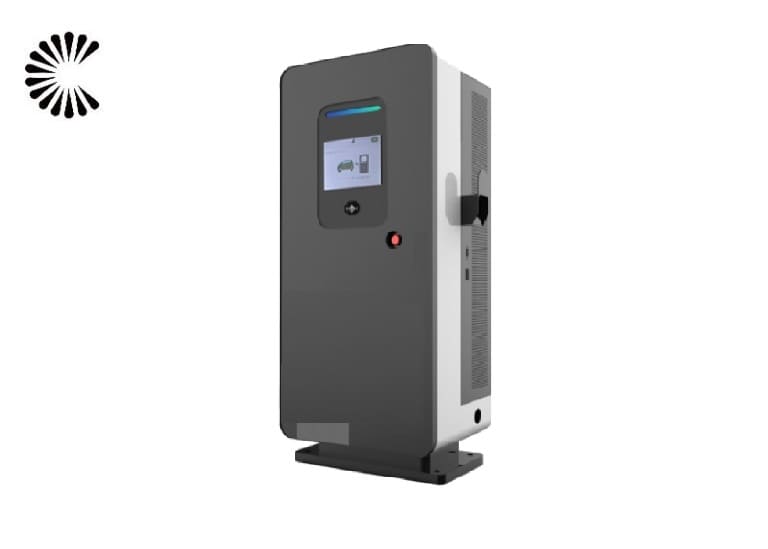
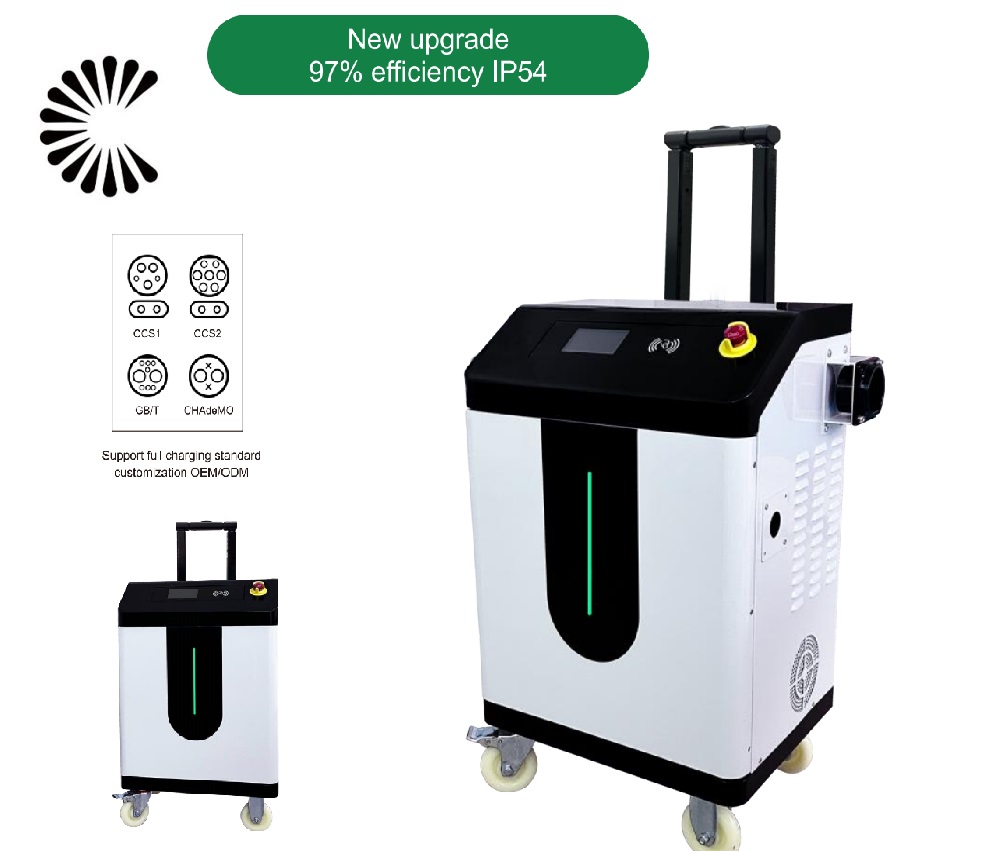
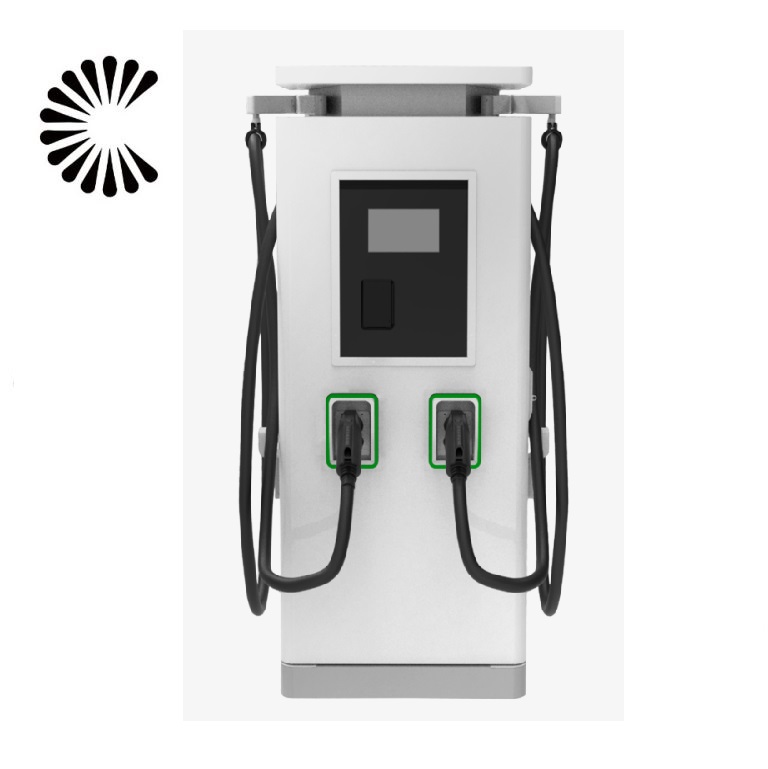
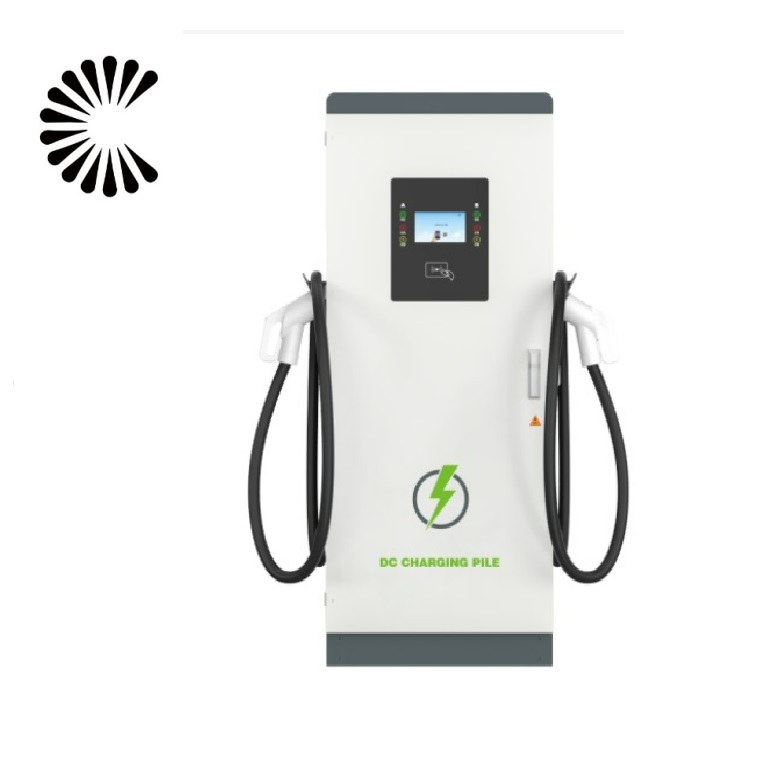
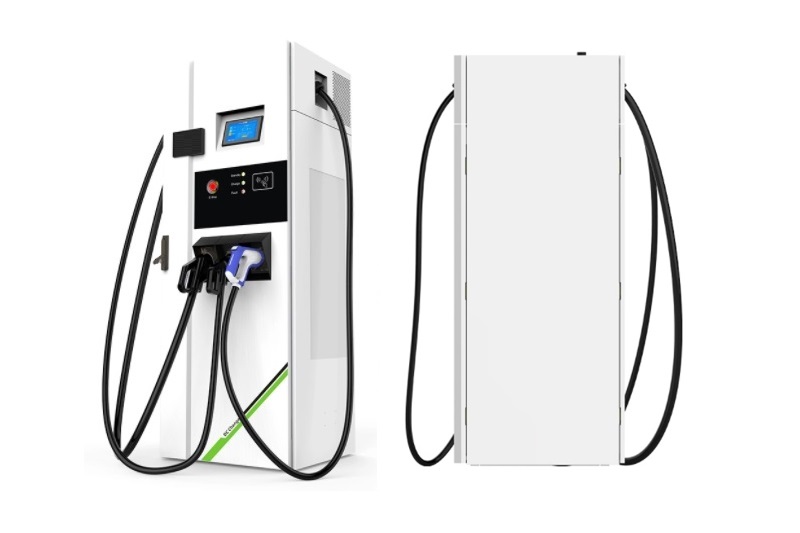
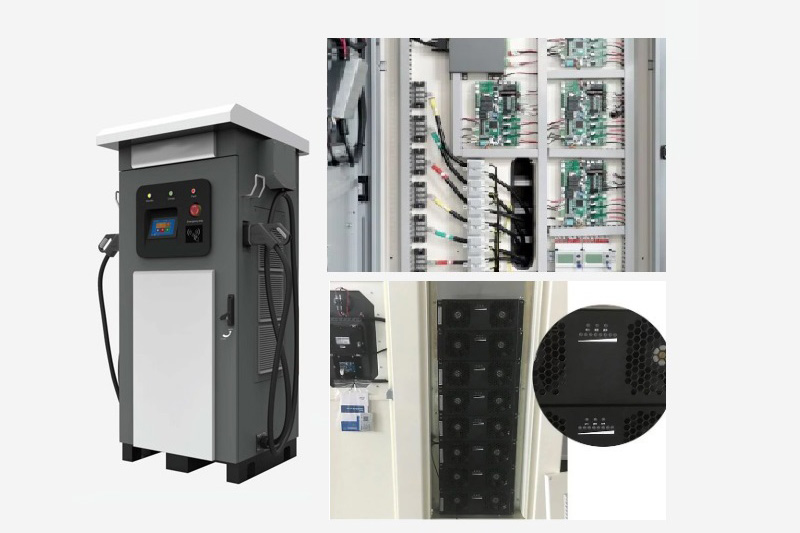
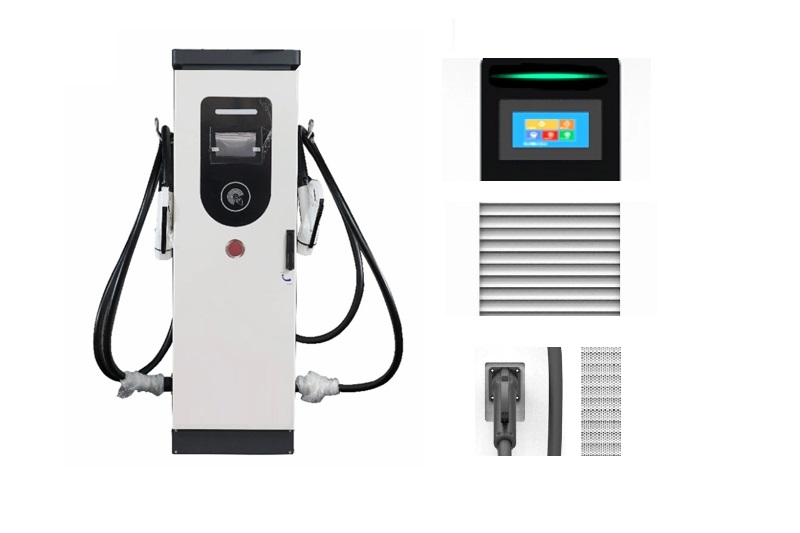
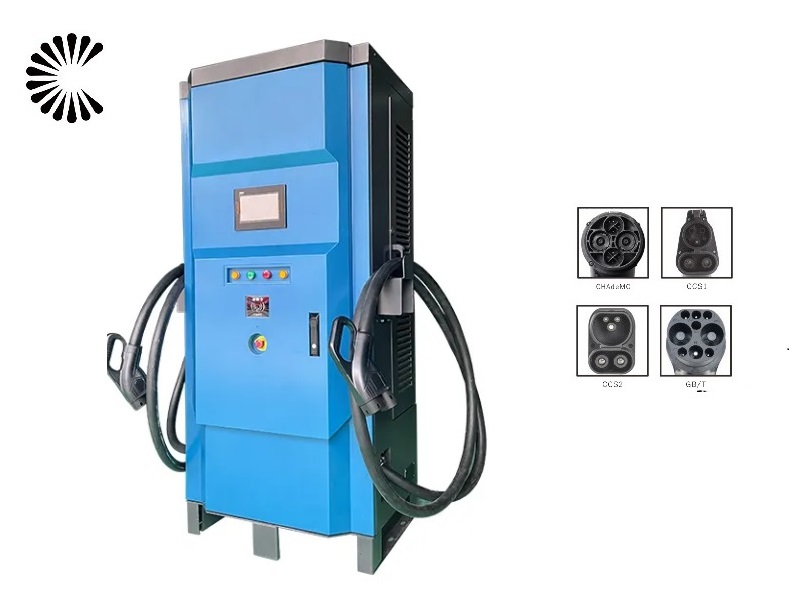
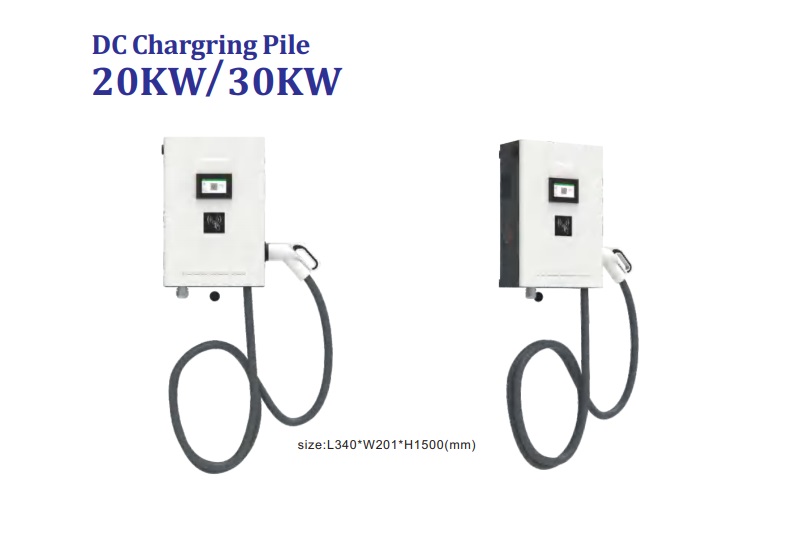
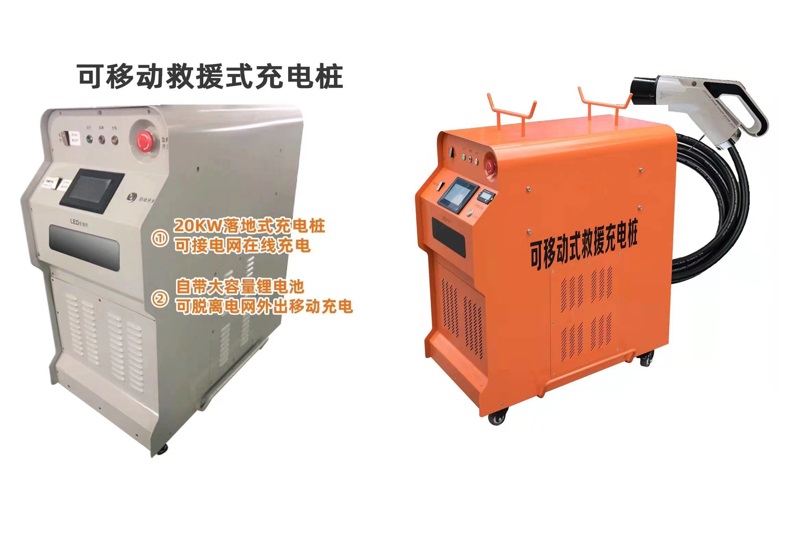
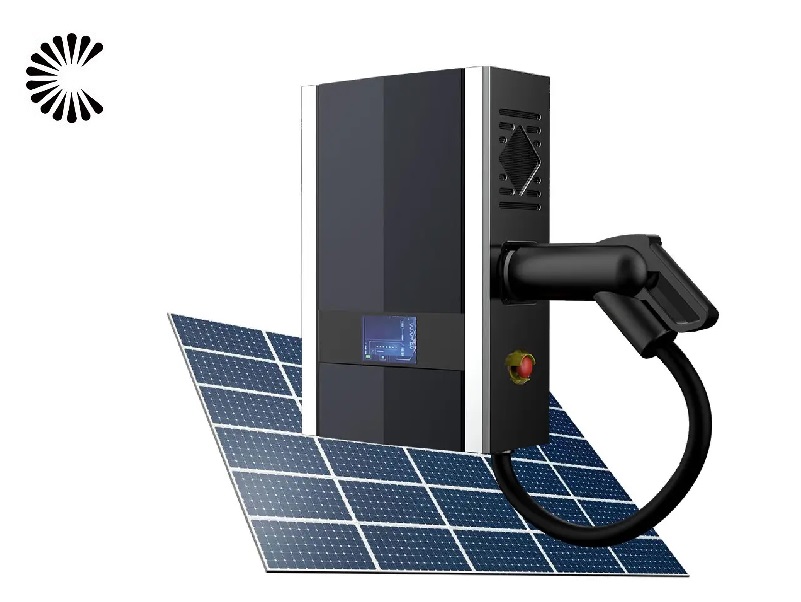
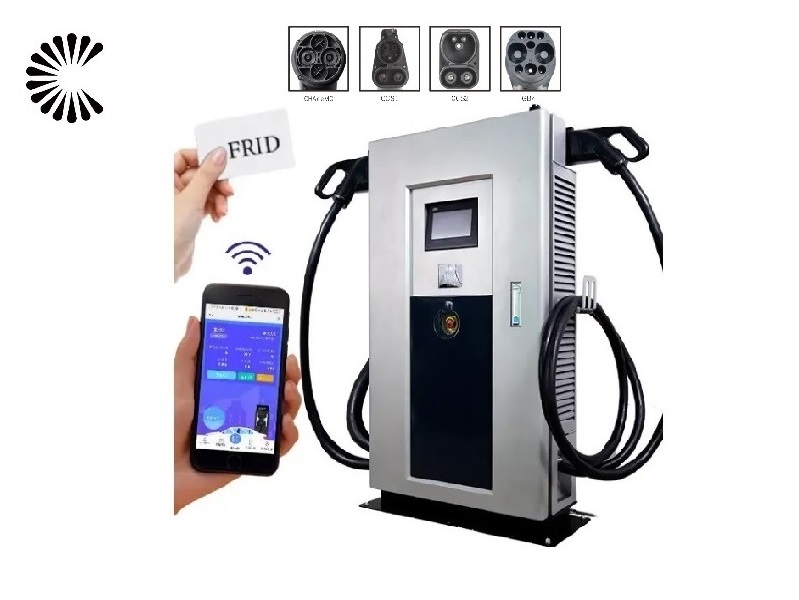
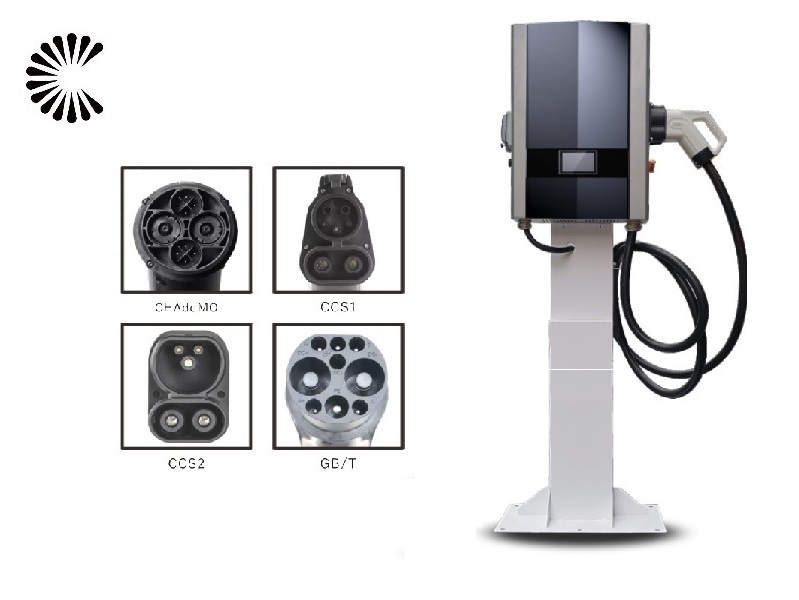
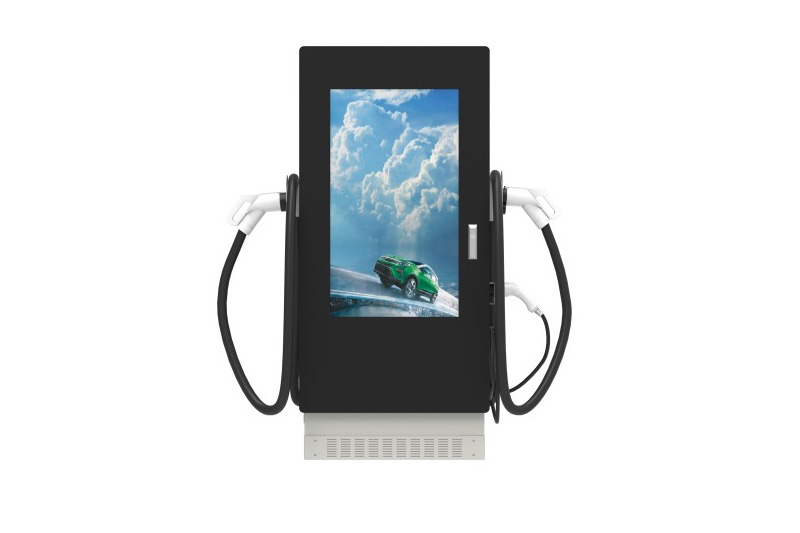
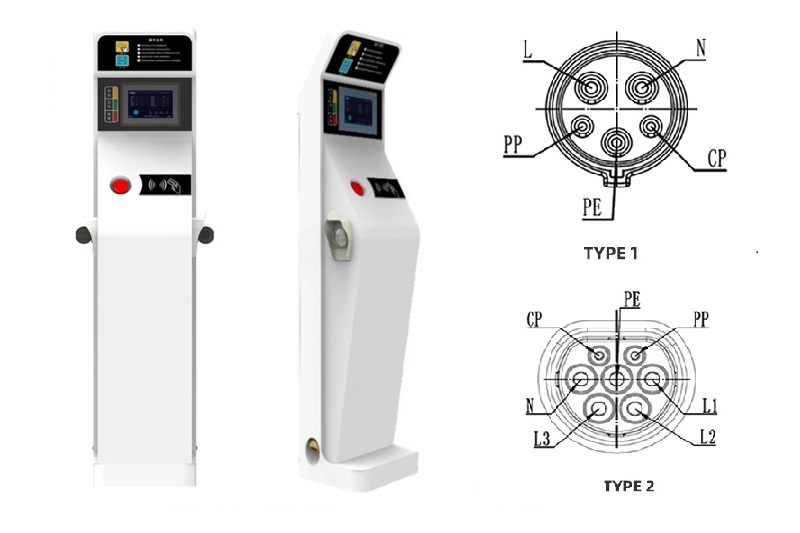
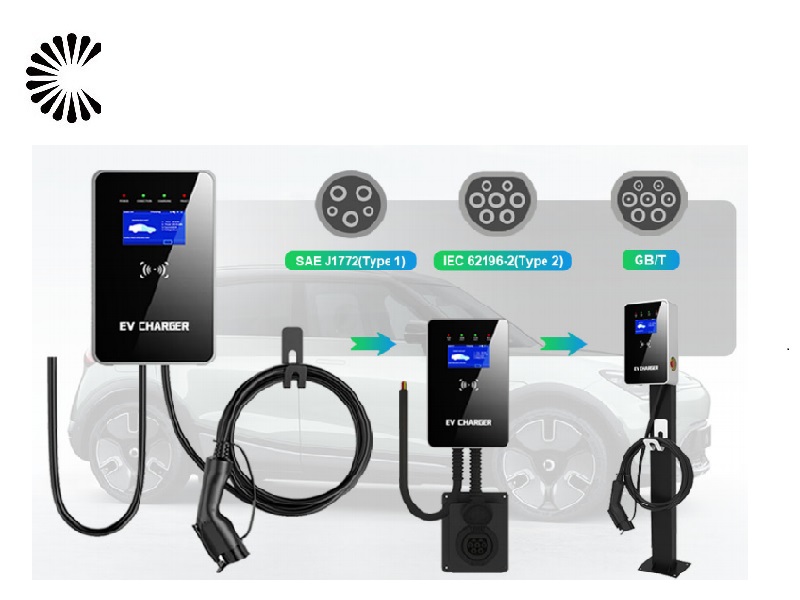
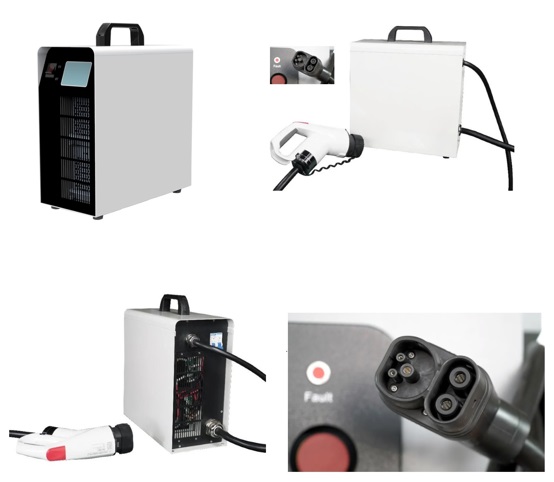
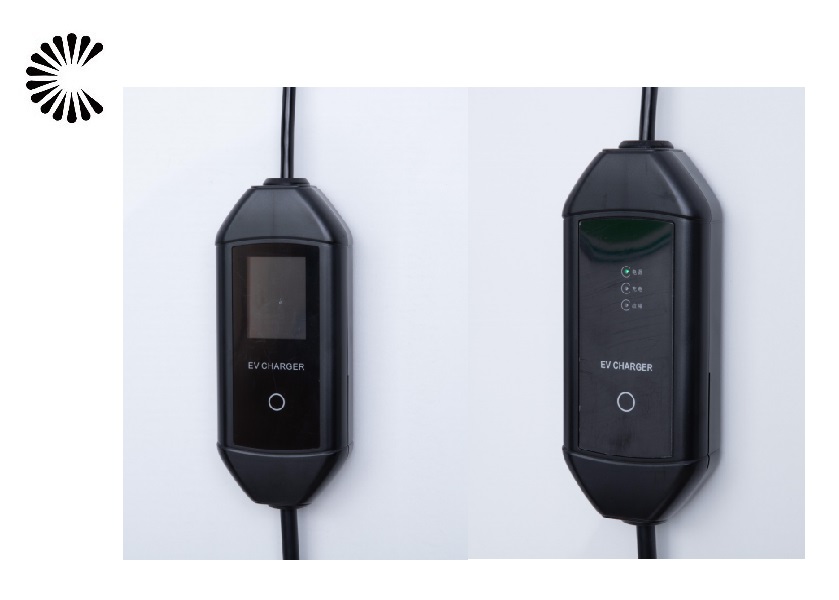
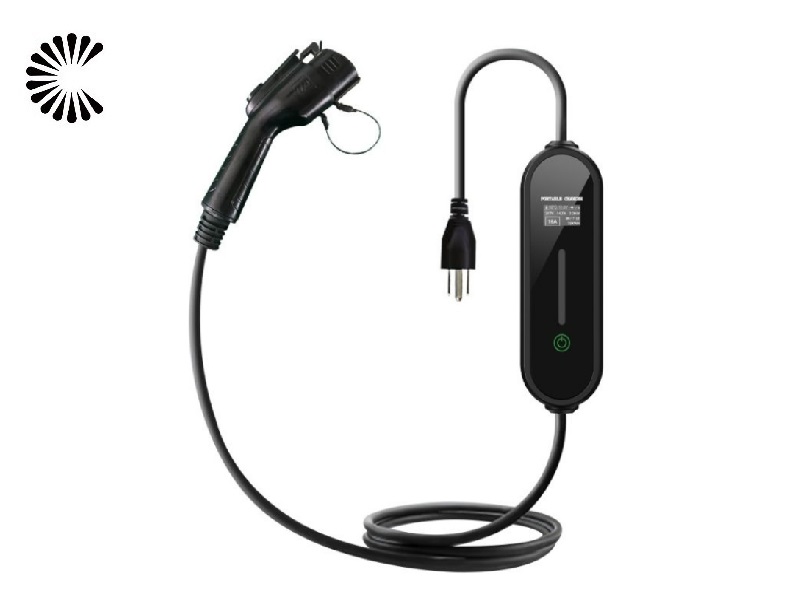
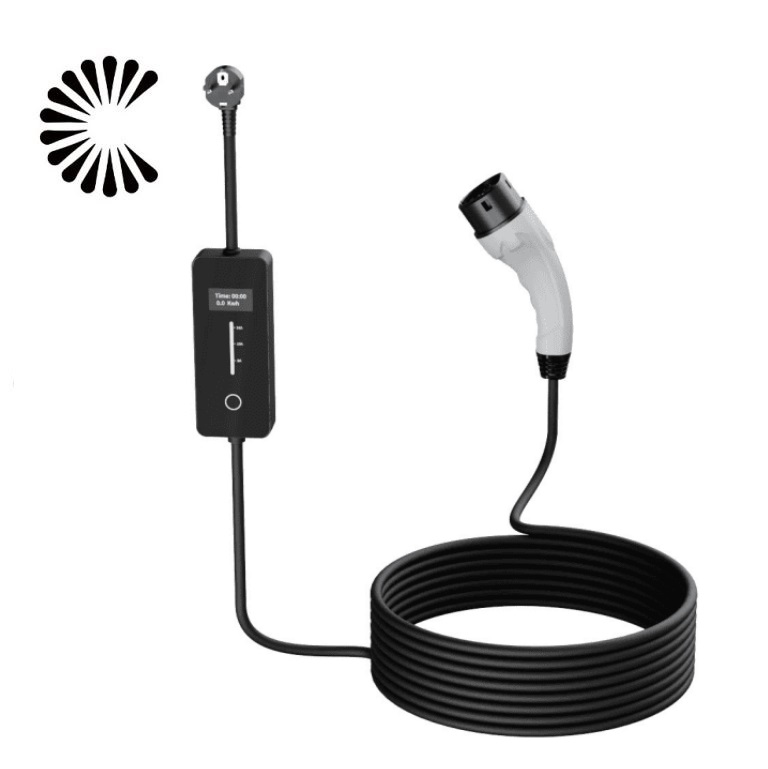
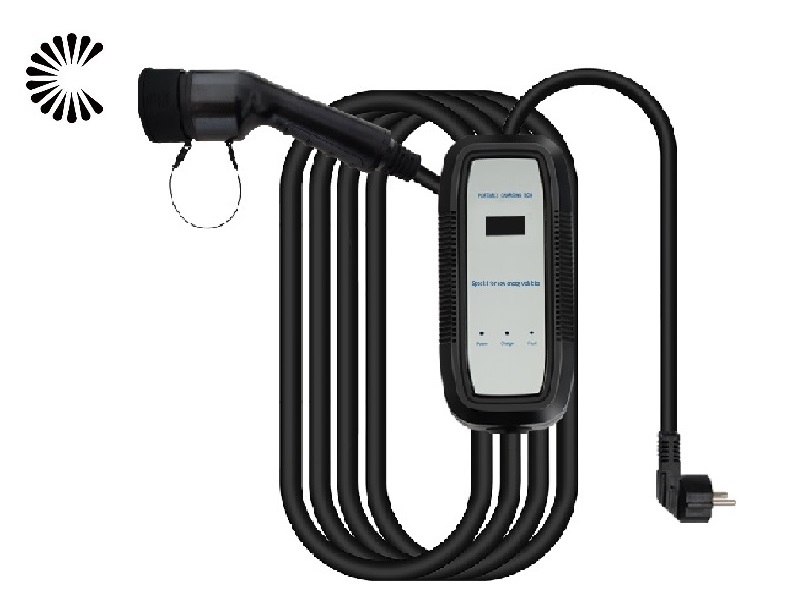
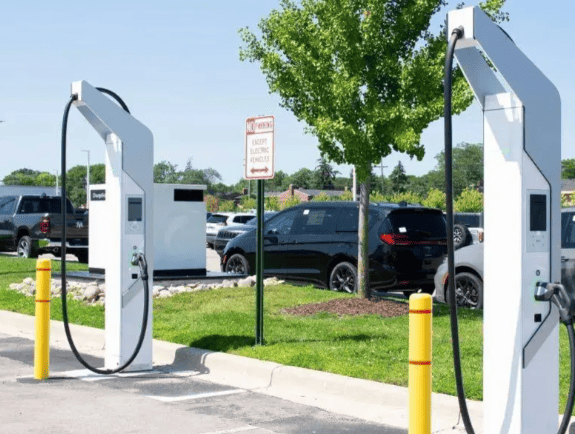
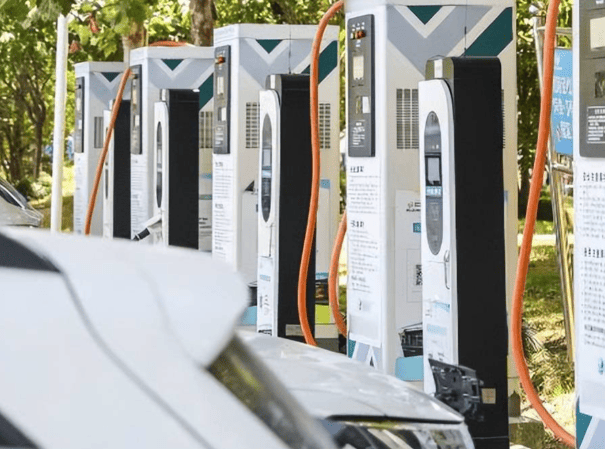
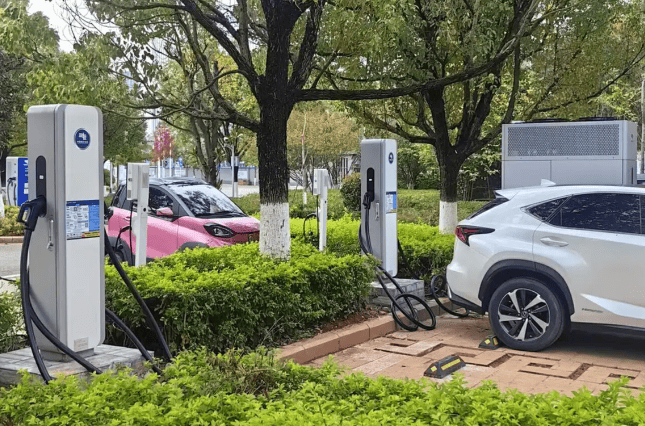
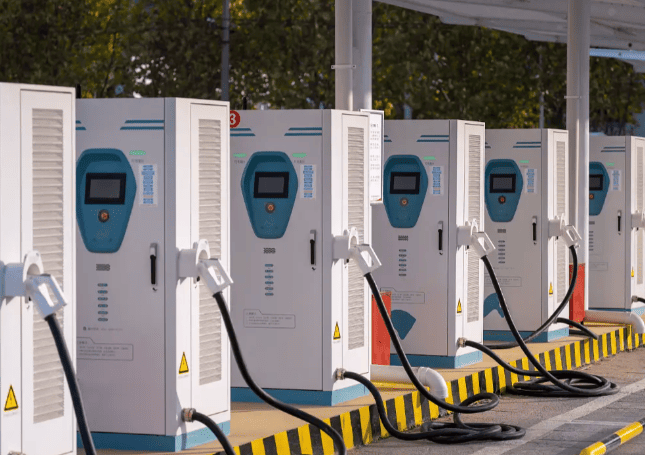
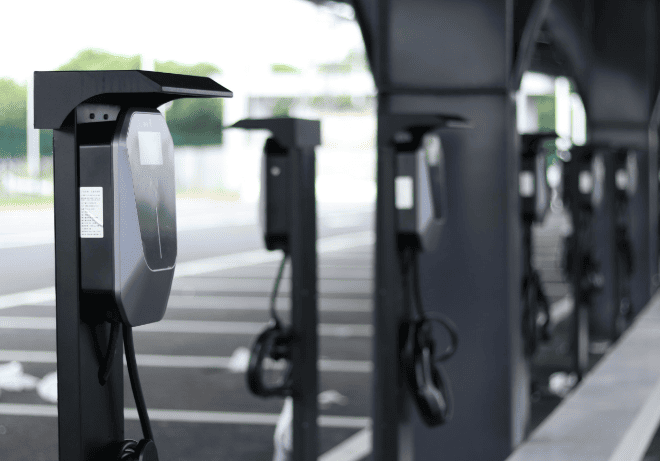
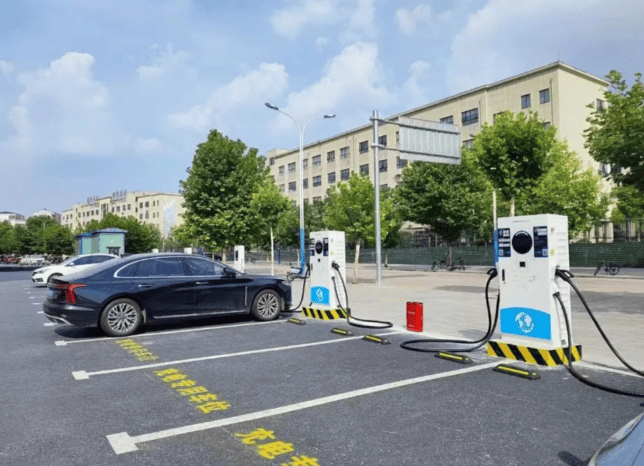
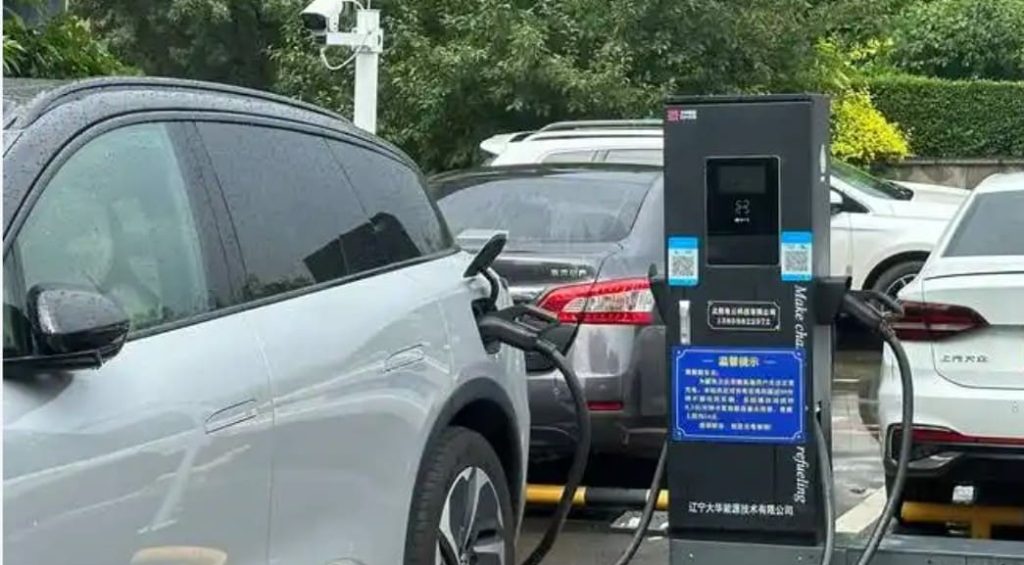
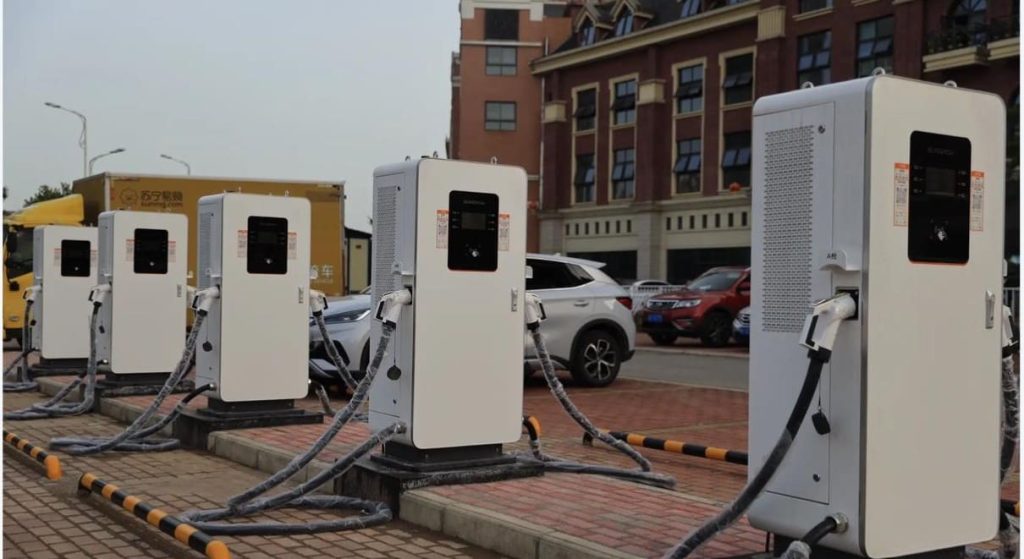
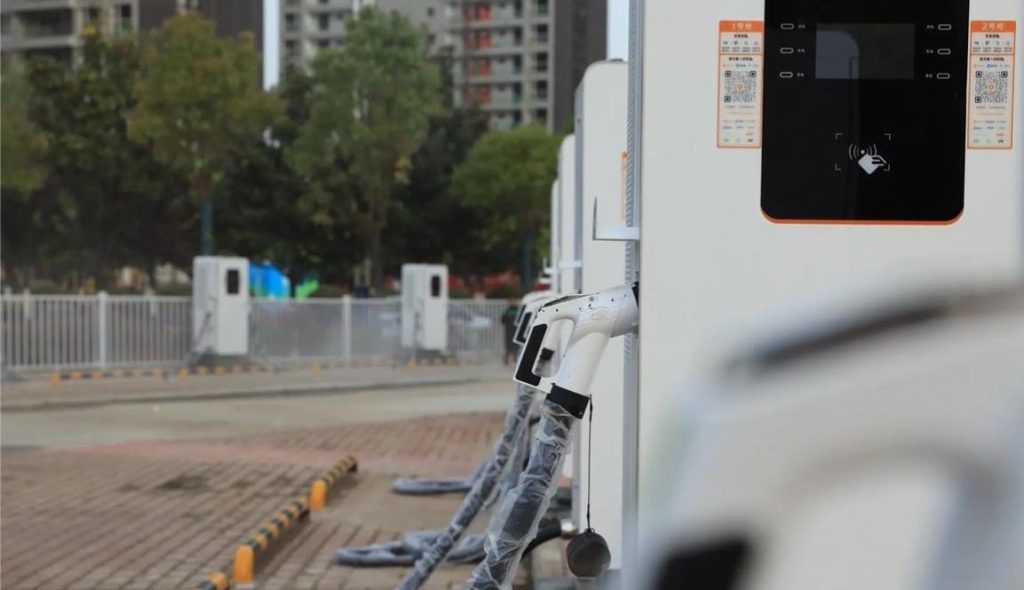
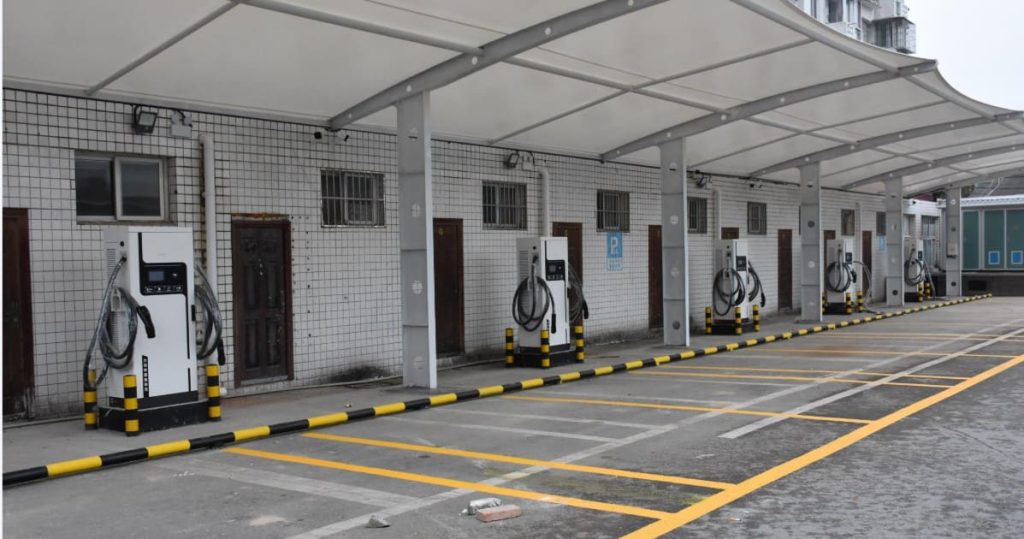
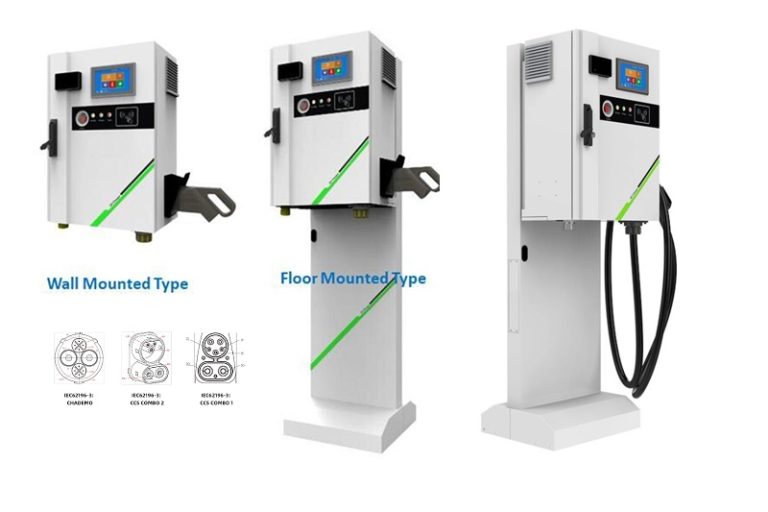
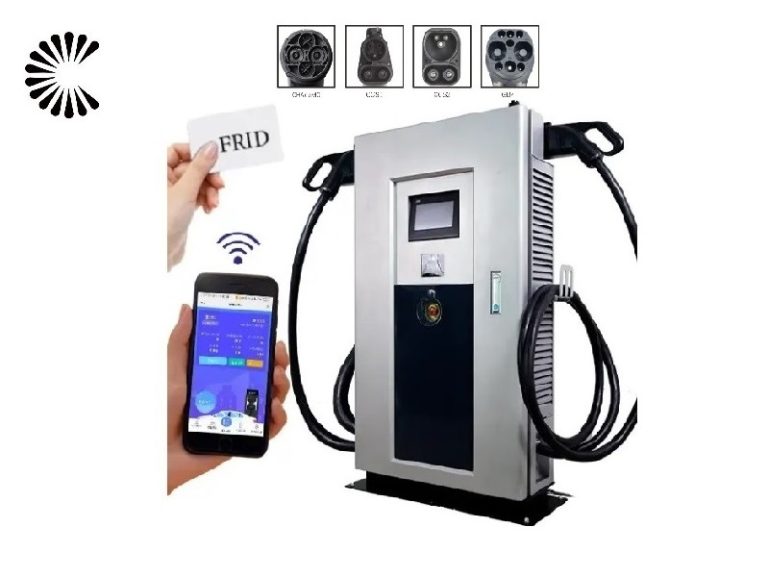
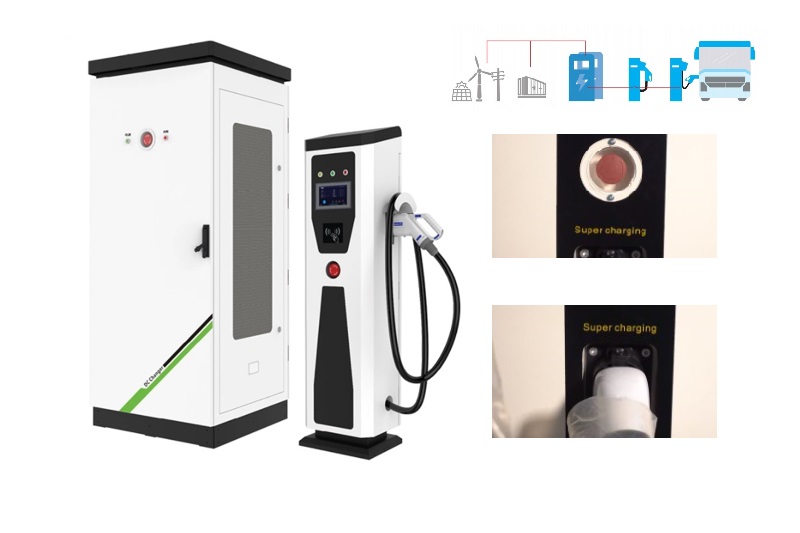
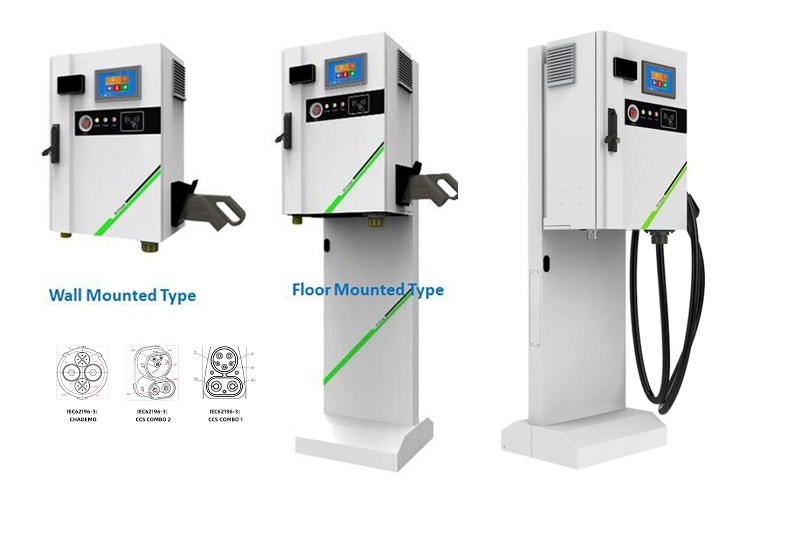
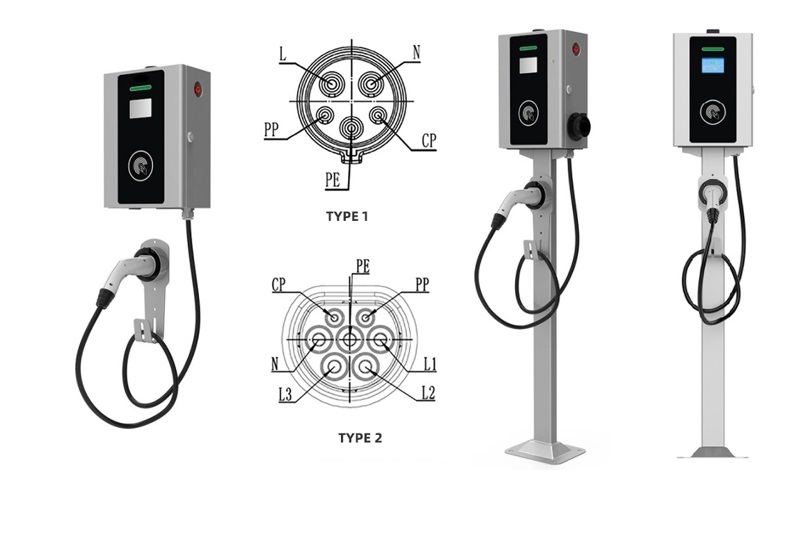
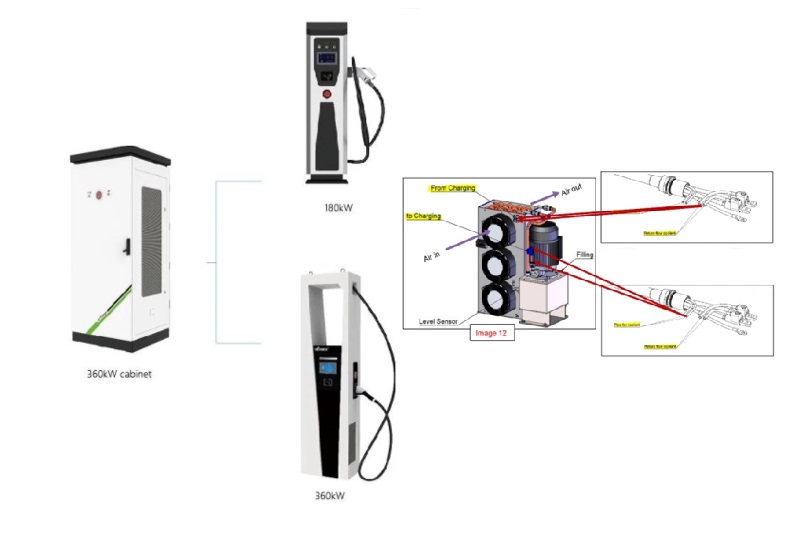
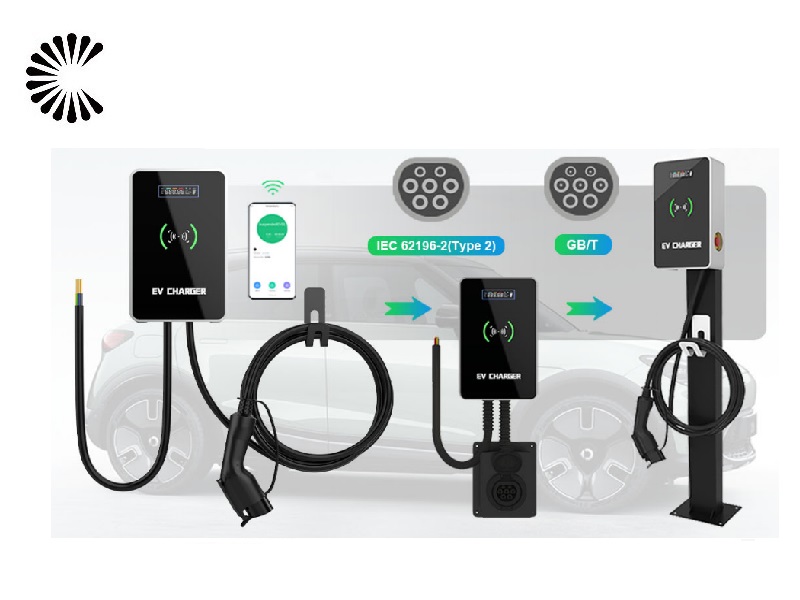
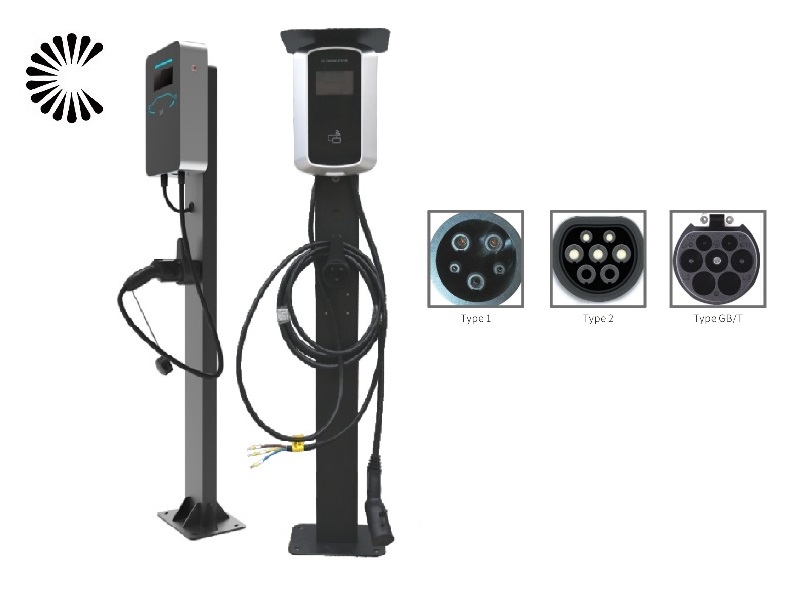
DC EV Charger
DC 60~360KW CE UL
Specification of DC EV Charger
Lead time:
| Quantity (pieces) | 1 – 1 | 2 – 10 | > 10 |
| Lead time (days) | 7 | 15 | To be negotiated |
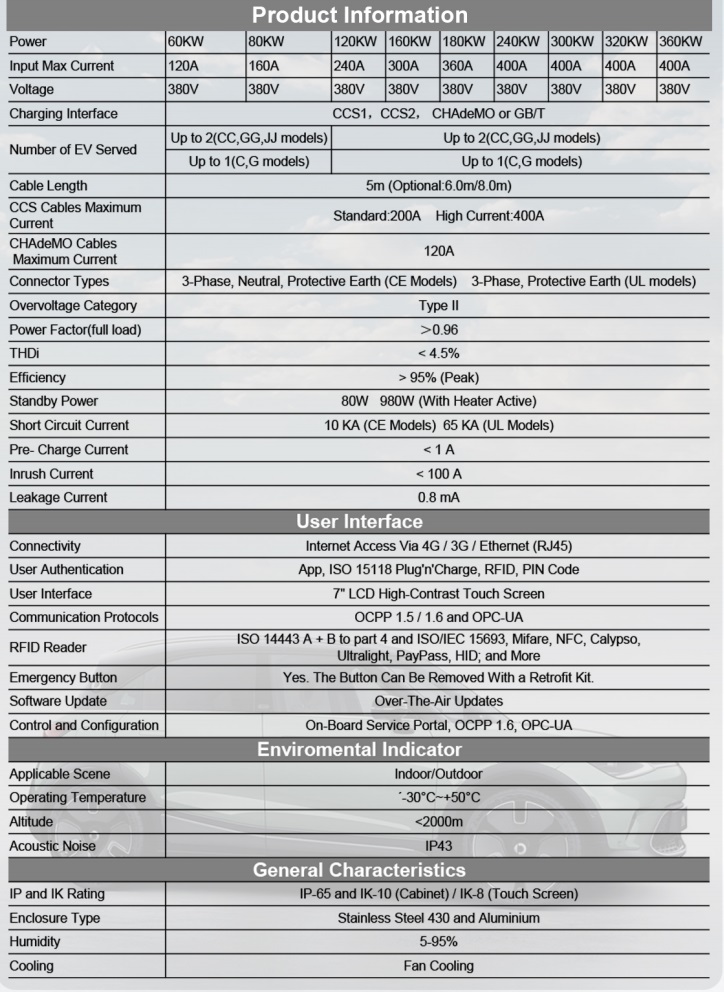
Power Parameters of DC EV Charger:
| Power | 60KW | 80K | 120KW | 160KW | 180KW | 240KW | 300KW | 320KW | 360KW |
| Input Max Current | 120A | 160A | 240A | 300A | 360A | 400A | 400A | 400A | 400A |
| Voltage | 380V | 380V | 380V | 380V | 380V | 380V | 380V | 380V | 380V |
Basic Parameters of DC EV Charger:
| Item | Paramters |
| Charging Interface | CCS1, CCS2, CHAdeMO or GB/T |
| Number of EV Served | Upto 2(CC,GG,JJ Models); Up to 1 (C,G models); |
| Cable Length | 5m (Optional : 6.0m/8.0m) |
| CCS Cables Max Current | Standard: 200A High Current:400A |
| CHAdeMO Cables Max Current | 120A |
| Connector Types | 3-phase, Neutral, Protective Earth(CE Models) (UL Models) |
| Overvoltage Category | Type II |
| Power Factor (full load) | >0.96 |
| THDi | <4.5% |
| Efficiency | >95%(Peak) |
| Standy Power | 80W 980W (With Heater Active) |
| Short Circuit Current | 10KA(CE Models) 65KA(UL Models) |
| Pre-charge Current | <1A |
| Inrush Current | <100A |
| Leakage Current | 0.8mA |
User Interface:
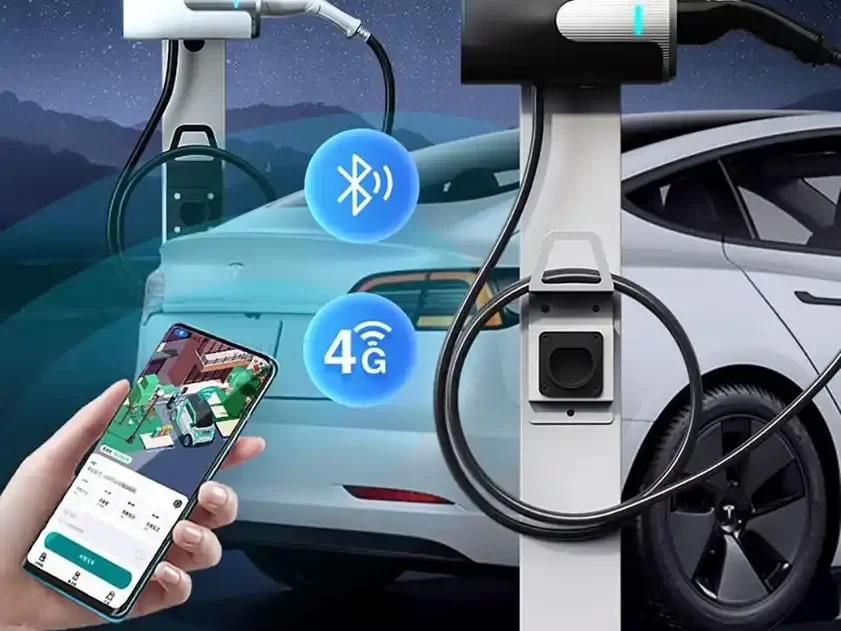
| Connectivity | Internet Access Via 4G/3G/Ethernet(RJ45) |
| User Authentication | App, ISO 15118 Plug’n Charge, RFID, PIN Code |
| User Interface | 7” LCD High- Contrast Touch Screen |
| Communication Protocols | OCPP 1.5/1.6 and OPC-UA |
| RFID Reader | ISO 14443A+B to part 4 and ISO/IEC 15693, Mifare, NFC, Calypso, Ultralight, PayPass, HID, and More |
| Software Update | Over-the-air Updates |
| Emergency Button | Yes, The Button Can be Removed With a Retrofit Kit. |
| Control and Configuration | On-board Service Portal, OCPP 1.6, OPC-UA |
Environmental Indicator:
| Applicable Scene | Indoor/Outdoor |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C~+50°C |
| Altitude | <2000m |
| Acoustic Noise | IP43 |
General Characteristic:
| IP and IK Rating | IP-65, IK-10(Cabinet)/IK-8 (touch screen) |
| Enclouser Type | Stainless Steel 430 and Aluminum |
| Humidity | 5-95% |
| Cooling | Fan cooling |
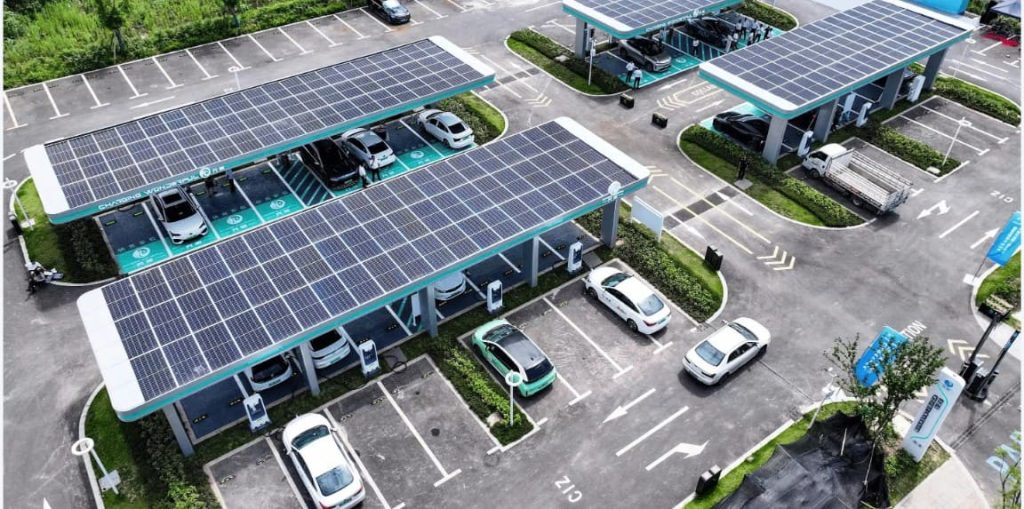
Introduction of DC EV Charger

A DC EV charger is a specialized charging station designed to quickly charge electric vehicles. Unlike regular chargers, which take longer to charge the vehicle’s battery, DC chargers provide a direct flow of high-power electricity to the battery, making the charging process much faster.
The main advantage of DC EV chargers is their rapid charging capability. They can charge an electric vehicle to 80% capacity in under 30 minutes, which is much faster than conventional chargers. This makes electric vehicles more practical for long-distance travel and reduces “range anxiety,” the fear of running out of battery power during a journey.
DC chargers are equipped with connectors for both fast DC charging and standard AC charging. They are compatible with most electric vehicles that support fast charging, making them a versatile choice for charging electric cars.
These chargers often come with smart features and are connected to networks, allowing users to access real-time information, monitor the charging progress, and make payments using smartphone apps or RFID cards. This added convenience makes it easier for EV owners to find and use charging stations.
By deploying DC EV chargers strategically in public places and along major roads, we can create a widespread and reliable EV charging infrastructure. This infrastructure expansion is essential for the wider adoption of electric vehicles, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system.
In summary, DC EV chargers are critical components of the electric vehicle ecosystem, enabling faster charging, reducing range anxiety, and promoting the transition to greener and more eco-friendly transportation.

Advantages of DC EV Charger
A DC EV charger is a specialized charging station designed to quickly charge electric vehicles. Unlike regular chargers, which take longer to charge the vehicle’s battery, DC chargers provide a direct flow of high-power electricity to the battery, making the charging process much faster.
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity and become an integral part of our transportation landscape, the need for efficient and reliable charging solutions has become increasingly important. DC EV chargers, also known as fast chargers or Level 3 chargers, have emerged as a key technology in the EV charging infrastructure, offering several significant advantages that make them an appealing option for EV drivers and charging network providers alike.
Rapid Charging Speed:
One of the most prominent advantages of DC EV chargers is their rapid charging speed. Unlike AC chargers, which use the vehicle’s onboard charger to convert AC power to DC power for the battery, DC chargers directly supply DC power to the battery. This direct current flow allows for significantly faster charging rates, reducing the time required to recharge an EV. For instance, DC chargers can add hundreds of miles of range in as little as 30 minutes, making long-distance travel more practical and convenient.
Long-Range Travel Facilitation:
With the increasing adoption of EVs, the demand for long-range travel capabilities has grown. DC EV chargers play a pivotal role in addressing range anxiety by enabling EVs to cover long distances without prolonged charging stops. As these chargers become more widespread along major highways and travel routes, the fear of running out of power on a lengthy trip diminishes, encouraging more people to embrace electric mobility.
Infrastructure Scalability:
DC EV chargers are highly scalable, making them suitable for various applications and locations. Their fast charging capabilities allow a higher turnover of vehicles, which is particularly valuable in high-traffic areas like urban centers, shopping malls, and rest areas. With their ability to cater to multiple vehicles in a shorter time span, DC chargers can accommodate the increasing number of EVs on the road more efficiently than slower AC charging alternatives.
Reduced Waiting Times:
For both individual EV drivers and businesses operating charging stations, minimizing waiting times is critical. DC chargers’ accelerated charging speeds translate into reduced waiting times at charging stations, leading to enhanced driver satisfaction and higher customer turnover for charging station operators. This aspect is particularly crucial as the number of EVs grows, reducing the likelihood of encountering congested charging stations.
Enabling Cross-Country Travel:
The deployment of a robust network of DC EV chargers is vital to facilitate cross-country travel for EV drivers. Long-distance journeys often require quick charging stops to keep up the pace, and DC chargers offer the ideal solution. By ensuring that EV drivers have access to fast charging infrastructure throughout the country, it becomes more feasible to embrace electric vehicles for a broader range of travel scenarios.
Utilization of Renewable Energy:
The faster charging times of DC EV chargers allow for more efficient utilization of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. By drawing power directly from these sources and feeding it into EV batteries at high speeds, DC chargers can optimize the integration of clean energy into the transportation sector. This alignment with renewable energy goals is essential in the fight against climate change and reducing the carbon footprint of transportation.
Battery Health Considerations:
DC chargers often come equipped with sophisticated software and hardware that can communicate with the EV’s battery management system. This communication enables optimized charging profiles, mitigating potential damage to the battery and extending its overall lifespan. By closely monitoring and managing charging currents and temperatures, DC chargers help preserve the longevity and health of EV batteries, resulting in long-term cost savings for EV owners.
Minimized Grid Strain:
As EV adoption continues to increase, concerns about the strain on the electricity grid arise. DC chargers can help alleviate this strain by efficiently distributing power during peak charging periods. Due to their higher charging speeds, EVs are connected to the charger for a shorter duration, reducing the overall demand on the grid during charging sessions. Additionally, the possibility of smart charging integration allows for further grid load management and optimization.
Investment Attraction:
The deployment of a well-established network of DC EV chargers can stimulate investment in EV infrastructure and related industries. As fast chargers become more prevalent, businesses, governments, and private entities are more likely to invest in electric mobility solutions, including charging station development and EV manufacturing. This increased investment can accelerate the growth of the EV ecosystem and promote technological advancements.
Technological Advancements:
The evolution of DC EV chargers has spurred various technological advancements in the field of electric vehicle charging. As the demand for faster, more efficient chargers grows, manufacturers and researchers continue to innovate, leading to improved charging hardware, software, and user interfaces. These advancements benefit both EV drivers and charging station operators, enhancing the overall charging experience.
In conclusion, DC EV chargers offer numerous advantages that make them a crucial component of the evolving electric vehicle ecosystem. From their rapid charging speed and long-range travel facilitation to their scalability, reduced waiting times, and potential for utilizing renewable energy, DC chargers address key challenges in the widespread adoption of electric mobility. As technology continues to advance and the charging infrastructure expands, DC EV chargers will play a pivotal role in shaping a cleaner, more sustainable transportation future.
| Business Type: | Manufacturer/Factory | Main Products: | EV Charger |
| Number of Employees: | 100 | Year of Establishment: | 2014.05 |
| Production Capacity | 5000Set/Year | After-sales Service: | Technical Support; on-line teach lessons |
| R&D Capacity: | ODM, OEM | Annual Output Value: | US$5 Million – US$10 Million |
| No. of R&D Staff: | 5 | No. of Production Lines: | 6 |
ChargersGO is a professional manufacturer for EV Charger. Our main product including slow charger, fast charger, DC EV Charger, AC EV Charger, commercial EV Charger, charger for home, EV charger level 1, level 2 and level 3 etc. All products in accordance with the China GMP design requirements. And also we have other certifications.
Business Philosophy
“Quality is the main policy of sales” and “integrity is the principle of success” are the business philosophy of our people. We carry out one-year warranty, lifelong maintenance service, with technical consultation and other services, and long-term supply of equipment. Welcome new and old customers to negotiate cooperation!
Small Charger Packing:
Retail Small EV Charger shipped with express.
Wsholesale Small EV Charger packed with export fumigation-free wooden cases, goes with bulk shipment or in container.
When packing small machines for sea shipment, it is important to take measures to ensure that the machines are protected from damage during transit. Here are some general steps that a manufacturer may follow when packing small machines for sea shipment:
- Clean and dry the charger: Before packing, the charger should be thoroughly cleaned and dried to prevent any moisture or debris from causing damage during transit.
- Disassemble the machine: If possible, the charger should be disassembled into its component parts to reduce its overall size and make it easier to pack.
- Wrap the charger in protective material: The charger should be wrapped in a layer of protective material, such as bubble wrap or foam, to protect it from scratches and impact during transit.
- Place the charger in a sturdy box: The wrapped charger should then be placed in a sturdy box that is appropriate for the size and weight of the machine. The box should be made of durable material, such as corrugated cardboard or plywood, and should be able to withstand the rigors of sea transit.
- Add packing material: The box should be filled with packing material, such as packing peanuts or air pillows, to provide cushioning and prevent the machine from shifting during transit.
- Seal the box: The box should be securely sealed with high-quality packing tape to prevent it from opening during transit.
- Label the box: The box should be clearly labeled with the charger’s name, weight, and any other relevant information, as well as the destination address and contact information.
Overall, the goal is to pack the small chargers in a way that will protect it from damage during transit and ensure that it arrives at its destination in good condition. It is important to follow proper packing procedures and use high-quality packing materials to minimize the risk of damage during sea shipment.

Large Machine Packing:
Packing a large machine for sea shipment can be a complex and challenging task. However, with careful planning and attention to detail, it is possible to pack a large machine for sea shipment in a way that will ensure that it arrives at its destination in good condition. Here are some general steps that a manufacturer may follow when packing up a large machine for sea shipment:
- Clean and prepare the machine: Before packing, the machine should be thoroughly cleaned and prepared. All fluids, such as oil or coolant, should be drained, and any loose or detachable parts should be removed.
- Disassemble the machine: If possible, the machine should be disassembled into its component parts to reduce its overall size and make it easier to pack. Each part should be carefully labeled and numbered to ensure that it can be easily reassembled at the destination.
- Protect delicate parts: Delicate or fragile parts should be wrapped in protective material, such as bubble wrap or foam, to protect them from damage during transit.
- Build a custom crate: A custom crate should be built around the machine to provide a secure and sturdy enclosure. The crate should be made of durable material, such as plywood, and should be designed to fit the machine snugly. The crate should also include braces or supports to prevent the machine from shifting during transit.
- Add cushioning material: The crate should be filled with cushioning material, such as packing peanuts or air pillows, to provide extra protection and prevent the machine from moving or shifting during transit.
- Securely fasten the machine: The machine should be securely fastened to the crate to prevent it from moving or shifting during transit. This may involve using straps, bolts, or other fasteners to hold the machine in place.
- Seal and label the crate: The crate should be securely sealed with high-quality packing tape, and should be clearly labeled with the machine’s name, weight, and any other relevant information. The destination address and contact information should also be clearly marked on the crate.
Overall, packing a large machine for sea shipment requires careful planning and attention to detail. It is important to use high-quality materials and follow proper packing procedures to ensure that the machine arrives at its destination in good condition. A professional packing and shipping company may be consulted to ensure that the machine is properly packed and prepared for sea shipment.

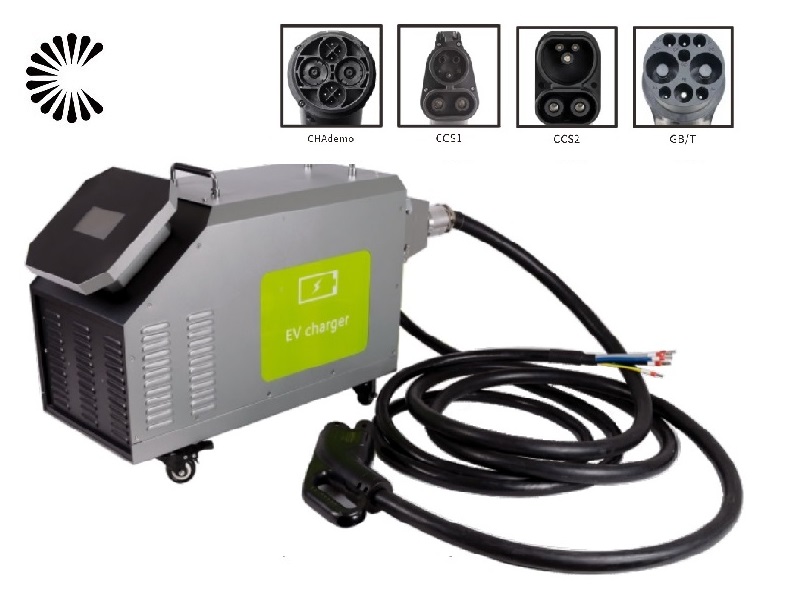
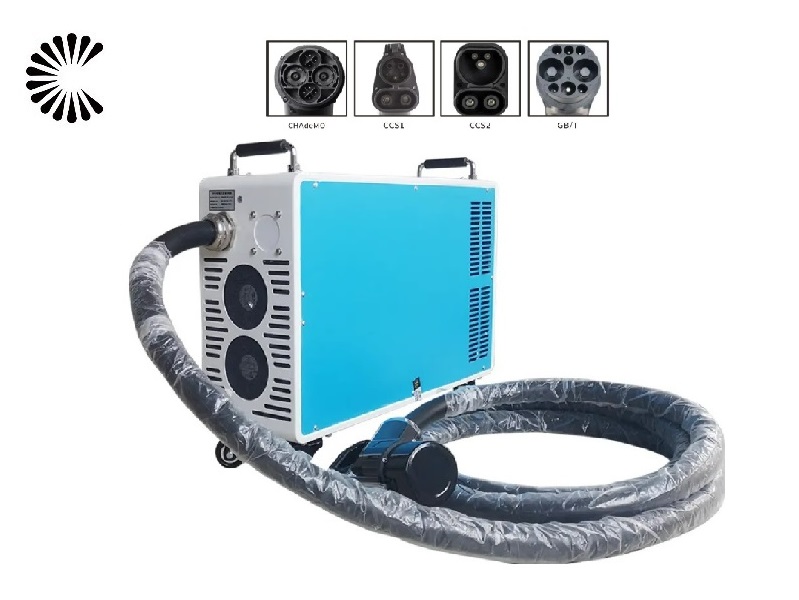
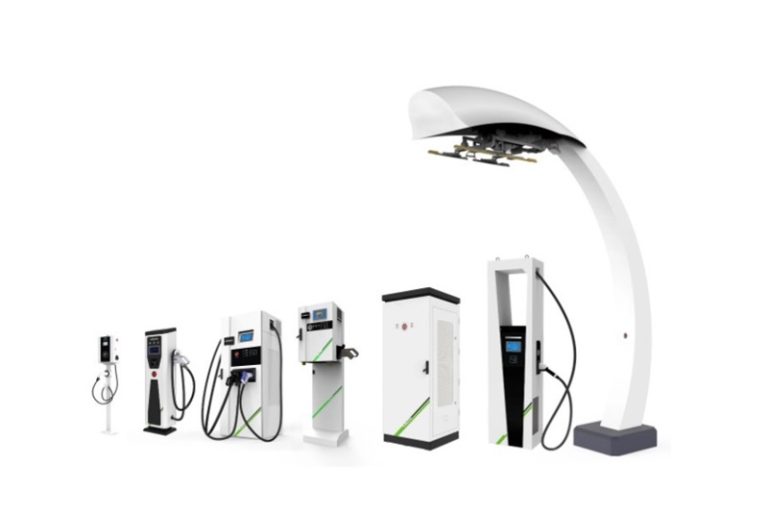
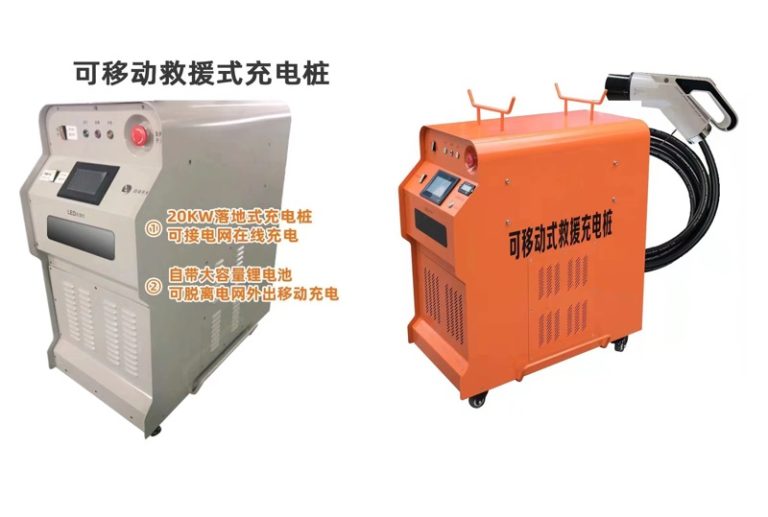
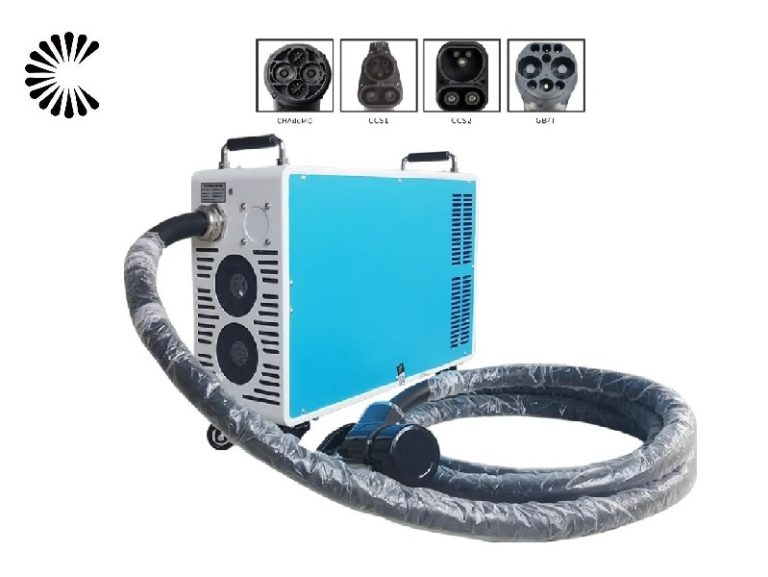
Other DC EV Chargers
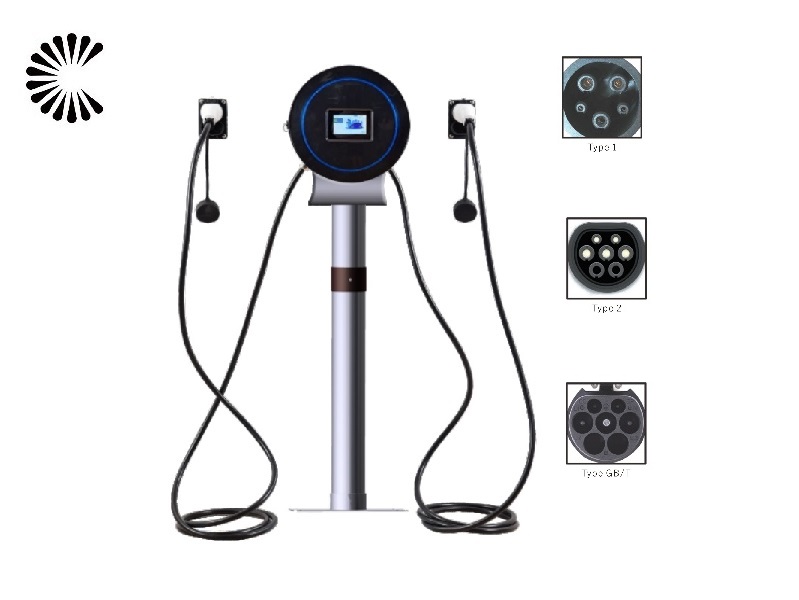
AC EV Chargers
DC EV Charger Wholesale Manufacturer In China
With the sudden emergence of new energy vehicles, the construction of charging piles is increasingly booming, and the capacity of the power grid is limited. At the same timethe policy direction of carbon peak and carbon neutrality provides an opportunity for the development of integrated optical storage and charging stations.
Related Products
Related Articles
Contact Us
Frequently Asked Questions (See More FAQ)
-
Are you a factory?
Yes, We are a professional manufacturer of new and sustainable energy applications for over 20 years. We have rich experience in new energy supply industry.
-
What is the warranty of the EV Charger?
Our product warranty period is 12 months. In this period, we will supply technical support and replace the new parts by free(not including the parts are damaged by human error).
-
What is the packing method for shipment?
Generally, we pack our goods in cartons. If you have legally registered patent, we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters. The packing method will be checked and confirmed with our customer for each order.
-
What is your payment terms?
T/T 50% as deposit, and 50% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
-
What is your terms of trade?
EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DAP,DDU,DDP
-
How about your delivery time?
Generally, it will take 3 to 7 working days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
-
Can you produce according to the samples?
Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
-
What is your sample policy?
We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
-
Do you test all your goods before delivery?
Yes, we have 100% test before delivery.
-
What’s the difference between Movable Charger and Wallbox Charger?
In addition to the obvious appearance difference, the main protection level is different: wallbox charger protection level is IP54, available outdoors;And the Movable Charger protection level is IP43, rainy days and other weather can not be used outdoors.
-
What is a DC EV charger?
A DC EV charger, also known as a fast charger or Level 3 charger, is a type of electric vehicle (EV) charging station that directly provides direct current (DC) power to charge an electric vehicle’s battery. Unlike AC (alternating current) chargers, which require the vehicle’s onboard charger to convert AC power to DC power for the battery, DC EV chargers skip this step and supply the DC power directly to the EV’s battery.
-
Is AC or DC better for EV charging?
Both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) charging have their advantages and are suitable for different charging scenarios in electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. The choice between AC and DC charging depends on various factors, including charging speed, cost, infrastructure availability, and the specific needs of EV drivers.
AC charging is the most common type of charging available for electric vehicles. Most EVs come with an onboard AC charger that converts AC power from the charging station into DC power to charge the vehicle’s battery. AC charging is typically slower than DC charging, making it more suitable for overnight charging at home or during longer stops, such as at workplaces, shopping centers, and public charging stations.
On the other hand, DC charging, also known as fast charging or Level 3 charging, directly supplies DC power to the vehicle’s battery, bypassing the need for an onboard charger. DC chargers can charge an EV significantly faster than AC chargers, adding hundreds of miles of range in as little as 30 minutes. This makes DC charging ideal for long-distance travel and quick top-ups on the go, reducing the downtime associated with charging stops during extended journeys.
While DC charging offers faster charging speeds, it comes with higher infrastructure costs compared to AC charging stations. As a result, DC chargers are typically installed in locations where quick charging is essential, such as along major highways, travel routes, and busy urban centers.
In summary, both AC and DC charging have their advantages and are complementary in the EV charging ecosystem. AC charging is convenient for overnight charging and regular daily use, especially when EV drivers have sufficient time for the vehicle to charge. DC charging, on the other hand, is more suitable for long-distance travel and quick top-ups, providing the necessary infrastructure for rapid charging on highways and busy areas.
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, a combination of AC and DC charging infrastructure will be essential to meet the diverse charging needs of EV drivers, providing them with the flexibility and convenience required to embrace electric mobility fully. -
Is Tesla a DC charger?
Yes, Tesla is a DC charger. Tesla electric vehicles (EVs) come equipped with an onboard charger that allows them to accept both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) charging. When using Tesla’s Supercharger network, which is Tesla’s proprietary charging network, the vehicles can access high-power DC charging. This fast DC charging capability enables Tesla EVs to charge much faster compared to using standard AC chargers.
Tesla Superchargers are specifically designed for Tesla vehicles and provide a direct current to the vehicle’s battery, bypassing the need for the onboard AC charger to convert AC power. As a result, Tesla Superchargers can add significant range to the vehicle’s battery in a short amount of time, making them ideal for long-distance travel and quick top-ups on the go.
However, it’s important to note that Tesla vehicles can also charge using standard AC chargers found at homes, workplaces, and public charging stations. In these cases, the vehicle’s onboard charger converts the AC power to DC power to charge the battery.
Overall, Tesla vehicles are equipped with both AC and DC charging capabilities, with the Tesla Supercharger network providing the high-power DC charging option for faster charging times and enabling long-distance travel convenience for Tesla drivers. -
How fast can a DC charger charge an EV?
A DC charger can charge an electric vehicle (EV) at a much faster rate compared to a standard AC charger. The exact charging speed of a DC charger depends on the charger’s power output and the capacity of the EV’s battery. Generally, DC chargers are capable of adding a significant amount of range to an EV’s battery in a short amount of time, making them ideal for quick charging needs.
On average, a DC fast charger can add approximately 60 to 80 miles (about 97 to 129 kilometers) of range to an EV’s battery in just 20 minutes of charging. In some cases, particularly with high-power DC chargers like those found in Tesla’s Supercharger network or other ultra-fast charging stations, the charging speed can be even faster. These chargers can add hundreds of miles of range to an EV’s battery in about 30 minutes.
It’s important to note that while DC chargers provide rapid charging speeds, the charging rate may slow down as the battery approaches its full capacity. This is a common characteristic of lithium-ion batteries and is done to protect the battery from overheating or damage.
The fast charging capability of DC chargers is particularly beneficial for long-distance travel and situations where drivers need to charge their EV quickly and get back on the road. With the widespread deployment of DC fast chargers in public charging networks, EV drivers can enjoy the convenience of rapid charging and feel more confident about embarking on long journeys with their electric vehicles.