ev charger installation
EV Charger Installation: Costs, Process, and Location Selection
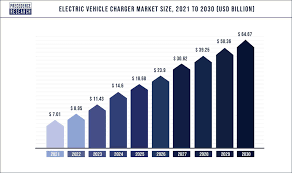
Installing an electric vehicle (EV) charger involves careful consideration of costs, a specific application and installation process, and strategic placement for optimal safety and convenience. Understanding these aspects thoroughly is crucial for a smooth transition to home EV charging. The overall installation cost typically ranges from several thousand to tens of thousands of RMB, influenced by various factors. The process requires preparation, utility approval, and professional installation, while the location must prioritize safety, accessibility, and practicality.

Installation Costs Explained in Detail
The overall cost of installing an EV charger varies greatly depending on a number of important factors and is not a fixed amount. The electrician’s basic work is covered by a basic installation fee, which typically ranges from 500 RMB to 2000 RMB. This entails mounting the charger unit firmly to a wall or pedestal, attaching it to the power source, setting it up and configuring it initially, and carrying out extensive functional and safety testing. Although longer or more complicated routes incur additional fees, simple wiring runs within a very short distance may also be included here.
A significant portion of the budget goes toward the price of cables and other required electrical accessories in addition to the basic labor. A minimum 6mm² (6 square millimeter) copper core cable is required and strongly advised for the most popular 7kW home AC chargers in order to safely manage the continuous current. This cable usually costs between 20 and 50 RMB per meter. Importantly, the distance that electricity must travel from your main distribution board (or a recently installed dedicated meter) to the charger location determines the entire cost of the cable. For the cable alone, a 20-meter run might cost 400–1000 RMB, whereas a 50-meter run might cost 1000–2500 RMB.Additionally, essential accessories like sturdy PVC conduit to protect the cable (especially if run externally or buried), high-quality waterproof junction boxes, heavy-duty cable glands, appropriate circuit breakers (like a 40A Type C MCB), a mandatory 30mA Residual Current Device (RCD) or leakage protector for safety, and reliable wiring terminals add another 200 RMB to 500 RMB to the materials bill.
The total investment may rise significantly due to a number of possible extra expenses. Increasing electrical capacity is frequently the most important. The main electrical service panel of many older residences or apartment complexes has little spare capacity. It might be necessary to upgrade the main service entrance cables or even the transformer that serves the property in order to install a high-power device like an EV charger (7kW draws about 32A continuously). Known as “power capacity increase” or “增容” (zēng róng), this procedure can cost several thousand RMB, and in more complicated cases, it may cost 10,000 RMB or more. It also entails application fees to the utility, new equipment (such as a larger meter or breaker panel), and a lot of labor. Another consideration is the rental of specialized equipment. If the installation site is difficult to access – for instance, requiring a scissor lift to reach a high ceiling in an underground garage, a crane to place equipment in a tight spot, or extensive scaffolding – rental fees for this machinery can add hundreds to over a thousand RMB. Finally, property management fees are common in apartment complexes or managed communities. The property manager (物业, wùyè) may charge fees for administrative processing, issuing permits, supervising the construction to ensure compliance with building rules, providing access to utility rooms, or allocating space within a shared electrical cabinet. These fees usually range from a few hundred RMB. It’s vital to clarify all potential extra costs with your installer and property manager upfront.
The EV Charger Installation Process Step-by-Step
The installation journey begins long before the electrician arrives and involves coordination with different entities. The first critical step is Preparation and Documentation. You absolutely must have a dedicated parking spot – ideally a privately owned property车位 or a long-term leased space with explicit permission from the property owner/manager for charger installation. Gather essential documents: your government-issued photo ID (身份证), proof of parking rights (车位产权证 for owned spots or a formal, stamped 车位租赁合同 for leases), proof of EV ownership (购车合同 or vehicle registration), and the technical specifications sheet for your specific charger model. Simultaneously, conduct a preliminary Site Assessment. While a professional will do a detailed check later, you can initially gauge the feasibility. Determine the approximate distance from your potential parking spot to the nearest possible electrical source (like the building’s main distribution room or your home’s meter panel). Check if there’s a communal electrical cabinet nearby that could house a new meter. Crucially, inquire with your property management about the building’s spare electrical capacity – it needs sufficient headroom (ideally ≥50kVA) to support the charger without overloading the system.
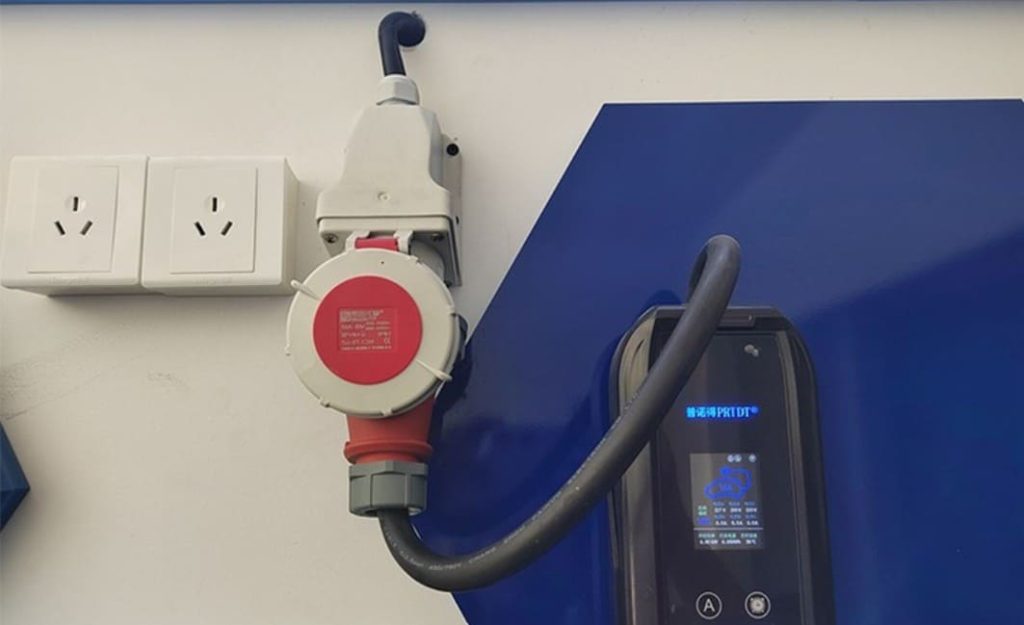
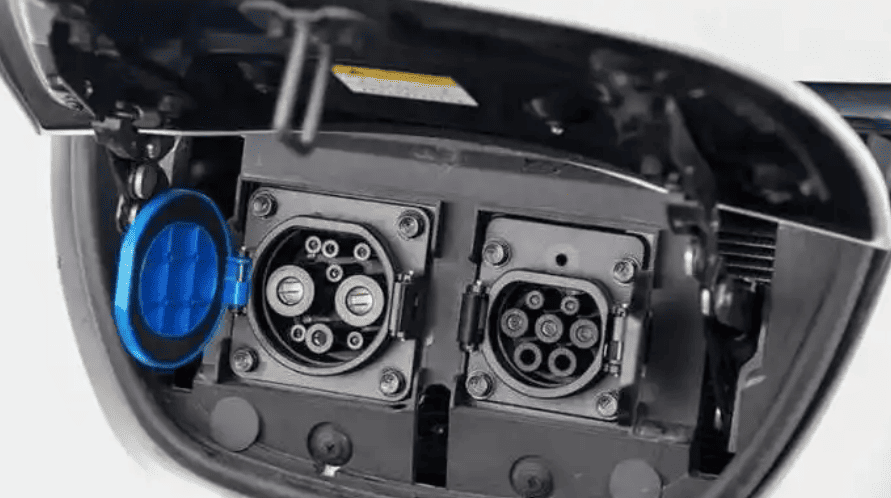
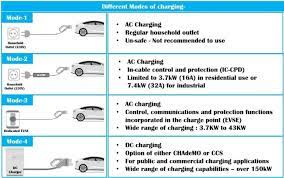
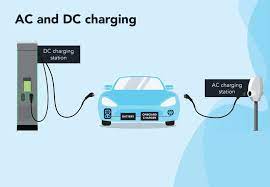
The next step is to apply for a dedicated meter from your electricity provider, usually State Grid (国家电网). Their “Online State Grid” app (网上国网 APP) is the most effective method. Make an account, find the “New Energy Vehicle Charging Meter Application” section, and send in clear photos or scanned copies of your ID, proof of parking, proof of EV purchase, and the installation permission letter from property management. The property manager usually takes care of this step when applying for a commercial parking space. Indicate the voltage you need: A 380V three-phase meter offers substantial future-proofing flexibility, even though a typical 220V single-phase meter is adequate for 7kW charging.It allows for potential upgrades to faster 11kW or even 22kW chargers later without reapplying for a new meter. The utility company will process your application, usually within 3-5 working days, and then schedule an on-site survey. A technician will visit to confirm the feasibility, assess the best meter location, and finalize the plan. Once approved, they will return to install the dedicated meter, clearly labeled for EV charging use.
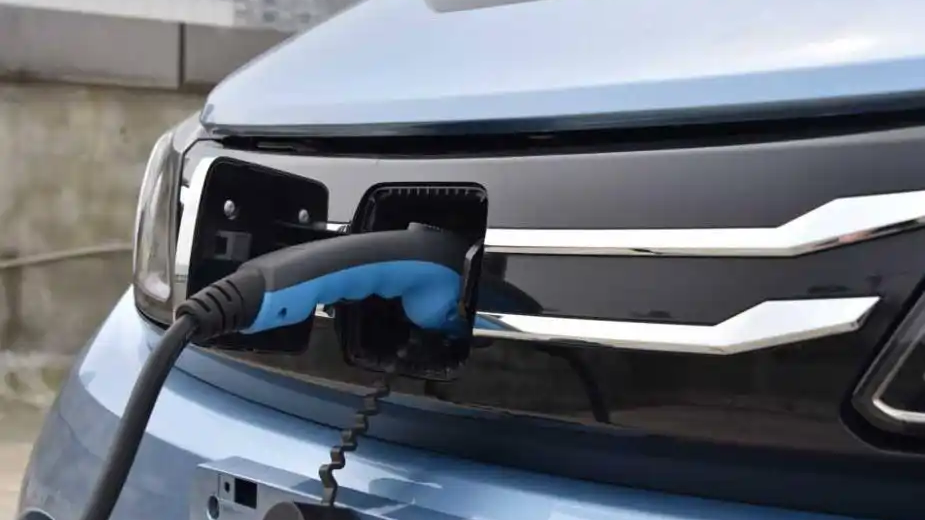
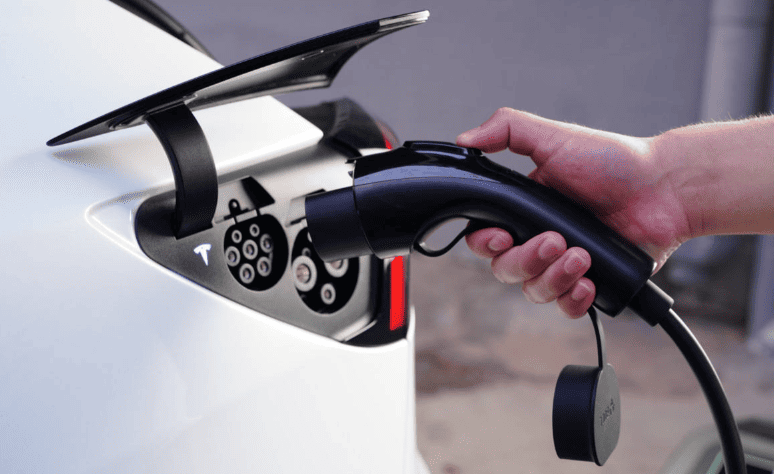
With the meter physically installed and energized, you can proceed to the Charger Installation Phase. Contact your chosen EV charger supplier or their authorized installation partner to schedule this. A qualified electrician will handle the core tasks: Running the Cable from the new meter location to your chosen charger mounting point. This involves carefully measuring, cutting, and threading the appropriate gauge cable (e.g., 3-core 6mm² for 7kW/220V) through protective conduit, securing it neatly along walls, ceilings, or under flooring, and ensuring all bends meet electrical code requirements to prevent damage. Costs increase with distance (approx. +150 RMB per 10m beyond standard). Mounting the Charger securely to the wall or a pedestal base at the predetermined location. Connecting the Wiring meticulously at both ends – linking the cable to the dedicated circuit breaker and meter at the supply end and terminating it correctly within the charger’s terminals. Installing Safety Devices like the dedicated circuit breaker (MCB) and the crucial Residual Current Device (RCD) or leakage protector at the supply origin. Final Testing and Commissioning is critical. The electrician will rigorously test all connections for tightness, measure insulation resistance, verify correct grounding, test the RCD trip function, power up the unit, and perform a test charge cycle to ensure everything operates safely and efficiently. They should also guide you on basic charger operation and app connectivity if applicable.
Finalization and Activation mark the end of the process. Usually, especially in managed properties, this entails a formal inspection and sign-off. A final walkthrough may be conducted by representatives of the utility company (if necessary), the installation company, and the property management to make sure that all building codes, safety regulations, and property rules are followed. All parties sign documents such as a compliance form or installation certificate. Your charger is fully functional after approval. Spend some time configuring the charger’s settings using the companion app or interface. Your energy bills can be significantly reduced over time by scheduling charging to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates (谷电). Make sure you comprehend the features of the charger, including any remote control functions, status indicators, and locking mechanisms.
Choosing the Optimal Installation Location
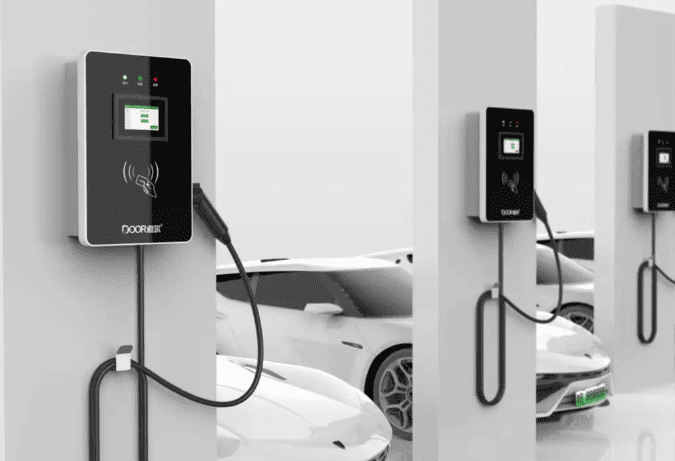
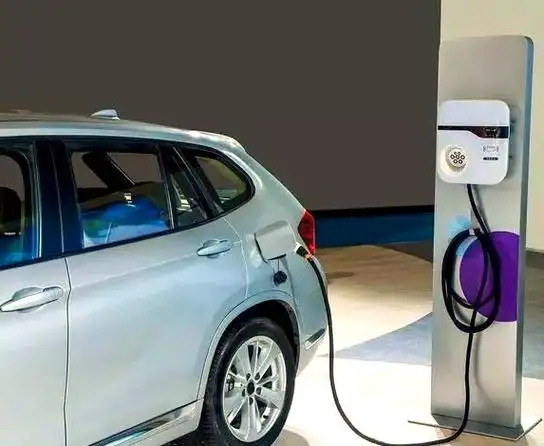
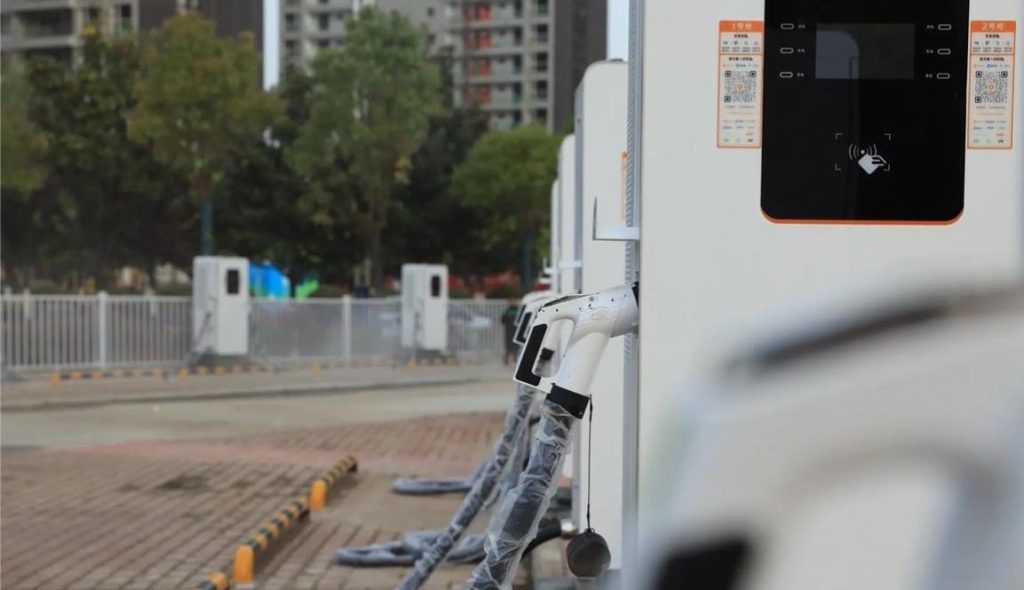
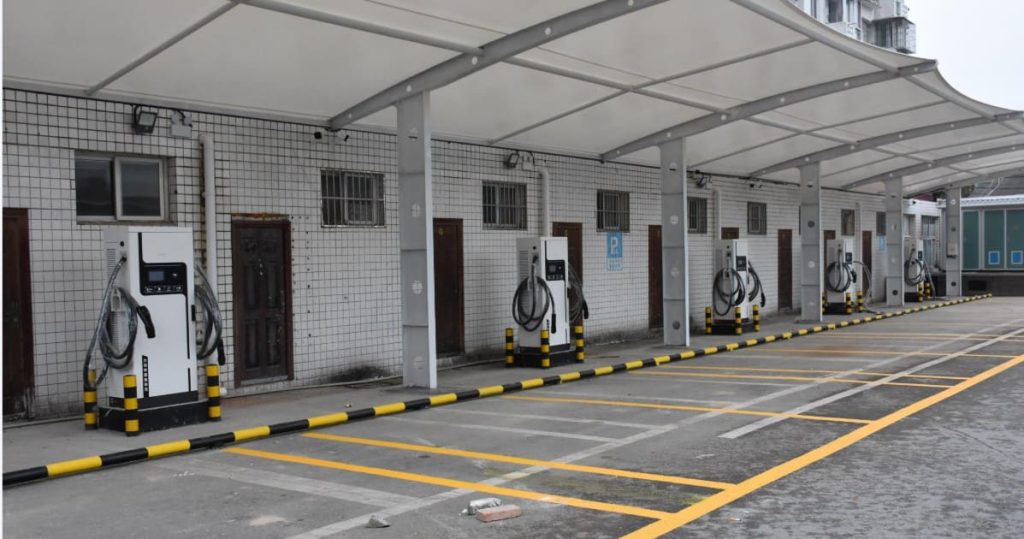
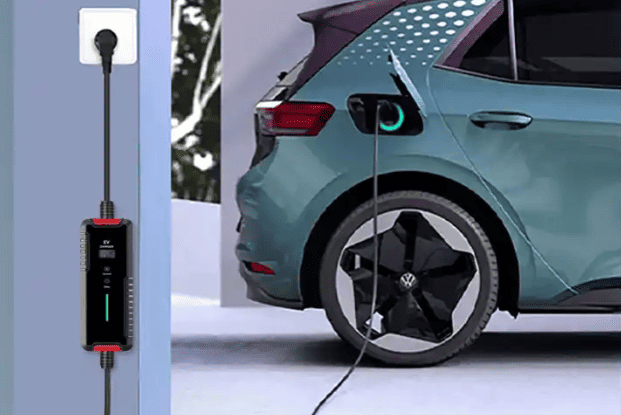
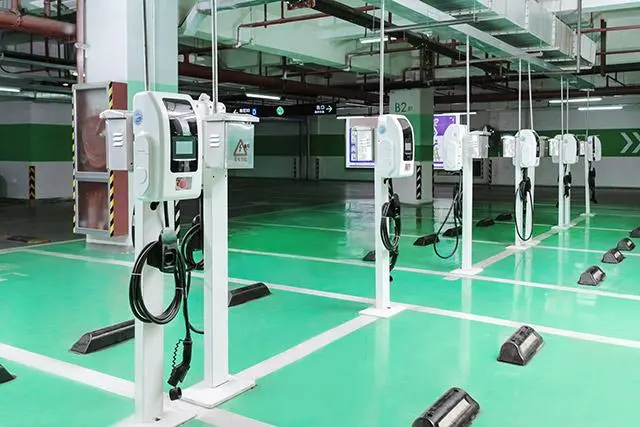
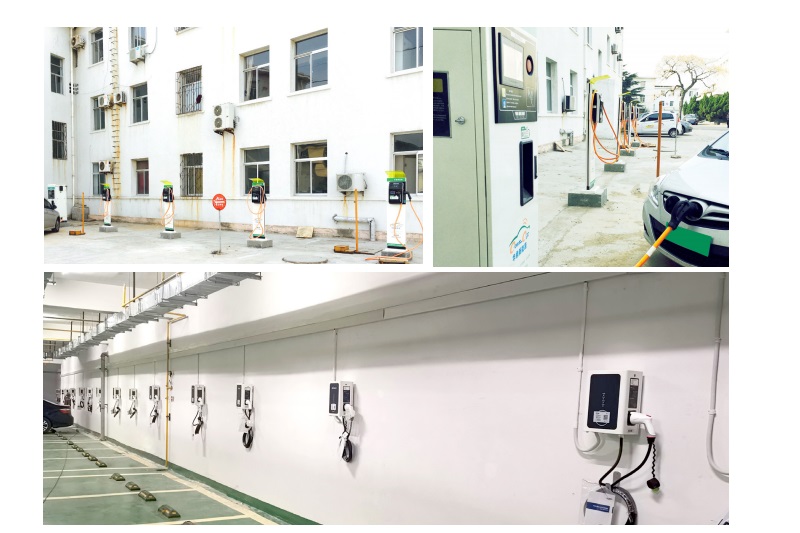
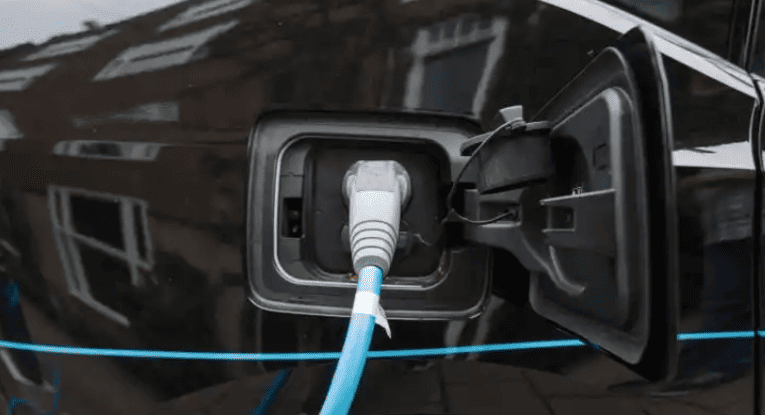
Selecting where to place your EV charger is a decision impacting daily convenience, safety, and charging efficiency. The Core Principles are paramount: Safety First is non-negotiable. The charger must be positioned well away from potential water sources (sinks, drains, sprinklers, areas prone to flooding), combustible materials (gas lines, fuel storage, paper, fabrics), and corrosive substances. It should be mounted securely on a stable surface to prevent accidental knocks or vibration damage. Weather Protection is essential unless specifically designed and rated for outdoor use. While many modern chargers are IP65 rated (dust-tight and protected against water jets), prolonged direct exposure to intense sunlight, heavy rain, snow, or extreme temperatures can shorten lifespan and potentially void warranties. Installing under an eave, inside a garage, or within a dedicated weatherproof enclosure is highly recommended. Accessibility and Convenience dictate that the charger must be easily reachable from your primary parking position, with the charging cable comfortably able to connect to your car’s port without stretching taut or dragging on the ground. Consider ease of plugging/unplugging, especially in adverse weather.
Practical Placement Considerations involve balancing these principles with real-world constraints. Proximity to the Car’s Charge Port is a major factor for daily ease. Since EV charge ports vary significantly in location (front left/right, rear left/right, front center), observe where your car’s port is. Ideally, mount the charger on the wall or post closest to where the port rests when parked. For example, if your port is on the rear left side, mounting the charger on a wall directly behind or slightly to the left of the parked car is optimal. This minimizes cable strain, trip hazards, and keeps the cable neatly coiled when not in use. Parking Space Dimensions matter significantly. Ensure the chosen location doesn’t obstruct vehicle movement. A minimum parking space width of 2.5 meters and length of 5 meters is often recommended to allow comfortable maneuvering while the cable is connected and to prevent the charger or cable from being accidentally hit by adjacent vehicles or doors. Electrical Source Proximity is a key cost driver. While convenient for the car, placing the charger far from the electrical panel or meter dramatically increases cable costs. Finding a spot that offers a reasonable compromise between proximity to the car’s port and proximity to the electrical supply source is ideal. Regulatory and Property Rules must be strictly adhered to. Apartment complexes often have designated areas for charger installation (like specific walls in garages or communal charging zones). Obtain explicit written permission from property management regarding the exact proposed installation spot before finalizing plans. Future-Proofing is wise. If you anticipate getting different EVs in the future with varying port locations, or if multiple EVs might use the charger, consider a central mounting point or ensure there’s flexibility in the cable routing to reach different areas of the parking space comfortably. Choosing a slightly more central location might offer better long-term versatility.
By meticulously planning for the costs, diligently following the installation process, and thoughtfully selecting the safest and most practical location, homeowners can successfully implement a convenient and efficient home EV charging solution, enhancing the overall electric vehicle ownership experience.