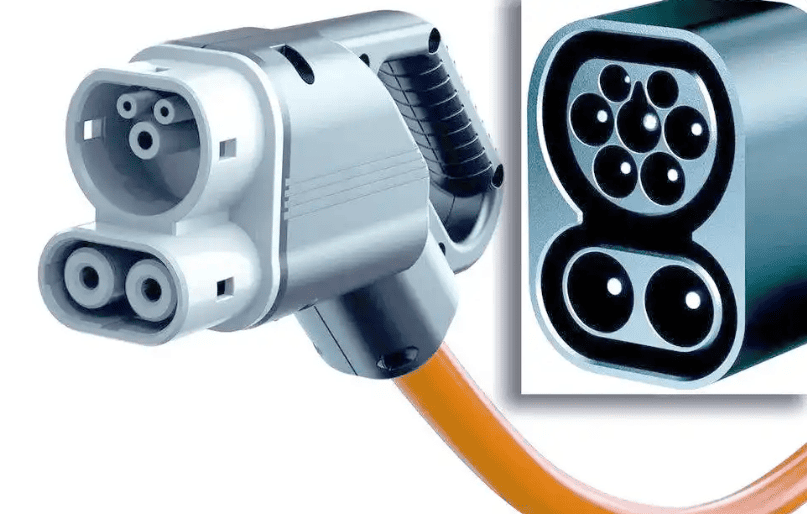

- North American EV Plug Standards Explained
◇ Household Plug Standards
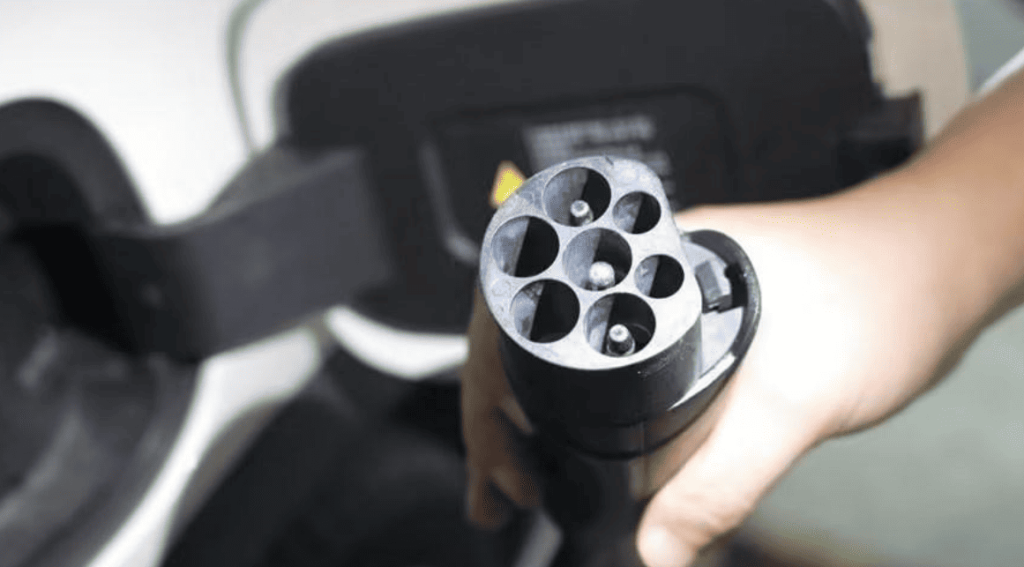
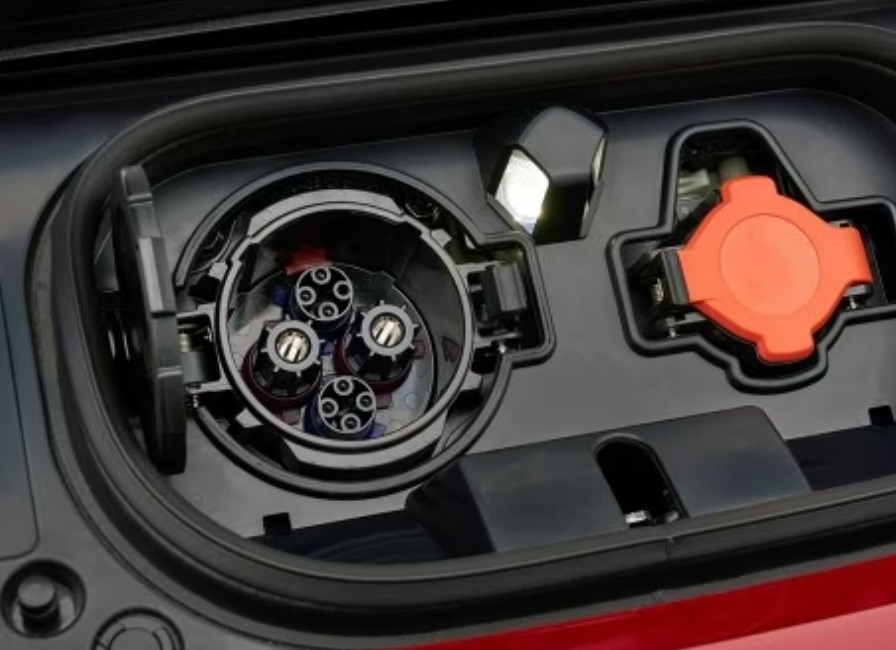
In North America, except for Tesla, other EVs use the SAE J1772 connector, also known as the J-plug. This plug is suitable for both Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V) charging. Tesla provides an adapter to accommodate J1772 sockets. While Tesla vehicles come with a proprietary plug, each Tesla includes a charging adapter, enabling owners to conveniently use J1772-compatible charging stations.
Tesla’s proprietary charging plug is only compatible with its own charging stations. Other EV brands cannot use these stations unless they have specialized adapters.
◇ DC Fast Charging Plug Standards
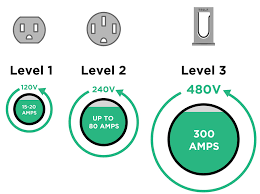
DC fast charging standards are more complex. Typically, Level 3 DC fast-charging stations are located along highways. These stations use 480V high voltage, capable of charging an EV to 80% in just 20 to 30 minutes. Notably, DC fast-charging stations feature three different types of plugs.
1.1 ◇ Combined Charging System (CCS)
CCS is the most widely used DC fast-charging standard in North America. The Combined Charging System ensures efficient charging at highway-side Level 3 DC fast-charging stations. With 480V high voltage, EVs can reach 80% charge in 20 to 30 minutes, meeting the energy demands of long-distance travel.
CCS is not only used at highway fast-charging stations but is also compatible with household Level 2 J1772 charging interfaces. This system ingeniously combines the J1772 plug with high-speed charging pins, making it a widely recognized standard in North America, endorsed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). In North America, nearly all major automakers—including General Motors, Ford, Dodge, Jeep, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, and Audi—have adopted this standard to offer a more convenient and efficient charging experience.
1.2 ◇ CHAdeMO Standard
Developed by the Japanese Electrical Safety & Environment Technology Laboratories (JET), CHAdeMO is a charging standard designed to provide efficient and convenient charging solutions for EVs. This standard has gained global recognition and is widely used in many countries and regions.
CHAdeMO is particularly prevalent in Japan. Originally created by JET, CHAdeMO aims to offer a high-efficiency charging method for EVs. With growing global adoption, the standard has taken root in many regions. Notably, the Japanese utility company Tepco has further promoted CHAdeMO, making it the official standard in Japan. As a result, nearly all DC fast chargers in Japan use CHAdeMO connectors. However, in North America, only Nissan and Mitsubishi EVs are sold with CHAdeMO charging ports.
Currently, the Nissan LEAF and Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV are the only EVs in North America equipped with CHAdeMO charging technology. Unlike CCS, CHAdeMO connectors do not share the J1772 inlet, requiring an additional port on the vehicle and an expanded charging area to accommodate two separate sockets.
◇ 2. Tesla and CHAdeMO
Tesla, a globally renowned EV manufacturer, does not use the CHAdeMO standard. Instead, Tesla has developed its own charging technology and network. This choice highlights the diversity of EV charging solutions.
Tesla uses a unified plug design for Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 fast charging. This proprietary plug supports various voltages, enabling fast charging without changing connectors. Tesla’s Supercharger stations, built and maintained by Tesla, are exclusively for Tesla owners, offering a seamless charging experience. Thus, Tesla owners enjoy a complete charging solution for both home and fast charging. Owners of other EV brands cannot use Tesla Superchargers but face no limitations with other charging methods.
How Do Tesla Solar Panels Differ from Conventional Solar Panels? A Comprehensive Comparison Reveals the Answer!
Tesla solar panels differ significantly from conventional solar panels in several aspects. Below, we delve into the similarities and differences, providing a thorough understanding of what sets Tesla solar panels apart.