Is 100 amp service enough for ev charger?

Is 100 amp service enough for ev charger? Depending on the type of EV charger you install, your current household electrical loads, and whether load management techniques are required, a 100-amp electrical service may be adequate for a home EV charger.
Understanding Your Home’s Electrical Service and EV Charger Needs
The electrical service in your home serves as the entry point for power, and its capacity—which is expressed in amperes, or amps—determines the maximum amount of electricity that can be used at any one time. For many older homes, a 100-amp service is a common, albeit progressively outdated, standard.
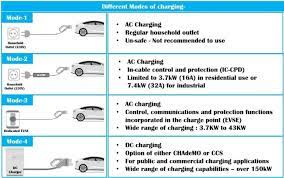
Simultaneously, Level 2 EV chargers, which are the most practical for home charging, require a dedicated circuit and draw a significant amount of power. Their amperage can vary, commonly ranging from 16 amps up to 50 amps or more. The higher the amperage of the charger, the faster it will charge your vehicle.
The central question isn’t just about the EV charger’s needs in isolation, but about the combined electrical demand of the charger plus all the other appliances and devices in your home (like air conditioners, electric stoves, dryers, and water heaters). You must ensure that adding an EV charger doesn’t cause your total electrical demand to consistently exceed your service’s capacity, which could trip breakers or, in worst-case scenarios, create safety hazards.
The Importance of Load Calculation and Real-World Assessment
To determine if your 100-amp service can handle an EV charger, a professional load calculation is essential. This is more sophisticated than simply adding up the amp ratings of all your appliances. It considers how you actually use your electricity, accounting for the fact that not all devices run simultaneously or at their maximum draw all the time.
Historical demand data from your utility company can be particularly valuable for this assessment. It provides a record of your home’s actual peak electricity usage over time. If this data shows your household’s peak demand is already consistently near or above 80 amps (the safe continuous load limit for a 100-amp service is 80 amps), adding a substantial EV charger load would likely be problematic.
However, if the data indicates your typical usage is significantly lower—for instance, if your home is equipped with gas appliances for heating, cooking, and drying, thereby reducing electrical load—there may be ample capacity for an EV charger. For example, if your historical load analysis shows a peak demand of only 50-60 amps, adding a 30- or 40-amp EV charger circuit could be feasible without overloading the system.
Solutions and Strategies for 100-Amp Services
If the initial assessment suggests your 100-amp service is borderline or insufficient for a standard EV charger, several solutions exist:
- Load Management Devices (EVEMS): This is often the most cost-effective solution. An Electric Vehicle Energy Management System (EVEMS), or a simple load-shedding device, can intelligently manage the power drawn by your EV charger. It monitors the total electrical consumption of your home in real-time. If it detects that the overall load is approaching the service’s capacity, it can temporarily reduce or pause the current flowing to the EV charger to prevent an overload. Once other loads decrease (e.g., the air conditioner cycles off), it resumes charging your car. This allows for the installation of an EV charger without the immediate need for a costly service upgrade.
- Lower-Amperage Charger Circuits: You don’t always need a 40- or 50-amp charger. Installing a charger on a 20-amp or 30-amp dedicated circuit (providing 16 or 24 amps of charging current) still offers a meaningful charge overnight and puts far less strain on your electrical system. For many commuters, this is entirely sufficient.
- Service Upgrade: In some cases, if the existing load is already high and future-proofing is desired, upgrading the electrical service from 100 amps to 200 or 400 amps might be the most robust and straightforward solution. This involves utility company work and significant investment but provides ample capacity for all future needs.
Professional Assessment is Key
Given the complexities and critical importance of electrical safety, consulting a licensed electrician is non-negotiable. They will:
- Perform a formal load calculation, considering NEC guidelines and your specific usage patterns.
- Assess the condition of your electrical panel and wiring.
- Recommend the most appropriate and code-compliant solution, whether that’s a load management system, a lower-amperage circuit, or a service upgrade.
- Ensure the installation is permitted and inspected, guaranteeing its safety and legality.
Conclusion and Final Recommendation
An EV charger can occasionally be installed in a 100-amp electrical service, especially in homes with low current electrical consumption or when used in conjunction with a load management device, but it is frequently at the limit of its capabilities.
The final response depends on a qualified evaluation of your particular circumstance. Don’t rely on speculation. Invest in an assessment by a licensed electrician who can examine your past usage, calculate your load precisely, and suggest a safe, code-compliant course of action. This guarantees that your EV charging system is completely safe for your family and home in addition to being convenient.