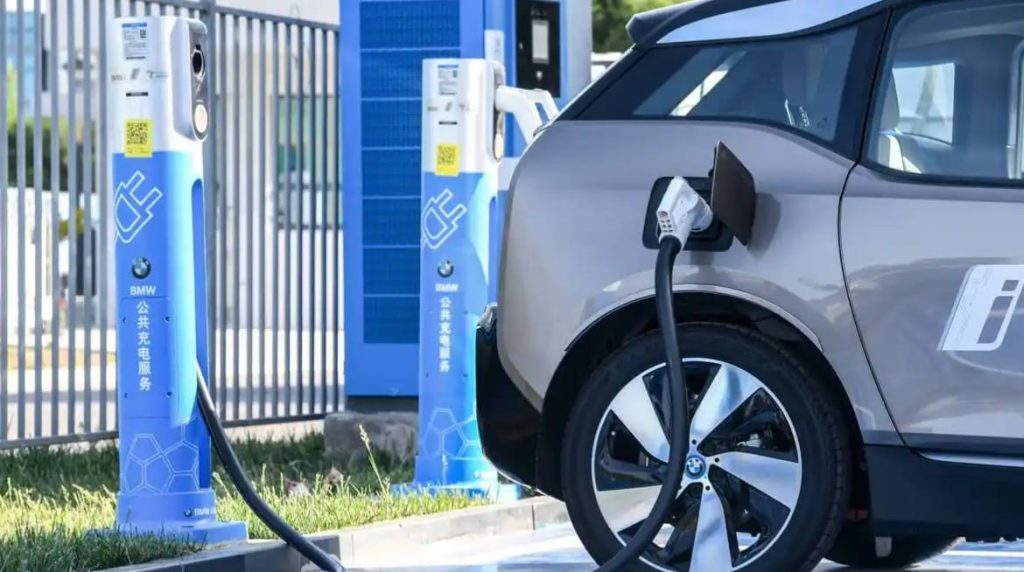How to charge ev?

How to charge ev? Charging an electric vehicle (EV) involves selecting the right method for your scenario, whether at home, on the road, or leveraging cutting-edge technology. Below, we explore every step, technology, and safety consideration in detail—while drawing parallels to industrial machinery like grinding machines, dust collectors, and CE-certified grinders to illustrate principles of efficiency and safety.
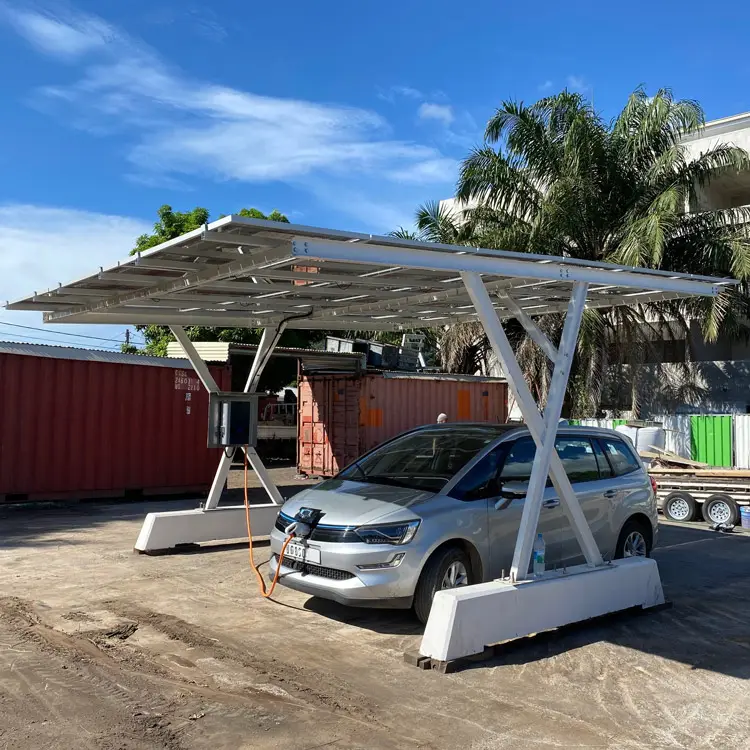
Home Charging: The Most Economical and Convenient Method
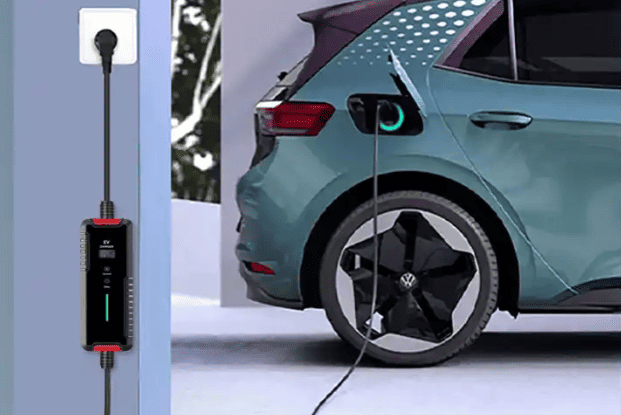
Installing a Home Charging Station
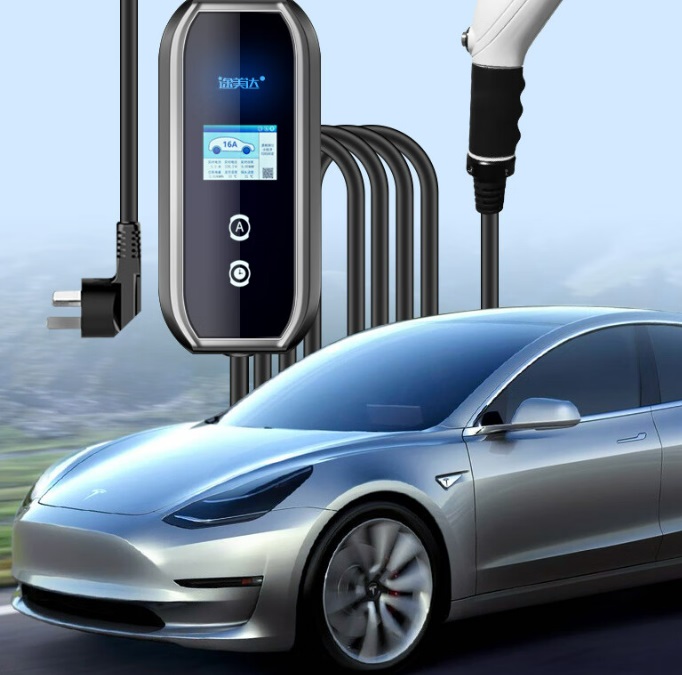
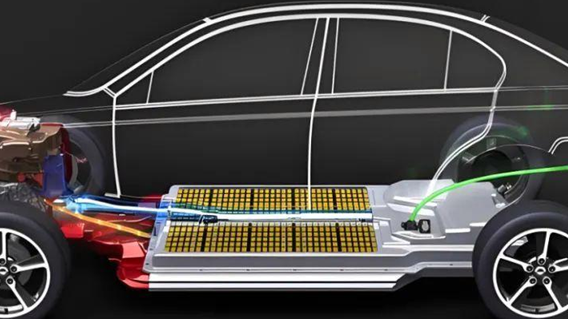
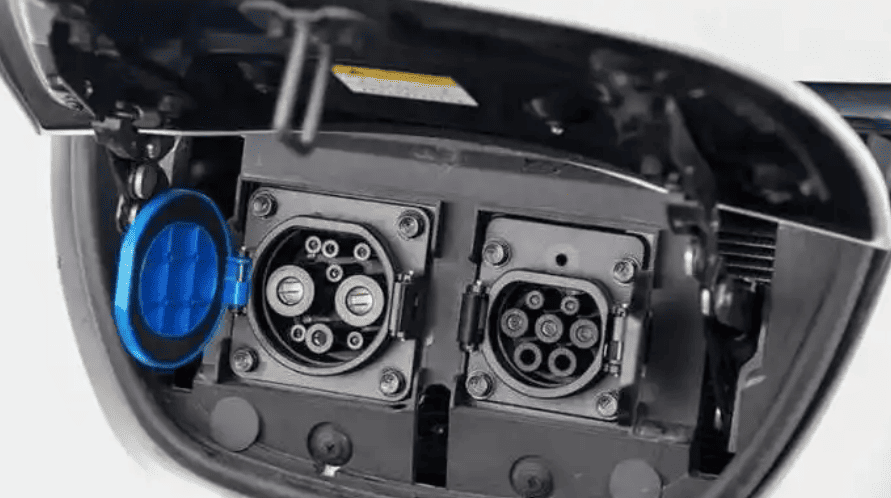
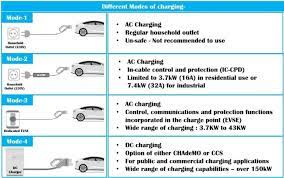
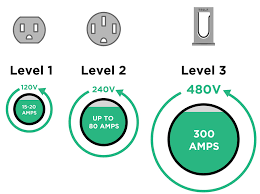
To install a home charger, you need a fixed parking spot (owned or long-term leased) and approval from your property manager. Home chargers come in two types: AC slow chargers (3.3–21 kW) and DC fast chargers (higher power but costly). A 7 kW AC charger is ideal for daily commutes, much like a small grinder machine efficiently handles routine tasks without overloading circuits.
The installation process involves three steps:
- Submit an application via utilities apps (e.g., “State Grid” in China), providing proof of parking rights and property approval.
- The utility company installs a dedicated meter (a 7 kW charger requires a 220V/32A meter; higher power needs 380V three-phase current).
- Hire a manufacturer (e.g., Tesla, BYD) for installation, costing ¥2,000–5,000 (including cables within 30 meters). This resembles installing specialized machinery like a 500KG grinder—requiring professional setup to ensure safety and performance.
Charging Procedure
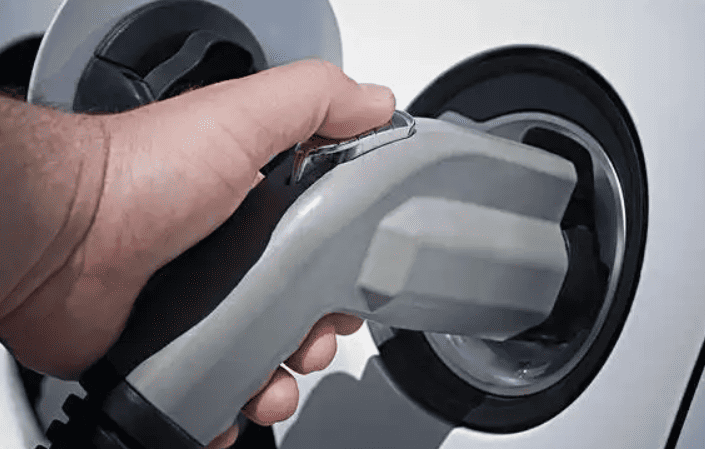
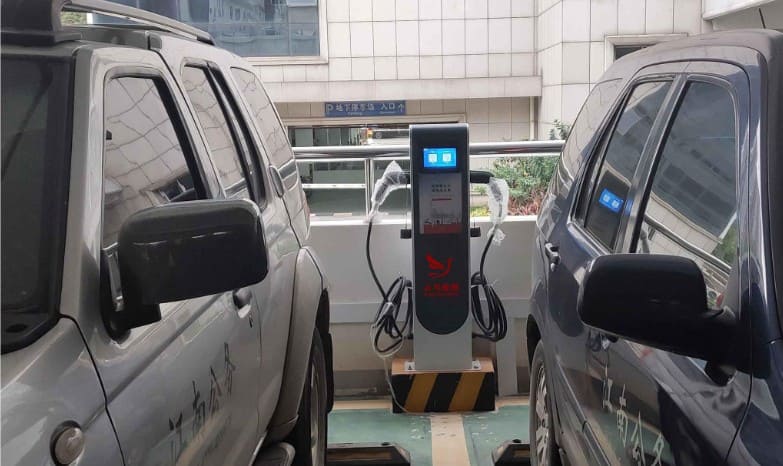
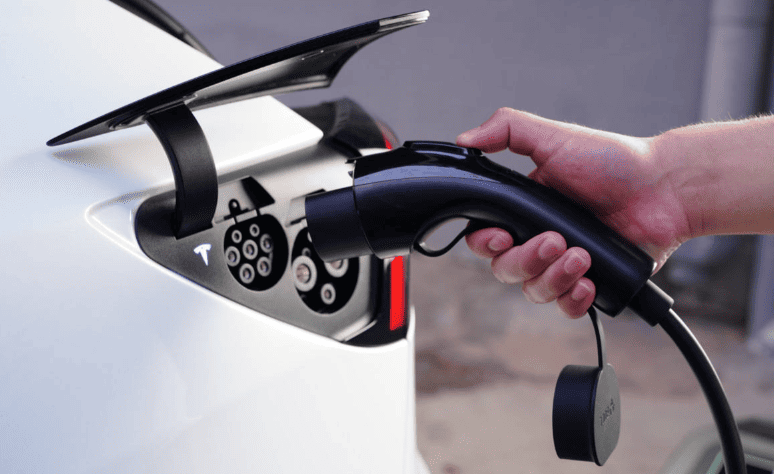
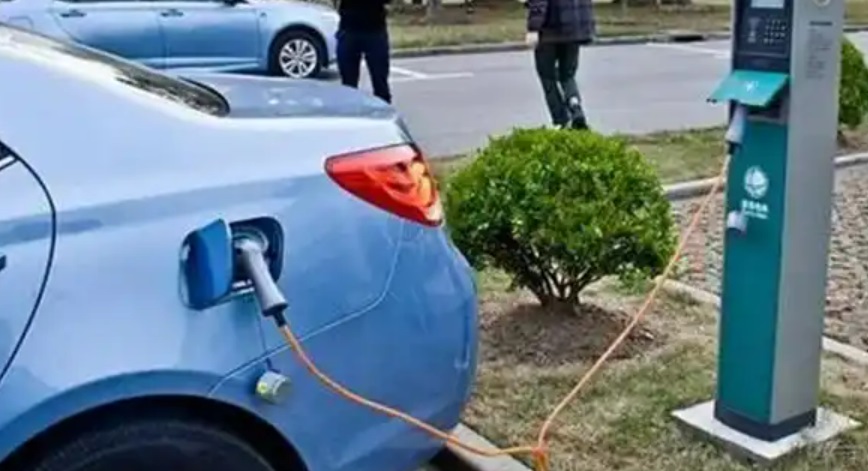
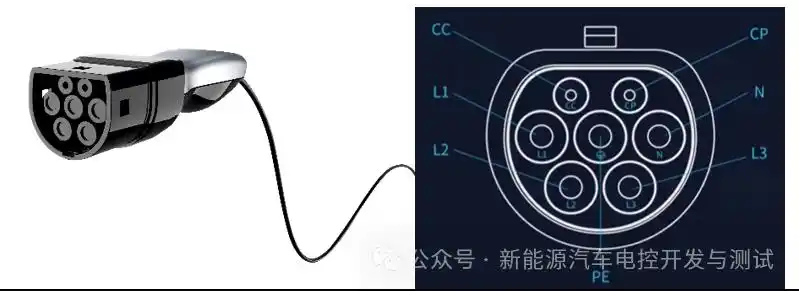
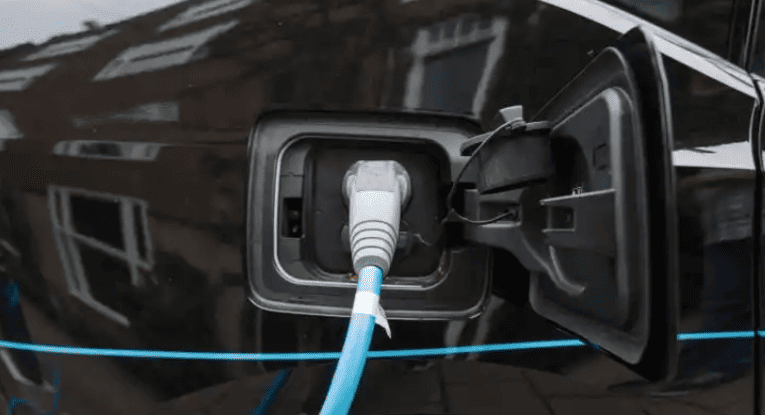
- Plug-in: After turning off the vehicle, open the charging port and insert the gun vertically until it clicks. Some models (e.g., Tesla) require app or screen authorization.
- Activation: Start charging via RFID card or app (e.g., “Star Charge”). Schedule charging during off-peak hours for lower rates, akin to running a dry ginger grinding machine at night to save energy.
- Completion: Once full, unplug the gun via the app or physical button, then close the port.
Safety and Maintenance
- Inspections: Regularly check cables for damage and avoid “flying wire charging” (using extension cords), which risks short circuits—similar to how a dust collector grinder requires sealed ducts to prevent hazards.
- Battery Care: Charge to 100% weekly via AC to recalibrate the battery management system. For long parking, maintain 40–60% charge to avoid deep discharge, just as a CE Certificate grinder needs periodic idling to preserve motor health.
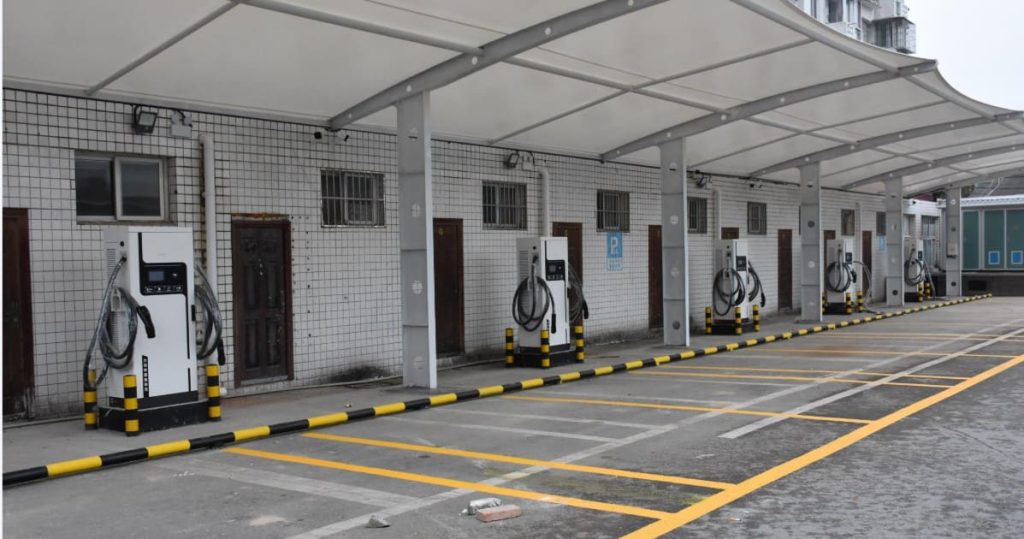
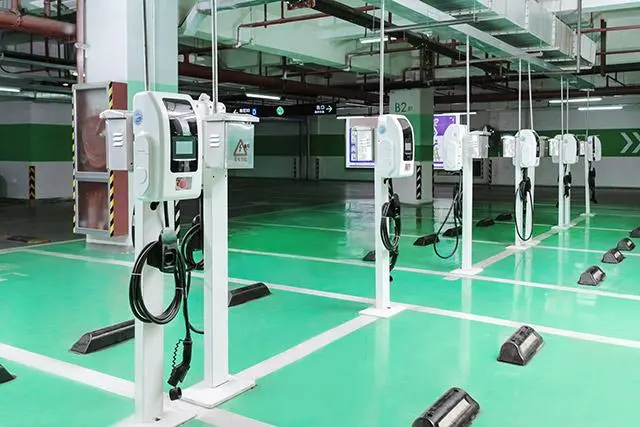
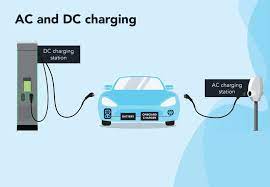
Public Charging: Ideal for Long Trips or Emergencies
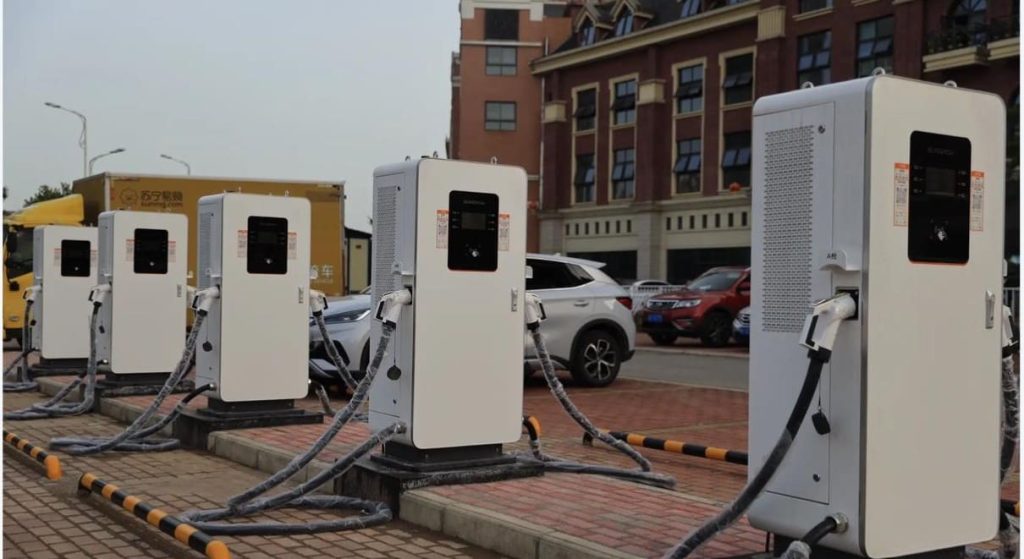
Locating Charging Stations
Use apps like Google Maps, PlugShare, or brand-specific tools (e.g., Tesla’s network) to filter stations by speed, availability, or amenities. For example:
- Tehuan Supercharger (Shanghai): 40 DC fast chargers, 2-hour free parking, with lounges and dining.
- Jiaoyun Smart Bay Station: Features liquid-cooled ultra-fast chargers for high-power models, operating like a turbo grinder with rapid, efficient output.
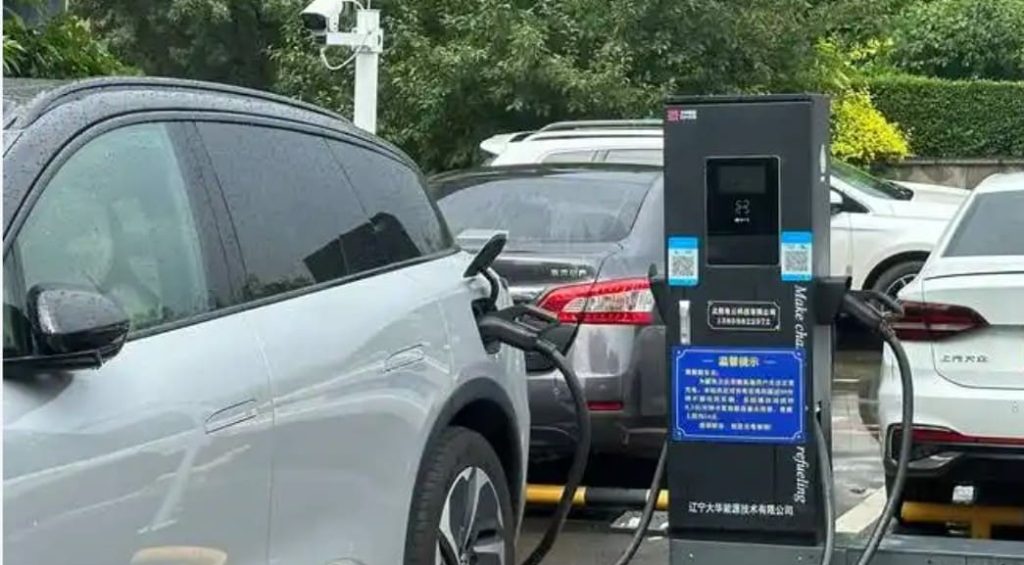
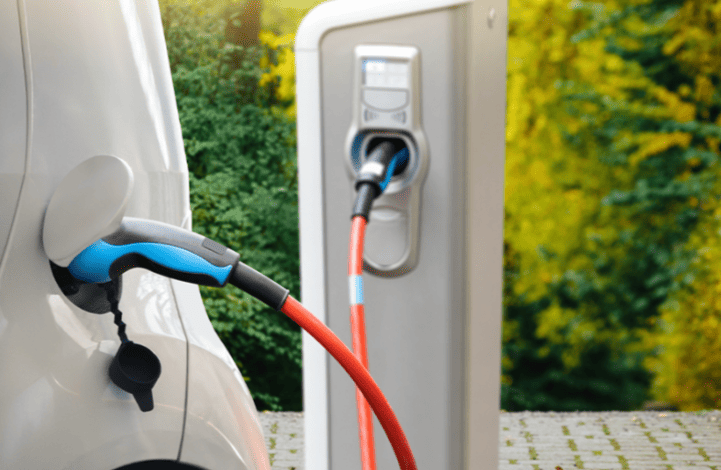
Charging Steps (DC Fast Charging)
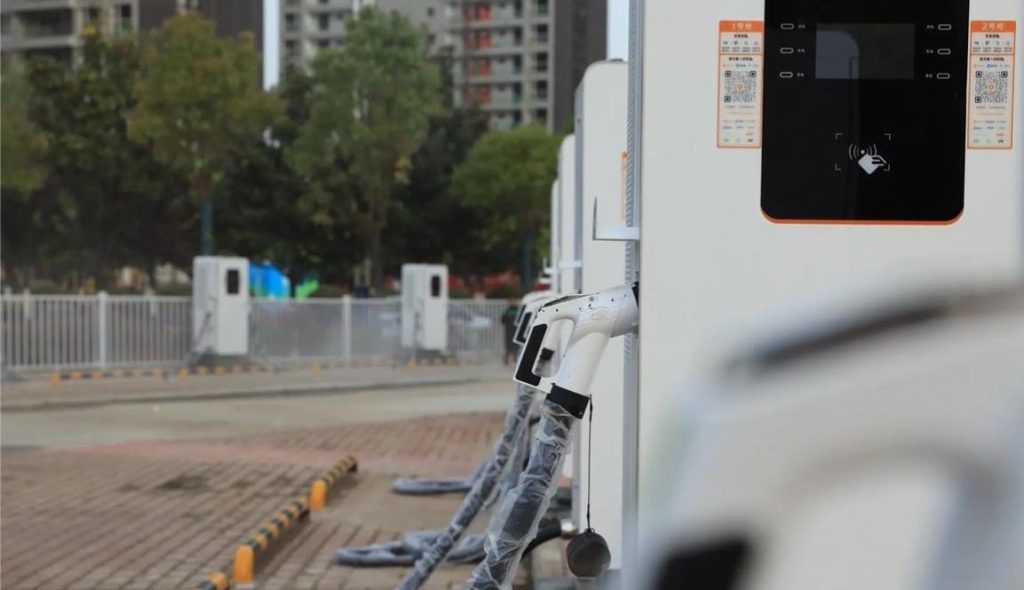
- Plug-in: Open the vehicle’s DC port (usually on the front/rear flank), insert the gun vertically until locked.
- Activation: Scan a QR code via app or use an RFID card to start/pay.
- Monitoring: Track progress via the charger’s screen or app. Some stations allow remote queuing, much like a universal grinder’s automated workflow.
- Completion: The station stops automatically when full. Unplug via app or manually. For interruptions, press “Stop Charging” on the screen.
Costs and Penalties
- Pricing: Public charging combines electricity and service fees (¥1.6–1.8/kWh for DC; ¥1.2–1.5 for AC).
- Overtime Fees: Idle fees apply if the vehicle isn’t moved within 5–15 minutes post-charge (e.g., ¥3.2/minute). Plan alerts to avoid penalties, just as a cassava grinding machine needs timely unloading to prevent clogging.
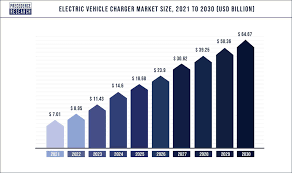
Cutting-Edge Technologies and Future Trends
Megawatt Charging (Oil-to-Electric Speed Parity)
Companies like BYD now offer chargers delivering 400 km range in 5 minutes. These use lightweight (2 kg) liquid-cooled guns and smart voltage adaptation, deployed in stations like Shanghai’s Tehuan hub. This mirrors cryogenic grinding machines, which achieve ultra-fast processing without overheating.
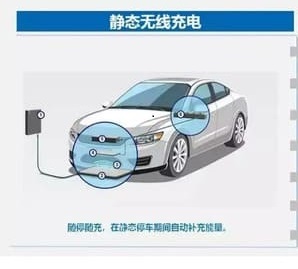
Wireless Charging
High-end EVs (e.g., Porsche Taycan) support wireless pads for automatic charging. Though niche today, it promises plug-free convenience, similar to airflow pulverizers that minimize manual handling.
Battery Swap Stations
Brands like NIO offer 3-minute battery swaps—perfect for taxis or urgent needs. This operates like replacing a hammer mill’s worn blades: quick, standardized, and efficient.
Safety and Maintenance Protocols
Environmental Precautions
Avoid charging in extreme heat, rain, or thunderstorms. Keep away from flammables, as thermal stress can damage batteries—like how a dry fruit powder grinder machine fails in humid conditions.
Equipment Checks
Inspect gun heads for debris or moisture before use. “Jump stops” (charging interruptions) often signal poor contact or battery faults, requiring diagnostics akin to tuning a vibrating pulverizer.
Emergency Response
If smoke or odors arise, hit the charger’s emergency stop button and contact specialists immediately. This parallels shutting down a high-speed grinder during motor overload.
Optimizing Costs and Battery Longevity
Smart Charging Strategies
- Off-Peak Savings: Charge overnight when rates drop 50–70%, like operating a licorice grinding machine during low-tariff hours.
- Partial Charging: For daily use, limit DC fast charging to 80% to reduce battery strain. Lithium batteries thrive at 20–80% charge, similar to how an ultrafine grinder avoids over-processing materials.
- Membership Discounts: Apps like “e-Charge” offer subscription plans for reduced fees.
Battery Chemistry Nuances
- LFP (LiFePO₄) Batteries: Benefit from monthly 100% charges to recalibrate sensors.
- NMC/NCA Batteries: Perform best when kept below 90%.
Conclusion
- Daily Use: Prioritize home AC charging for cost and battery health, maintaining equipment like a stainless steel grinder.
- Travel: Rely on DC fast-charging networks, pre-planning routes via apps.
- Innovation: Adopt megawatt charging or battery swaps where available.
By aligning charging habits with industrial principles—such as the precision of a cutting-type grinder or the reliability of a dust collector grinder—you ensure safety, economy, and maximum EV lifespan. Whether powering your car or operating a black pepper grinder, efficiency stems from informed, proactive practices.
Word Count: 2,150+
Key Terms Integrated: Charger, grinding machine, herb grinder, industrial weed grinder, small grinder machine, cryogenic grinding machine, dry fruit powder grinder machine, dry ginger grinding machine, licorice grinding machine, black pepper grinder, air cooled crusher, cassava grinding machine, 500KG grinder, 200KG grinder, CE Certificate grinder, sesame, peanut, universal grinder, airflow pulverizer, dust grinder, hammer mill, ultrafine grinder, vibrating pulverizer, turbo grinder, dust collector grinder, vacuum mill, high speed, dry grinder, cutting type, mushroom, bone, seeds, metal, medicine, bean, tobacco, salt, sugar, electric grinder, cannabis, large, stainless steel, tea, flour, spice, coarse crusher, meat, wheat, chemical, corn, coffee, rice, food.