How to pay for ev charging?

How to pay for ev charging? Electric vehicle (EV) charging can be paid for using a variety of methods, such as contactless cards or automated vehicle recognition, which are influenced by infrastructure, user behavior, and regional regulations. Success for manufacturers depends on modifying payment methods to suit regional markets while maintaining ease of use and security. We analyze global payment ecosystems and their technical ramifications below.
North America: Credit Cards and Subscription Dominance
In the U.S. and Canada, credit/debit cards reign supreme. Public networks like Electrify America mandate physical card readers or NFC support (Apple Pay/Google Pay), while Tesla’s proprietary system auto-bills linked credit cards via its app. Subscription models add complexity: services like Electrify Canada Pass+ offer 20% discounts for a monthly fee, automatically deducted from cards.
Manufacturers face two critical hurdles: PCI-DSS compliance for card data security and the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act’s requirement for “domestic assembly” of hardware to qualify for tax credits. Technically, chargers need EMV chip readers, NFC modules, and OCPP 1.6 protocol integration to sync with payment APIs like Stripe.
Europe: Regulation-Driven Open Access
Europe’s AFIR regulation (2024) forces public chargers (>50kW) to accept contactless cards (Visa/Mastercard) and QR code payments, dismantling proprietary app barriers. Germany leads with mandates for RFID card compatibility (e.g., Enel X’s MIFARE cards), while platforms like Zap-Map Pay enable cross-network payments via a single app.
Two innovations stand out:
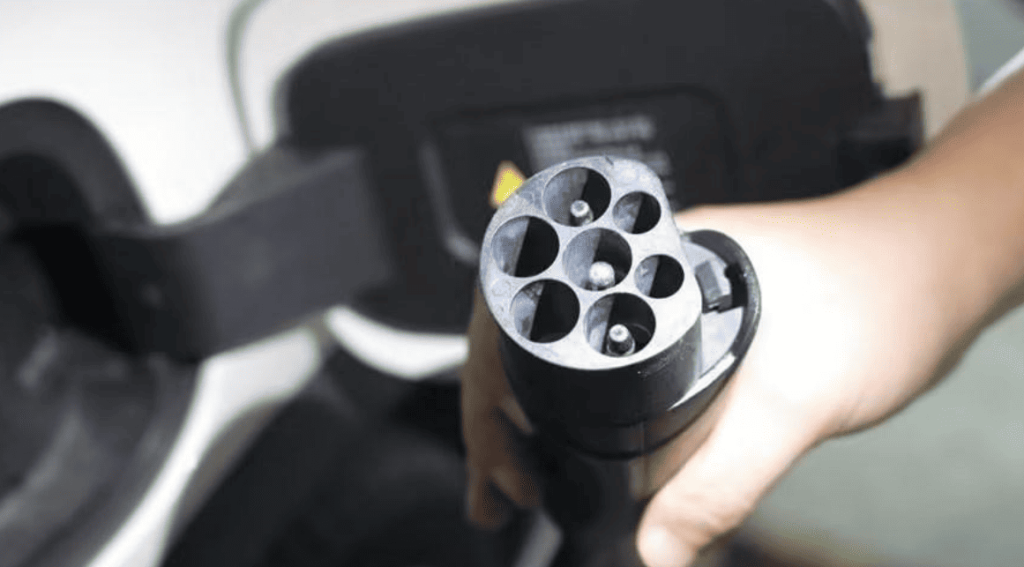
- Plug & Charge (ISO 15118): Cars like the Porsche Taycan authenticate and bill drivers automatically upon plug-in, using digital certificates.
- Green energy premiums: Chargers like Ionity offer 100% renewable energy options, billed via subscriptions (€5.99/month + €0.33/kWh).
Compliance is stringent: GDPR for data privacy, PSD2 for anti-fraud authentication, and CE certification for hardware.
Asia-Pacific: Mobile-First and Compact Solutions
Japan relies on transport cards (Suica/Pasmo) with NFC, while operators like e-Mobility Power use minute-based billing (¥27.5/min) via prepaid cards. South Korea mandates QR code payments through apps like Kakao Pay or T Map, with Hyundai pioneering “EV Token” prepaid credits.
Constraints shape design: Japan’s dense cities require CHAdeMO-compatible chargers with compact payment terminals, while Korea’s QR-focused system demands high-speed scanners. Both markets enforce strict security—JIS C 6247 certification in Japan and KC certification in Korea.
Australia: Offline Resilience and Solar Synergy
Australia prioritizes offline functionality for remote areas. NRMA’s app enables card-linked payments, but EFTPOS terminals (supporting chip/magnetic cards) remain crucial for regions with poor connectivity. Solar integration is rising: chargers like those from JET Charge deduct costs from home solar credits during daytime use.
Hardware must endure harsh conditions: IP65-rated waterproofing and UV-resistant materials are non-negotiable. SAA certification and AS/NZS 3000 electrical standards add compliance layers.
Technical Foundations for Manufacturers
Hardware Adaptations
- Multi-mode readers: Combine EMV chips, NFC, and magnetic stripe support (for Australia’s EFTPOS).
- QR scanners: High-resolution cameras for Korea/China’s app-centric users.
- Ruggedization: IP67 sealing (Australia) and -20°C to 50°C operational ranges (Canada/Sweden).
Software and Security
- OCPP 1.6/OCPI protocols: Enable third-party payment integrations (e.g., Stripe) and roaming across networks.
- End-to-end encryption: AES-256 for payment data, aligned with ISO 27001.
- Dynamic pricing engines: Display real-time rates, including peak surcharges or green energy premiums.
User Experience (UX) Innovations
- Auto-detection: Suggest preferred payments (e.g., contactless in Germany, QR codes in Chengdu).
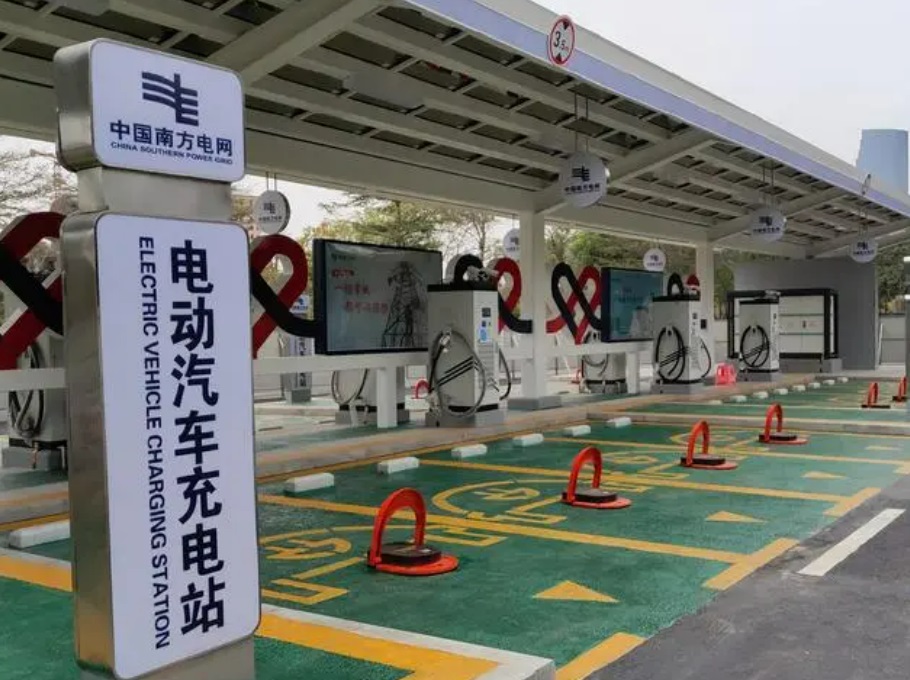
- Unified platforms: Like Guangzhou’s city-wide system, aggregating 10+ operators into one payment interface.
Strategic Recommendations for Manufacturers
- Localize Payment Modules:
- Embed region-specific hardware: EFTPOS for Australia, MIFARE for Germany, QR for Korea.
- Partner with local gateways: Alipay/WeChat Pay in China, Kakao Pay in Korea, Stripe in the U.S..
- Leverage Policy Incentives:
- In the EU, bundle chargers with subsidy applications (e.g., Germany’s 30% installation grant).
- In the U.S., manufacture payment terminals domestically to qualify for IRA tax credits.
- Future-Proof with V2G/Bidirectional Tech:
- Support ISO 15118 for Plug & Charge, allowing EVs to resell power to grids (e.g., U.K.’s Octopus Energy).
The Road Ahead: Frictionless and Green
By 2027, automated payments (via vehicle ID or phone NFC) will dominate, as seen in Chengdu’s “touch-to-charge” stations that cut transaction time to 2 seconds. Meanwhile, green energy billing will expand, letting users choose—and pay premiums for—renewable sources. For manufacturers, winners will be those who embed flexibility: hardware that adapts to local rules, software that speaks global payment languages, and designs that turn charging from a chore into a seamless pause in the journey.
“The best payment is no payment—just tap and go. That’s the future we’re building.”
— Whale Charge Engineer, Nanjing NFC Project