What is a level 2 ev charger ?

What Is a Level 2 EV Charger?
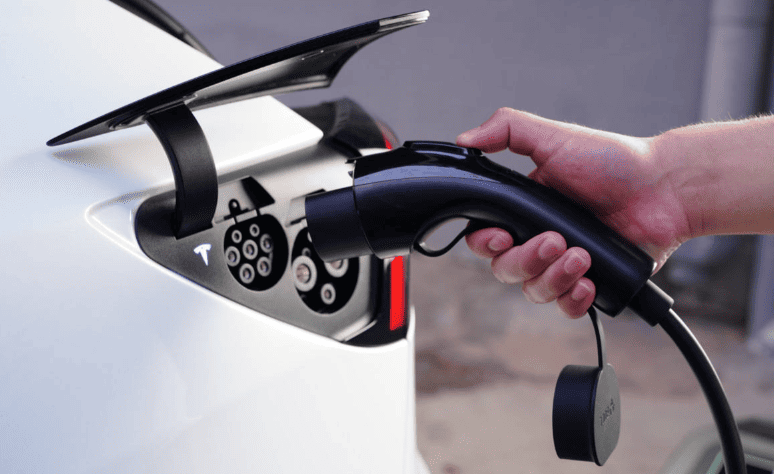
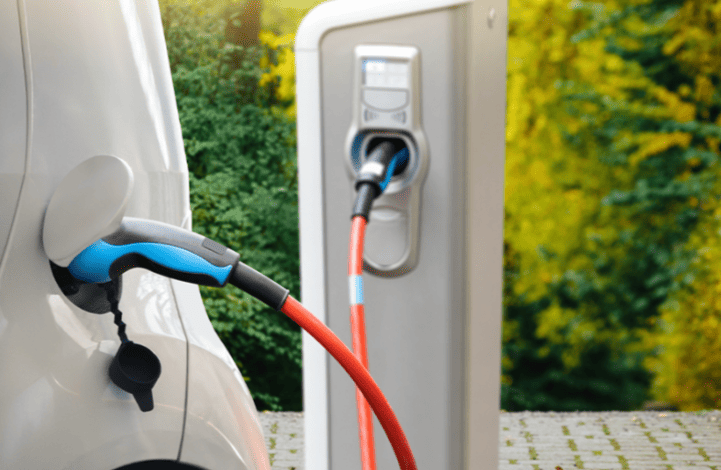
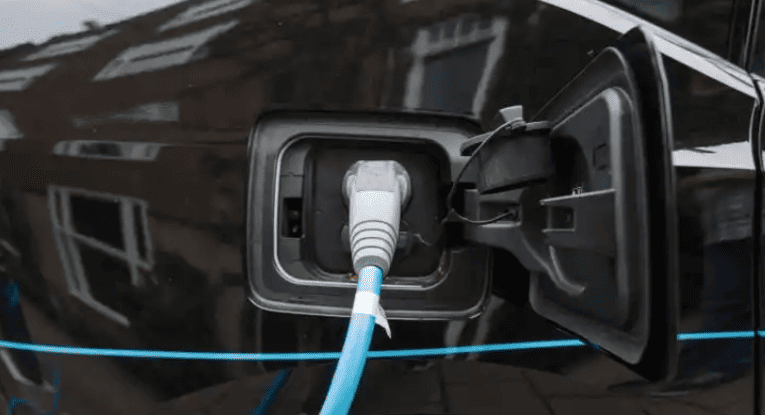
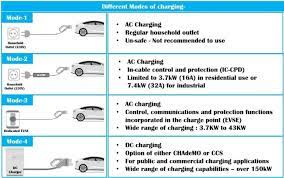
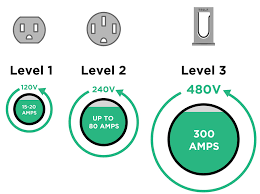
An essential solution for overnight home charging and workplace top-ups, a Level 2 EV charger is a 220–240-volt charging system that delivers 3.3–22 kW of power, bridging the gap between slow household outlets and pricey DC fast chargers. In contrast to low-end Level 1 chargers or powerful public stations, Level 2 units strike a balance between affordability, speed, and usefulness for daily EV ownership. We break down its technology, uses, and practical implications below.
Defining the Level 2 Charger: Core Specifications
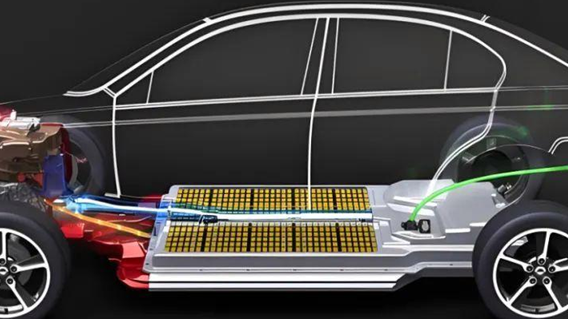
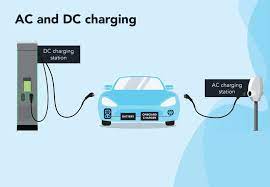
Unlike Level 1 chargers, which run on 110–120V household plugs, Level 2 chargers run on a 220–240V AC circuit (global standard). Five to eight times faster than Level 1, their power output ranges from 3.3 kW to 22 kW, which translates to 20 to 130 km of range per hour. Although they are technically referred to as “AC charging stations,” they use the onboard charger (OBC) of the car to convert AC to DC so that batteries can be stored. DC fast chargers, on the other hand, require industrial infrastructure but avoid the OBC for quick charging.
Important identifiers consist of:
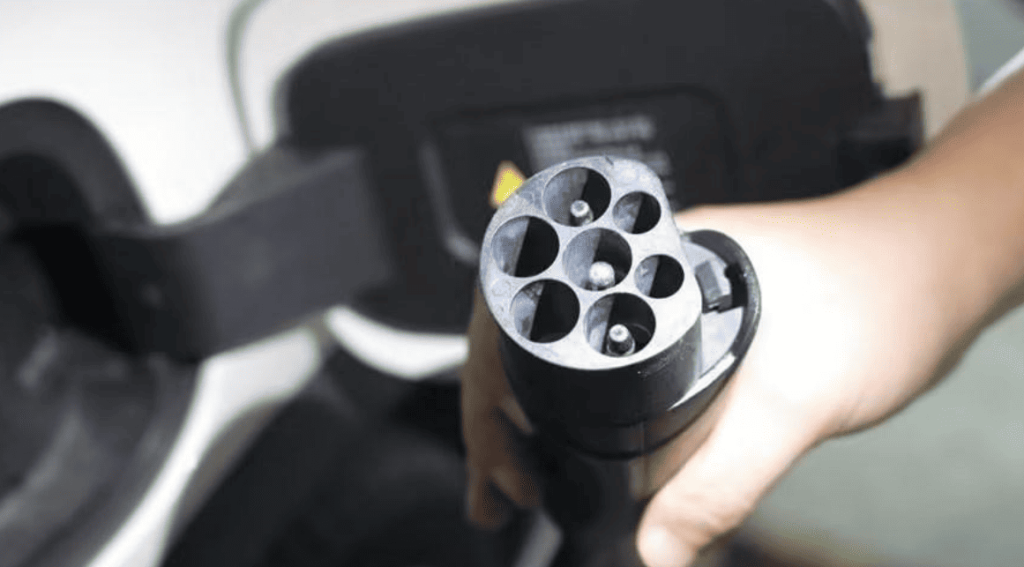
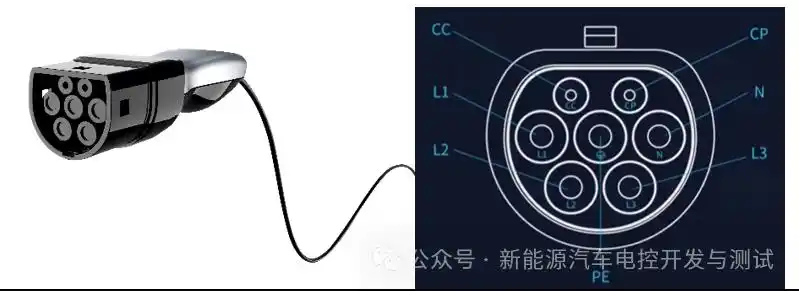
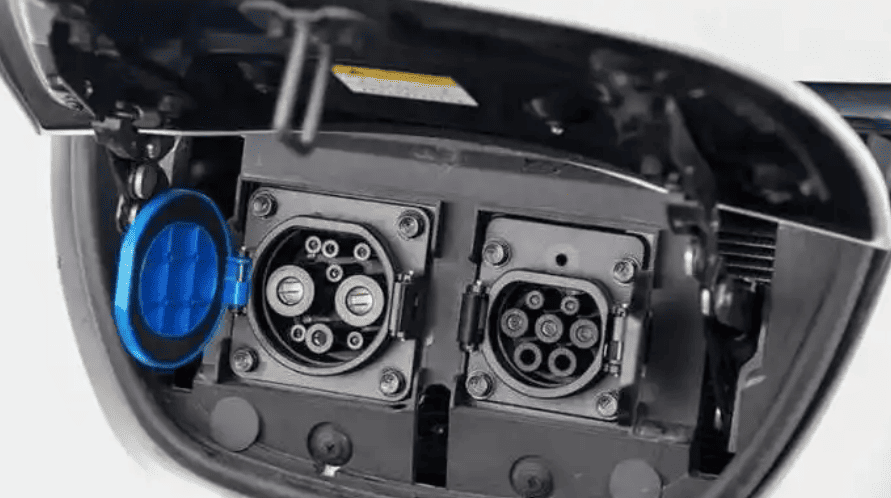
- Connectors: China’s GB/T (7-pin), North America’s J1772 (5-pin), Europe’s Type 2 (7-pin)
- Safety Ratings: IP54 (weather-resistant) or IP67 (waterproof) enclosures
- Control Systems: Smart models feature Wi-Fi/CAN bus communication for remote management
Technology Breakdown: How Level 2 Charging Works
A Level 2 charger functions through three integrated subsystems:
1. Power Delivery Module
This component draws 220V AC from your electrical panel via dedicated wiring (typically 6–10 mm² copper). Critical safety elements include:
- Ground-Fault Protection: Shuts off power within 0.025 seconds if current leakage exceeds 30mA
- Overvoltage Safeguards: Prevents damage during grid surges (e.g., lightning strikes)
- Thermal Sensors: Monitors cable/connector temperatures, throttling power if overheating occurs
2. Control & Communication Unit
The charger’s “brain” handles vehicle handshaking using protocols like:
- GB/T 27930 (China)
- IEC 61851 (Global)
- OCPP 1.6+ (Open Charge Point Protocol for networked stations)
This device communicates digitally with the EV’s battery management system (BMS) while it is plugged in in order to negotiate:
Maximum current that can be used
Tolerances for voltage
Duration of charging
Energy flow starts only after mutual verification.
3. User Interface & Safety Features
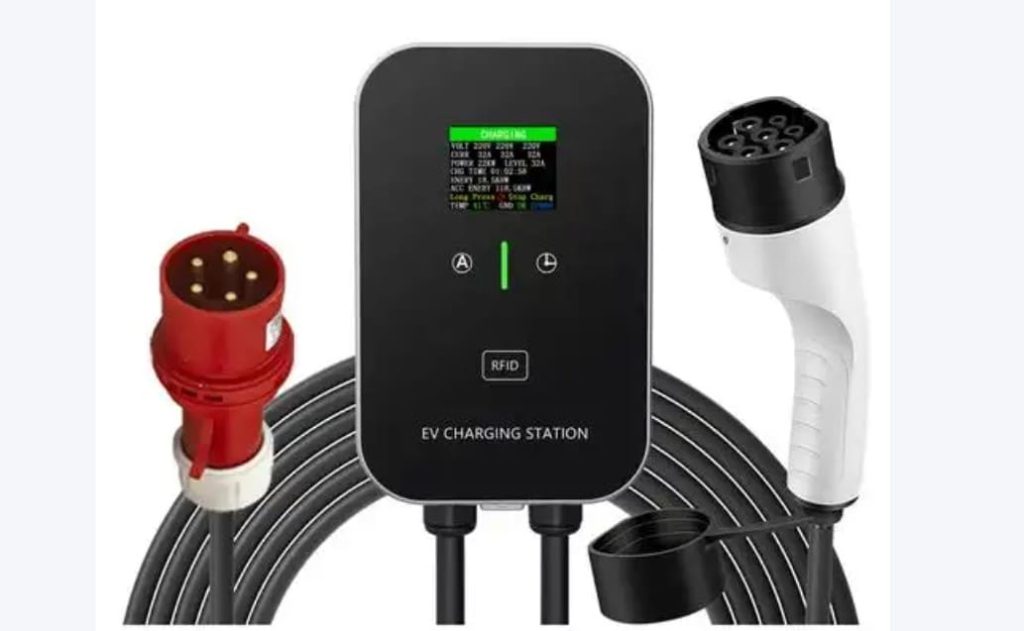
Commercial/public units add:
- RFID card readers or QR code payment systems
- LCD displays showing kWh delivered, cost, and time
- Emergency stop buttons
Home models prioritize simplicity with LED status lights and mobile app integration.
Speed Realities: What Level 2 Delivers
Charging rates depend on the lesser of two values: the charger’s capacity or the vehicle’s OBC limit. Common scenarios:
| Vehicle Model | OBC Limit | Level 2 Charger Output | Actual Charge Rate | Range Added/Hour |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BYD Dolphin (Standard) | 6.6 kW | 7 kW | 6.6 kW | 50 km |
| Tesla Model 3 RWD | 11 kW | 11 kW | 11 kW | 80 km |
| XPeng G9 (Performance) | 22 kW* | 22 kW | 22 kW | 130 km |
*Requires three-phase power
Note: Most residential installations max out at 11 kW due to single-phase limitations.
Home vs. Commercial: Two Worlds of Level 2
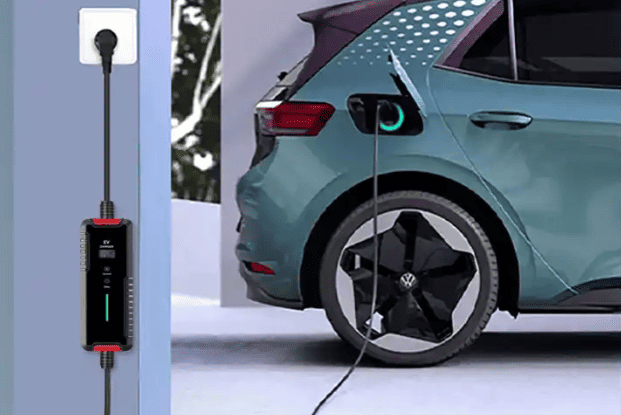
Residential Chargers (3.3–11 kW)
- Cost of Hardware: ¥1,000–6,000 ($140–850)
- Installation: 32–50A circuit breakers and specialized wiring are needed.
- Important attributes:
- Using an app to schedule charging (e.g., Tesla, Xiaomi)
- Monitoring of energy use
- Deterrents to theft (RFID/PIN codes)
- Case Study: A 7 kW Delixi charger (¥1,009) is used by a Nio ET5 owner in Shanghai. They add 300 kilometers for ¥6.60 ($0.90) when charging every night from 12 to 6 AM at ¥0.22/kWh, which is 90% less expensive than gasoline.
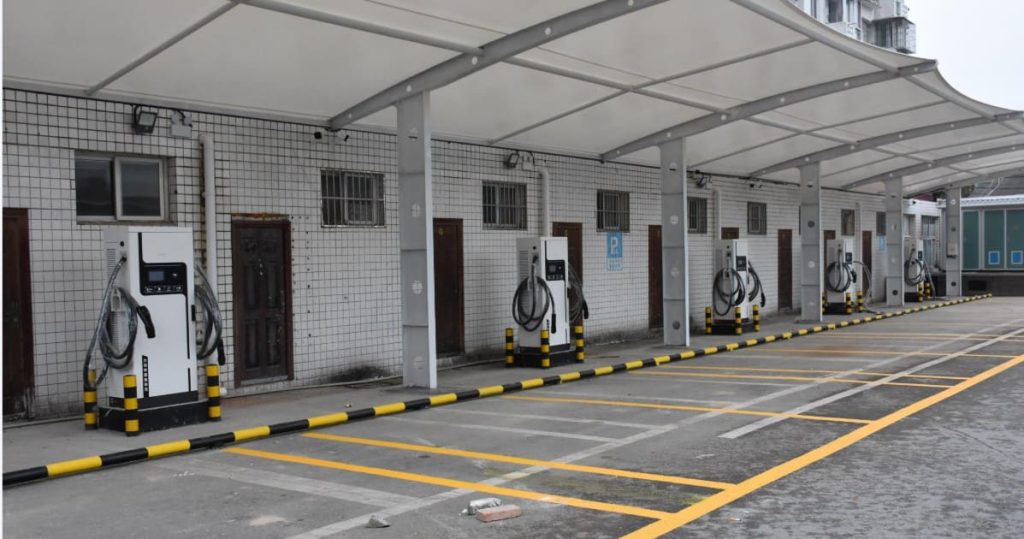
Commercial Stations (11–22 kW)
- Cost of Hardware: ¥8,000–20,000 ($1,100–2,800)
- Durability: IP65 industrial-grade casings can tolerate temperatures between -30°C and 55°C.
- Advanced Skills:
- Dynamic load balancing, which modifies power distribution among several EVs
- Network management through OCPP integration
- Configurations with two ports
- Example of Deployment: Twenty Teld 22 kW stations are installed in a shopping mall in Shenzhen. At ¥1.50/kWh (¥0.80 electricity + ¥0.70 service fee), each unit serves 8–10 EVs per day, bringing in ¥240 per day with an 18-month return on investment.
Critical Installation Requirements
Electrical Infrastructure
- Circuit Capacity: Minimum 40A breaker for 7 kW; 100A for 22 kW
- Wiring Specifications:
- 6 mm² copper for ≤7 kW (32A)
- 10 mm² for 11–22 kW (50A)
- Voltage Stability: Must maintain 220V±10% under load
Physical Space & Compliance
- Wall/pedestal mounting 1.2–1.5m above ground
- 1m clearance around unit for ventilation
- GFCI protection mandated by NEC (US) / GB standards (China)
Smart Charging: Beyond Basic Refueling
Modern Level 2 chargers enable:
- Solar Synchronization: Direct DC coupling with home PV systems (e.g., Tesla Powerwall)
- Vehicle-to-Home (V2H): Ford F-150 Lightning powers houses during outages
- Grid Services: Auto-adjusts charging speed during peak demand for utility rebates
Cost Analysis: Breaking Down Expenses
| Component | Price Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Charger Unit | ¥1,000–20,000 | Home vs. commercial grade |
| Electrical Wiring | ¥90–150/meter | 6–10 mm² copper conduit |
| Circuit Breaker | ¥300–800 | 40–100A capacity |
| Professional Labor | ¥1,000–5,000 | 4–8 hour installation |
| Permits/Inspections | ¥500–2,000 | Grid connection approval |
Total typical home setup: ¥3,000–12,000 ($420–1,700)
Optimization Strategies
- Peak Shaving: Program charging for off-peak hours (e.g., midnight–6 AM) when rates drop 50–70%
- Battery Preservation: Set max charge to 80% for daily use; 100% only before long trips
- Thermal Management: Avoid charging when battery temps exceed 40°C – precondition cabin first in winter
Evolution & Future Outlook
Level 2 technology is advancing through:
- 3-Phase Home Installations: Enabling 22 kW in residences (Europe/China)
- Plug & Charge: Auto-billing via ISO 15118 standard (e.g., Porsche Taycan)
- AI Predictive Charging: Syncs with calendar to ensure full battery before departure
Essentially, Level 2 charging turns EVs from high-maintenance innovations into useful everyday vehicles. “For 90% of EV owners, a properly installed Level 2 station eliminates range anxiety forever – it’s like having a gas pump in your garage that refills while you sleep,” observes Zhang Wei, an engineer at BYD. This technology continues to be the unsung hero of the electric revolution, delivering 50–500 km overnight without putting a strain on the grid or incurring excessive costs.