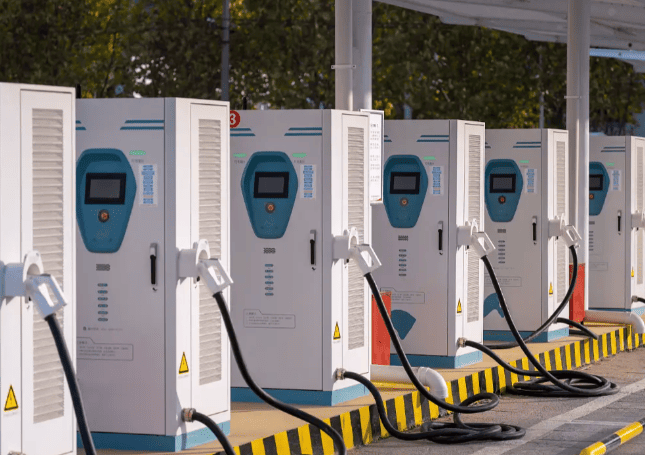
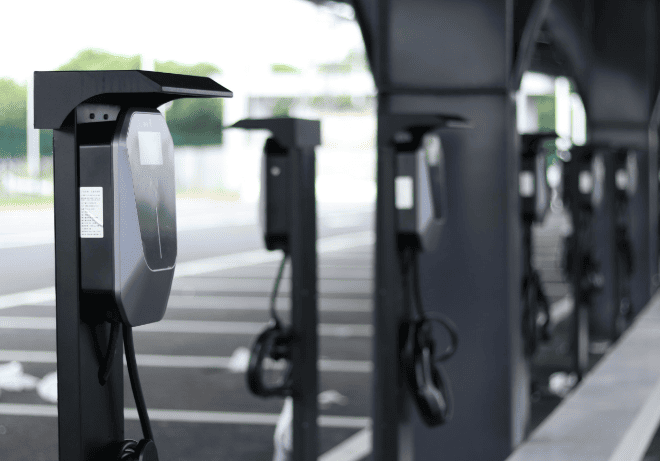
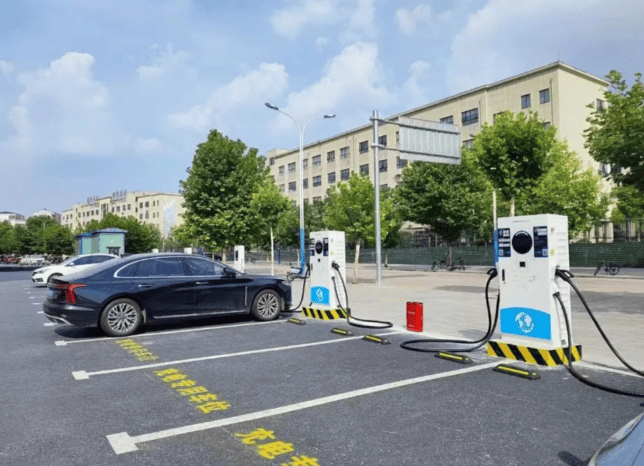
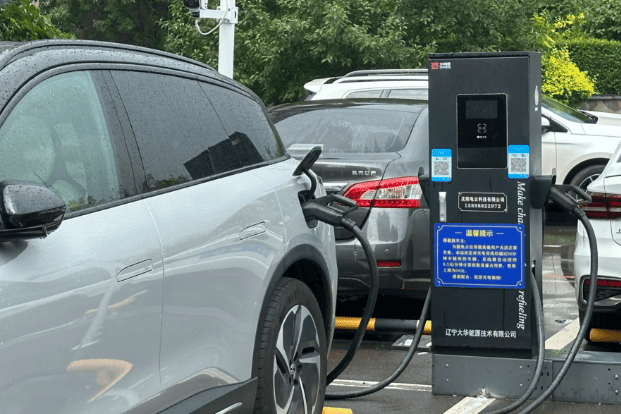
Who Pays for EV Charging Stations?
[ez-toc]
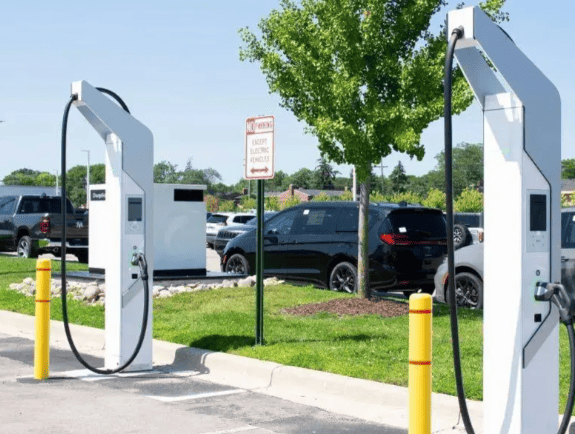
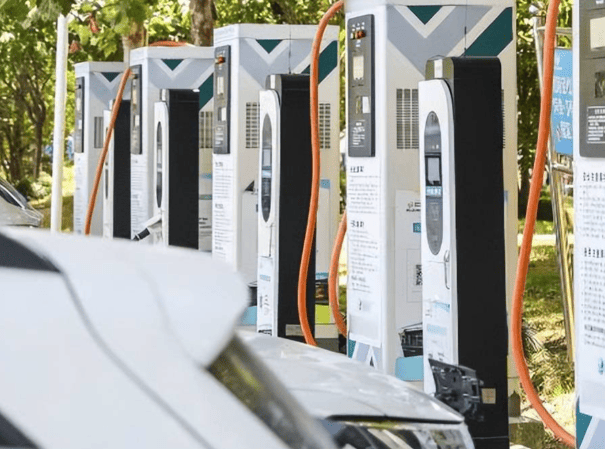
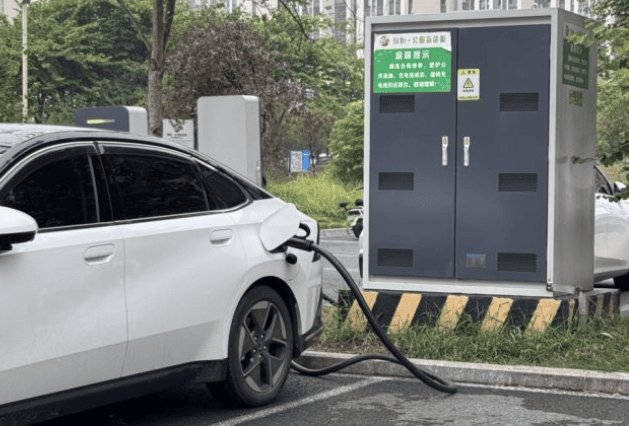
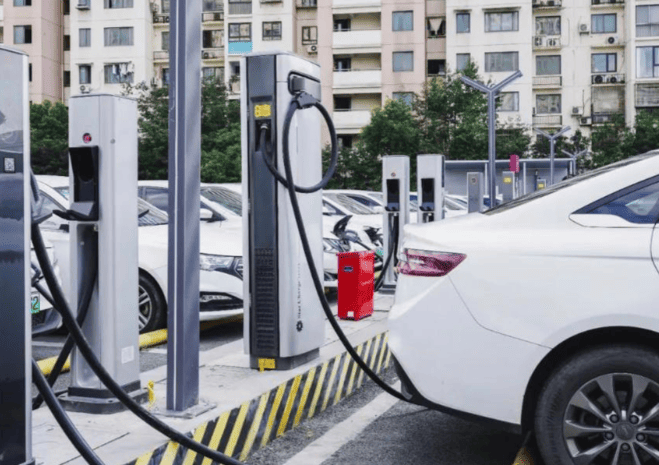
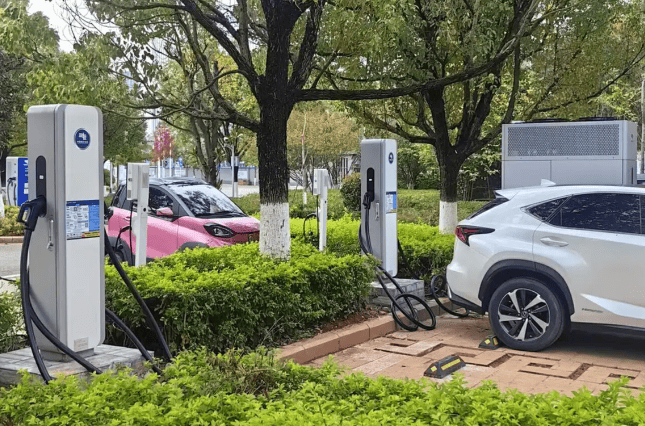
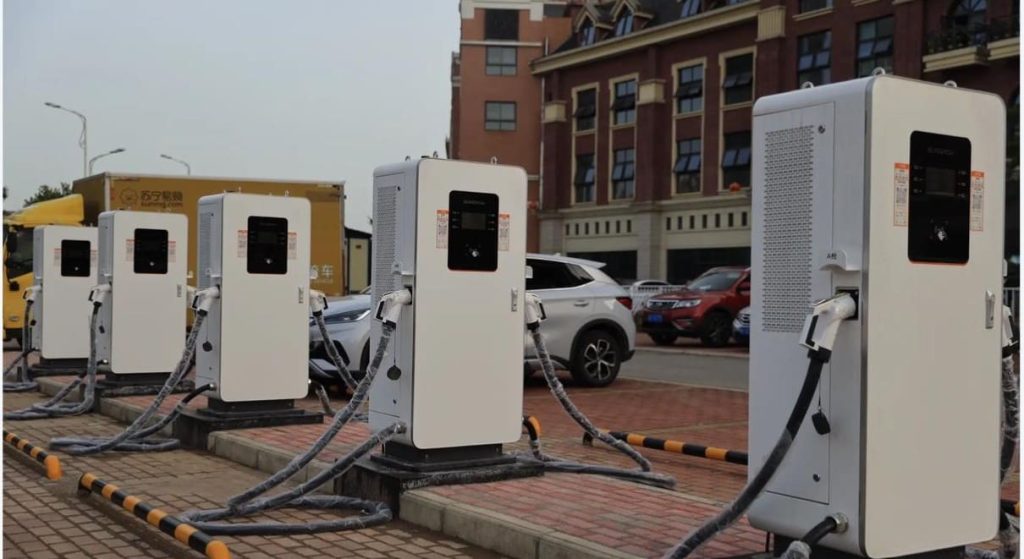
Curious about Who Pays for EV Charging Stations? The primary answer is actually electric vehicle (EV) drivers themselves. While the ideal scenario would involve complimentary charging for all EVs, reality doesn’t quite match up. Yet, the situation is more intricate than it seems. Numerous EV charging stations are indeed free, subject to certain conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the various locations where you’ll come across EV charging stations, identify those that offer free service, and provide insights into ways to minimize your expenses.
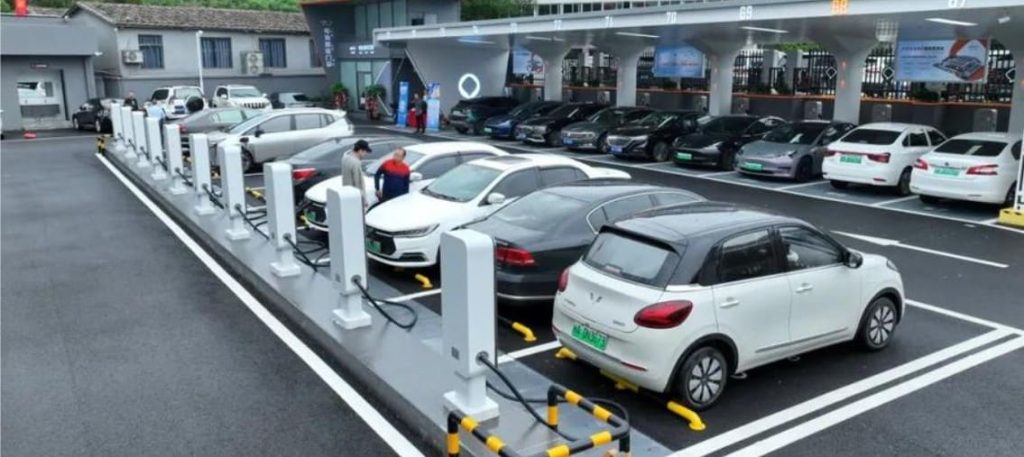
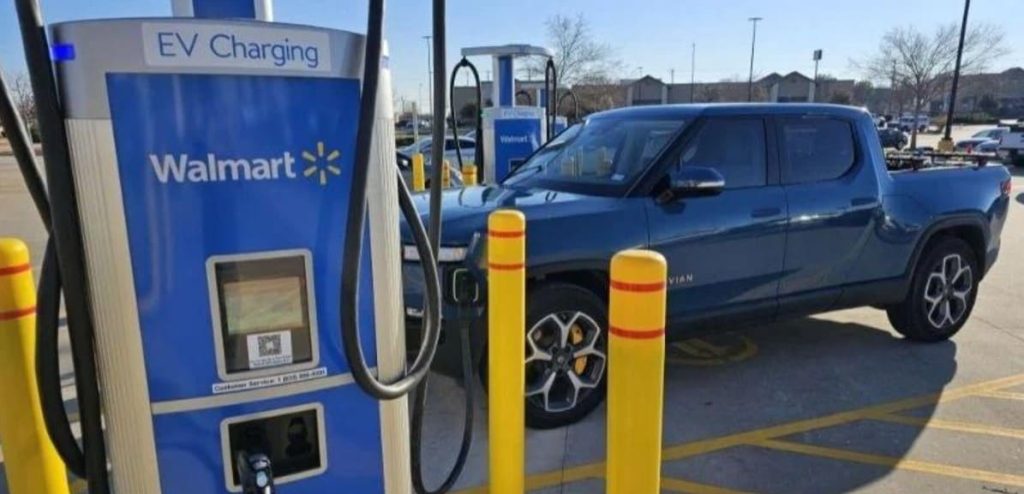
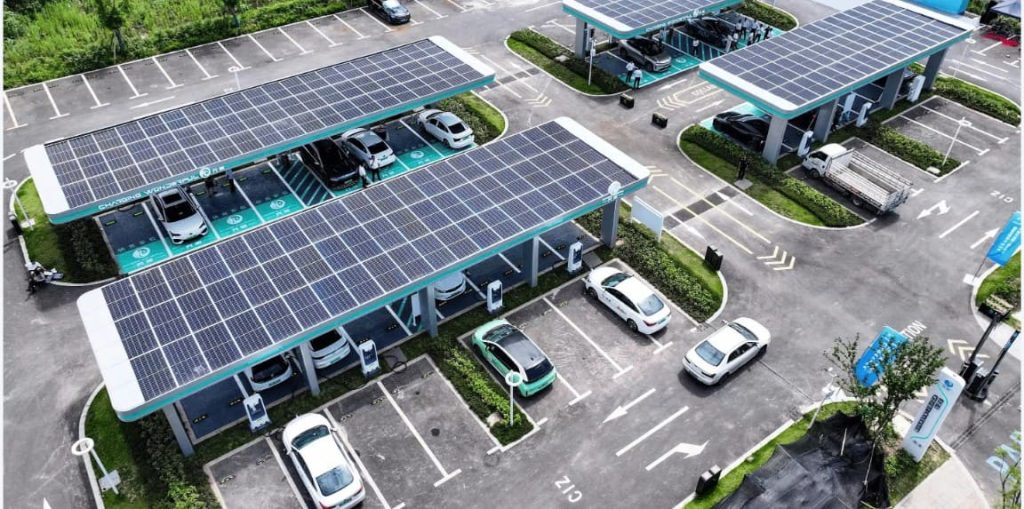
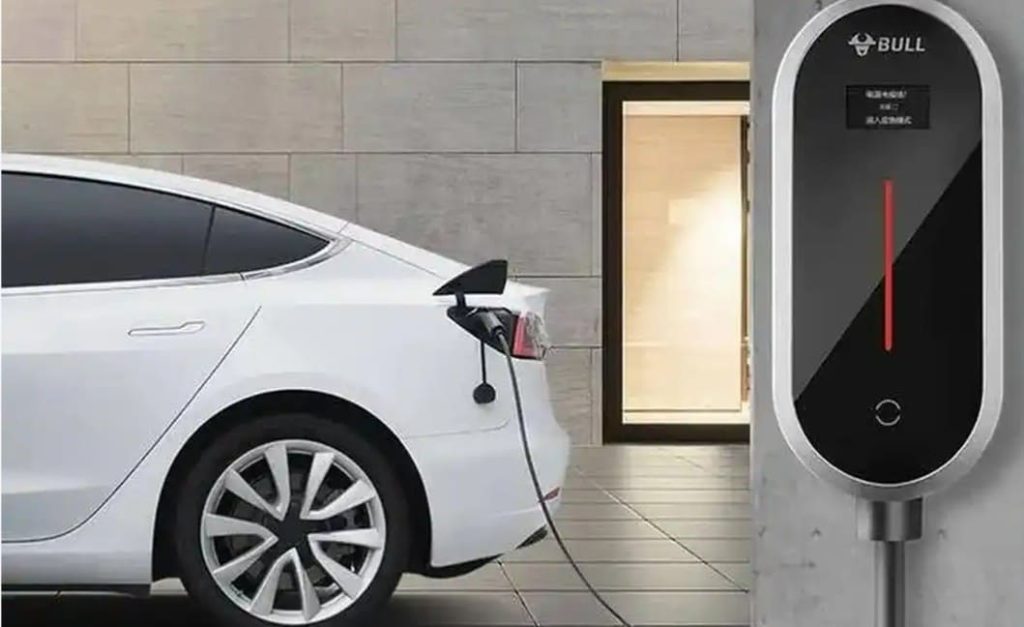
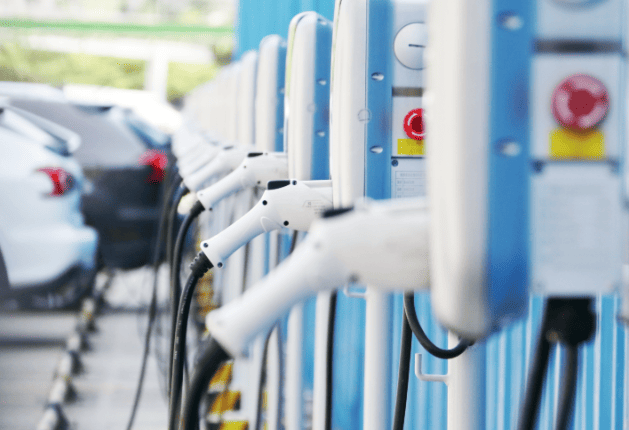
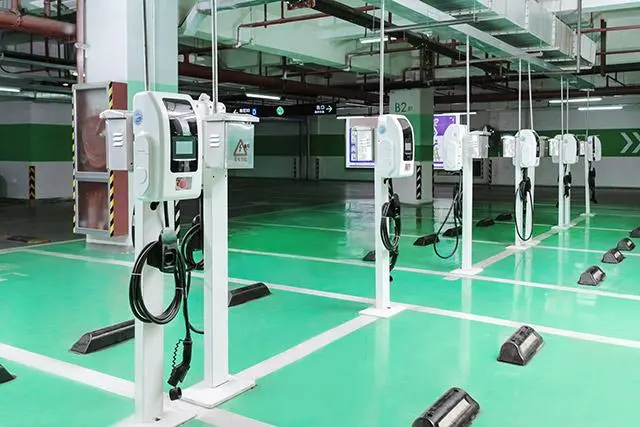
Specifically, there are three key settings where you’ll likely encounter charging stations: within your own residence, at your workplace, and in public spaces such as malls, hotels, or dedicated charging stations. We’ll delve into each of these contexts, guiding you through the details. Let’s begin this exploration.
FAQ (See more FAQ)
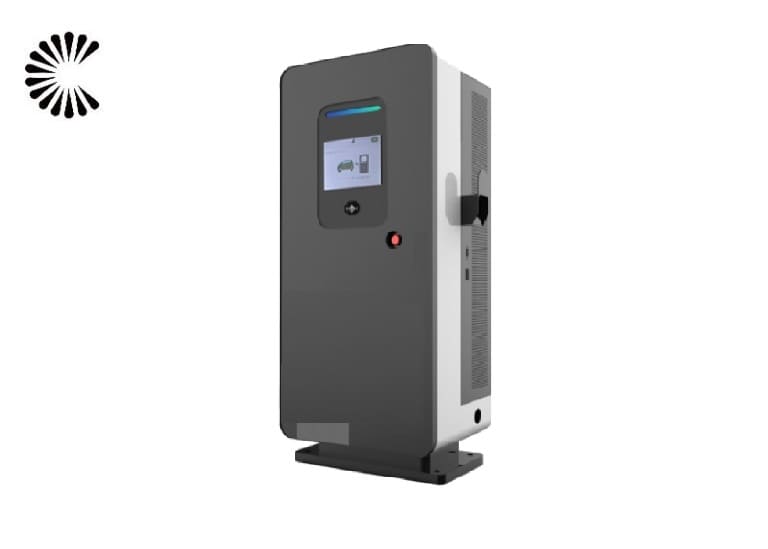
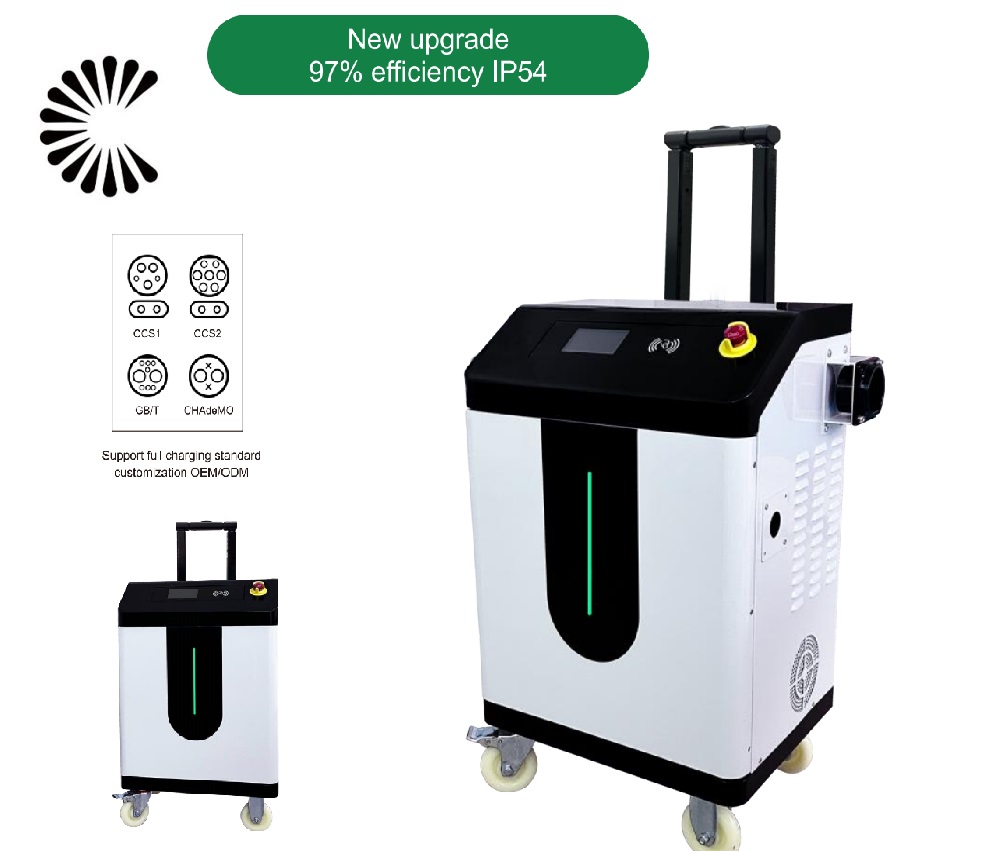
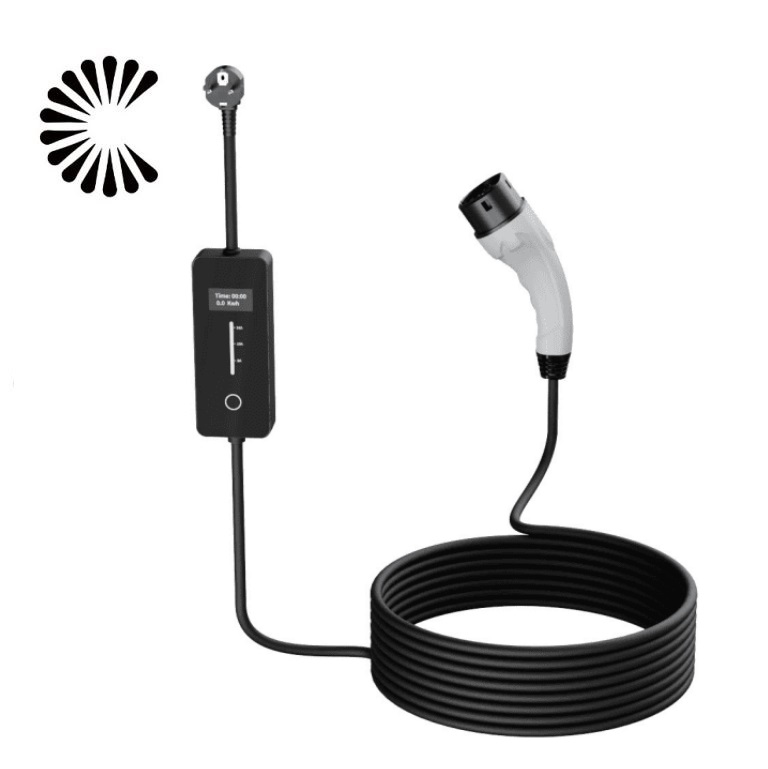
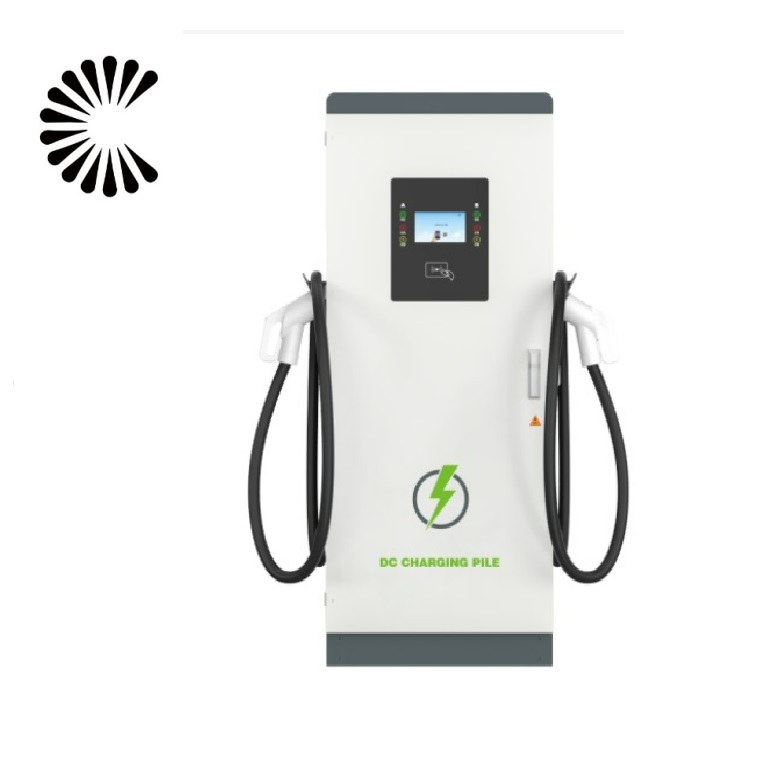
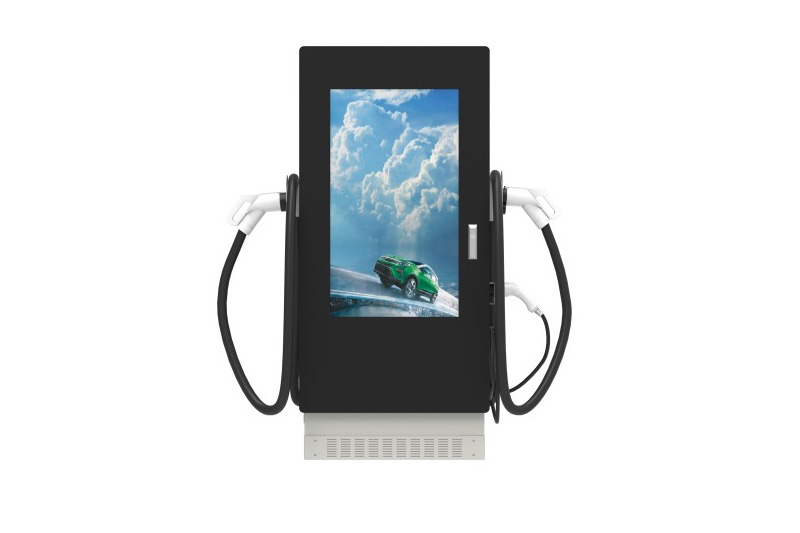
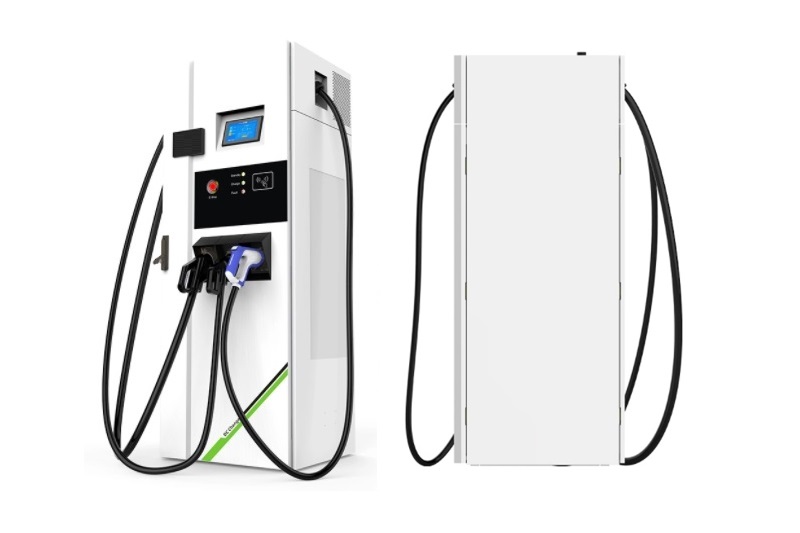
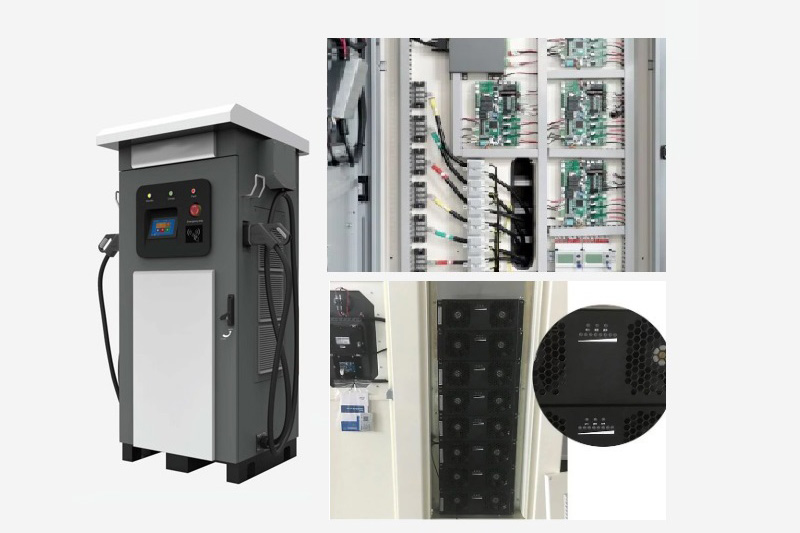
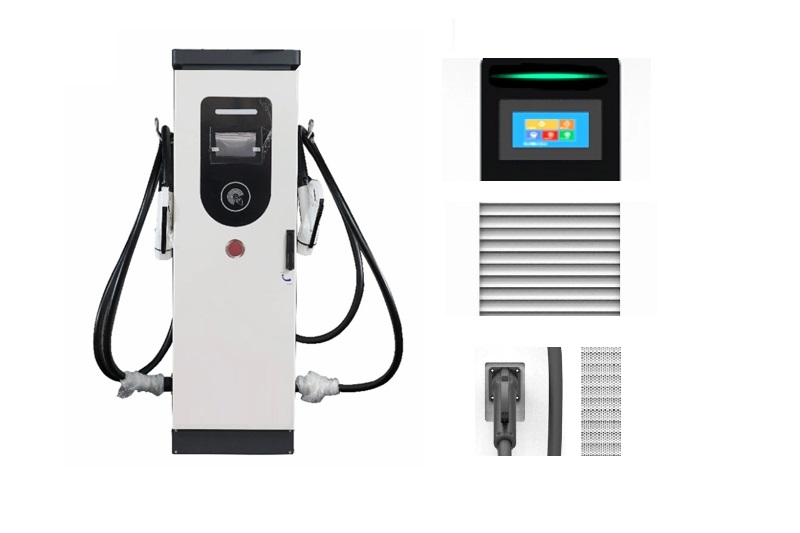
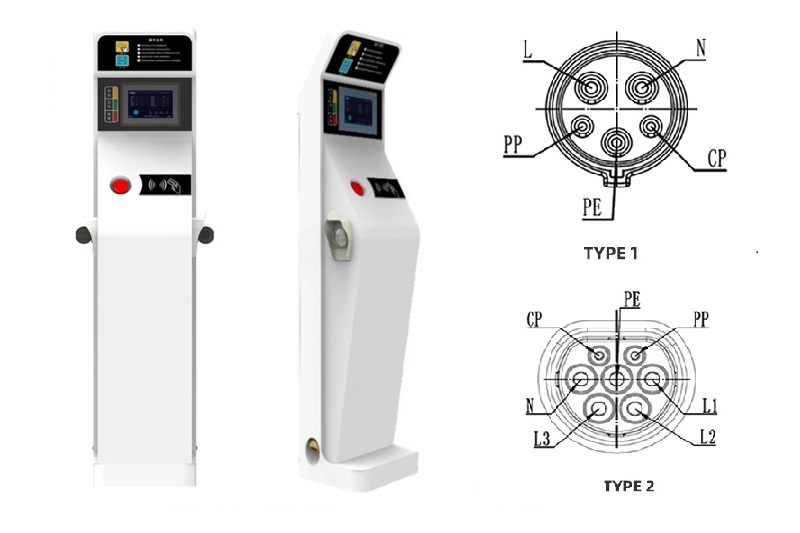
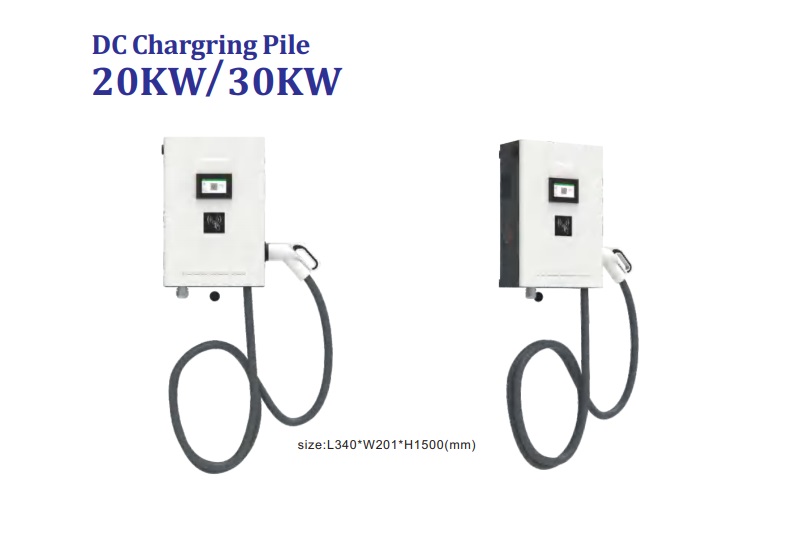
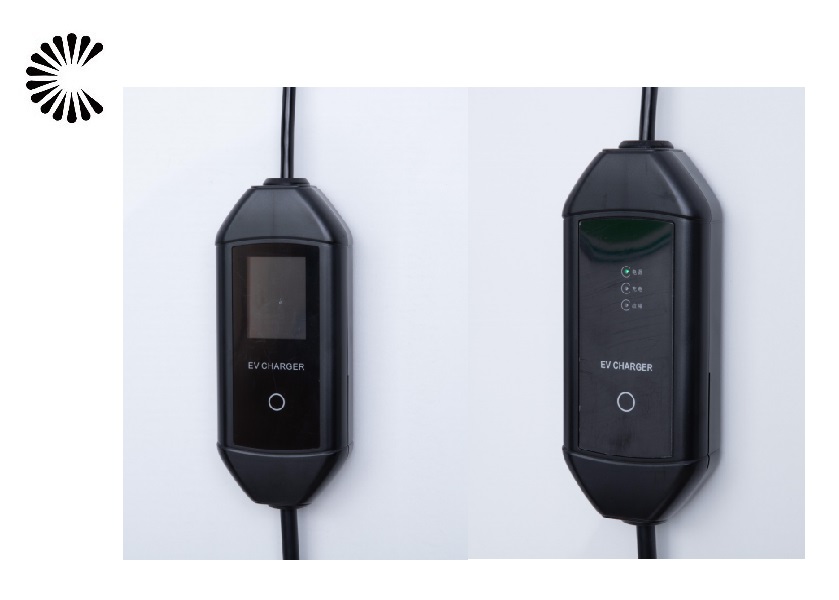
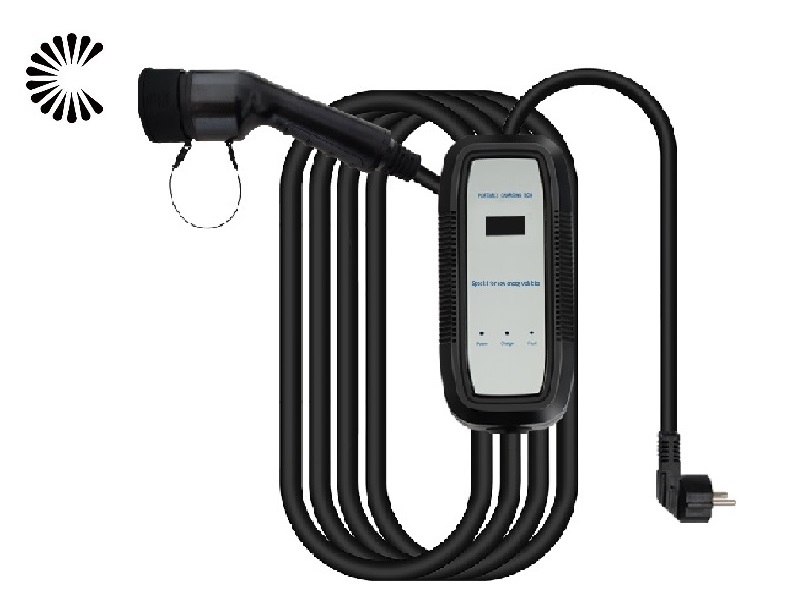
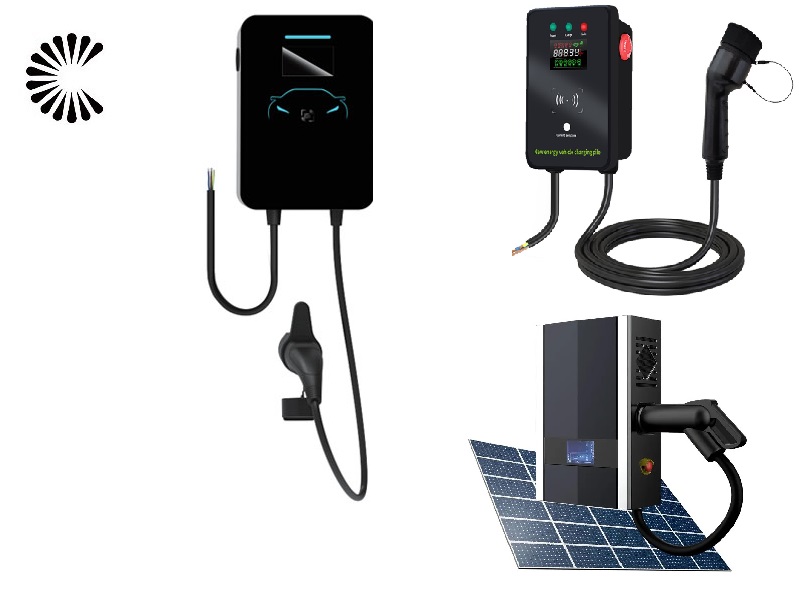
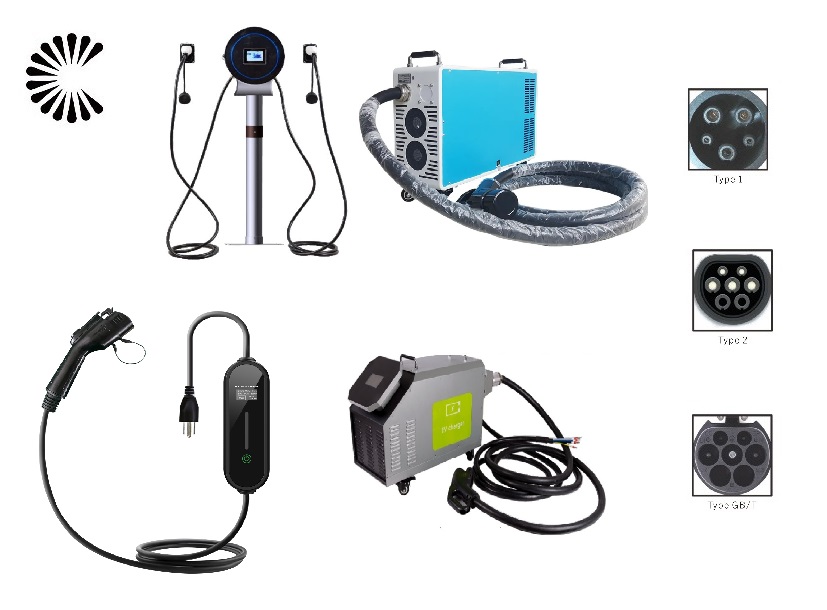
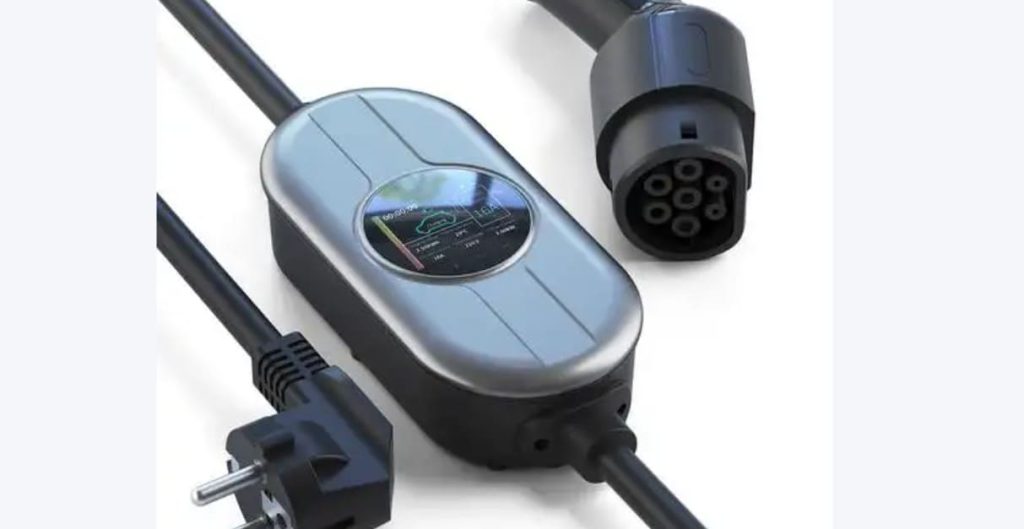
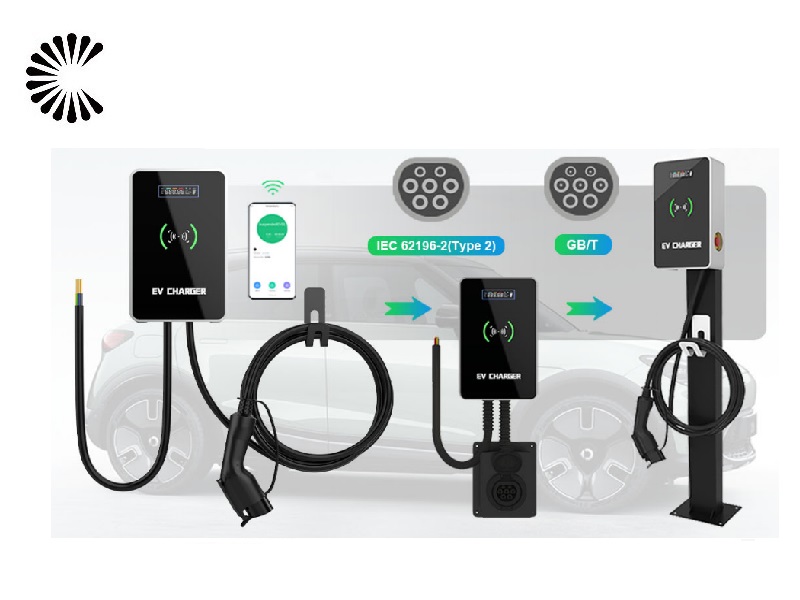
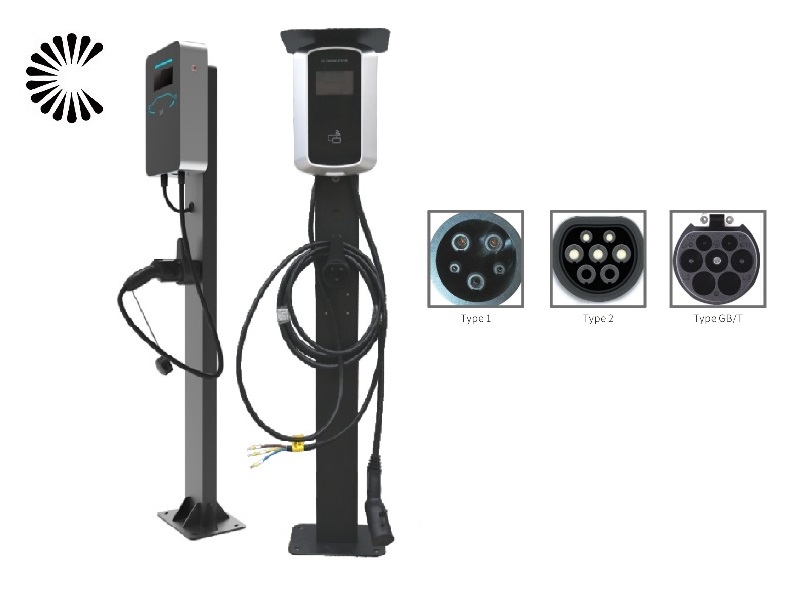
EV Chargers for Sale:
ChargersGO Factory Informations
Our EV Charger Factory Introduction:
| Business Type: | Manufacturer/Factory | Main Products: | EV Charger |
| Number of Employees: | 100 | Year of Establishment: | 2014.05 |
| Production Capacity | 5000Set/Year | After-sales Service: | Technical Support; on-line teach lessons |
| R&D Capacity: | ODM, OEM | Annual Output Value: | US$5 Million – US$10 Million |
| No. of R&D Staff: | 5 | No. of Production Lines: | 6 |
ChargersGO Factory is a reputable manufacturer specializing in Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers. Our extensive product range includes slow chargers, fast chargers, DC EV Chargers, AC EV Chargers, commercial EV Chargers, home chargers, and EV chargers of various levels, including level 1, level 2, and level 3. All our products adhere to strict China GMP design standards, ensuring top-notch quality and performance. Additionally, we take pride in securing various certifications to ensure the reliability and safety of our chargers.
Business Philosophy:
“Quality is the main policy of sales” and “integrity is the principle of success” are the business philosophy of our people. We carry out one-year warranty, lifelong maintenance service, with technical consultation and other services, and long-term supply of equipment. Welcome new and old customers to negotiate cooperation!
Production Process:
The production of an Electric Vehicle (EV) charger entails a meticulous process aimed at delivering top-notch quality, safety, and performance. It involves several essential stages:
By adhering to this comprehensive production process, EV charger manufacturers ensure that their products are efficient, reliable, and safe, contributing to the broader adoption of electric vehicles and sustainable transportation.
By following a well-structured production process and adhering to strict quality standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality EV chargers that contribute to the growth of electric mobility and a greener, sustainable future.

Certifications:

Small EV Charger Packing:
Retail and Wholesale Packaging of Small EV Chargers for Shipment
Retail Small EV Charger Shipment:
For retail orders, Small EV Chargers are shipped using express shipping methods.
Wholesale Small EV Charger Shipment:
For wholesale orders, Small EV Chargers are carefully packed in export fumigation-free wooden cases, suitable for bulk shipments or container transportation.
The primary objective of these packing measures is to safeguard the Small EV Chargers from any potential damage during sea shipment, ensuring they arrive at their destination in optimal condition. Employing correct packing procedures and utilizing high-quality materials minimizes the risk of harm during the journey.
Packing a Large EV Charger for Sea Shipment: Ensuring a Safe Voyage
Packing a large EV charger for sea shipment is a meticulous and demanding process, but with meticulous planning and precision, it can be done effectively to guarantee its safe arrival at the destination. Below are the essential steps a manufacturer may undertake when preparing a large machine for sea shipment:
Overall, packing a large EV charger for sea shipment demands precision and adherence to proper procedures. Employing high-quality materials and meticulous attention to detail ensures the machine’s safe and intact arrival at its intended destination. For added assurance, consulting a professional packing and shipping company can guarantee the machine is expertly packed and ready for its sea journey.


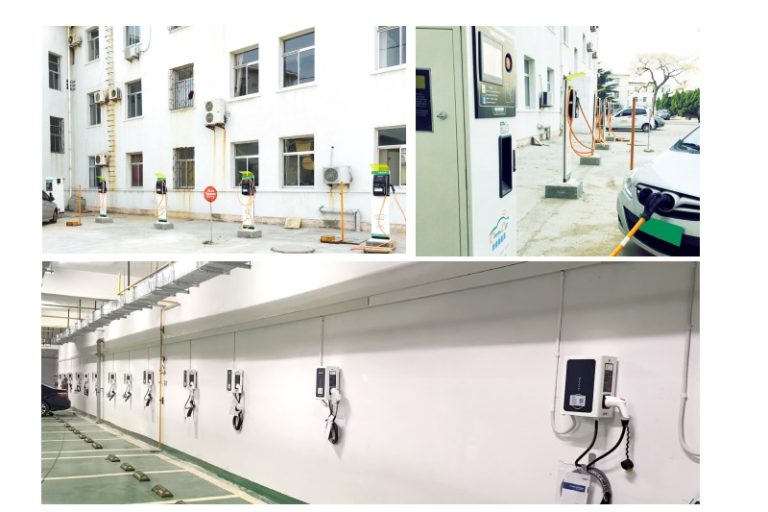
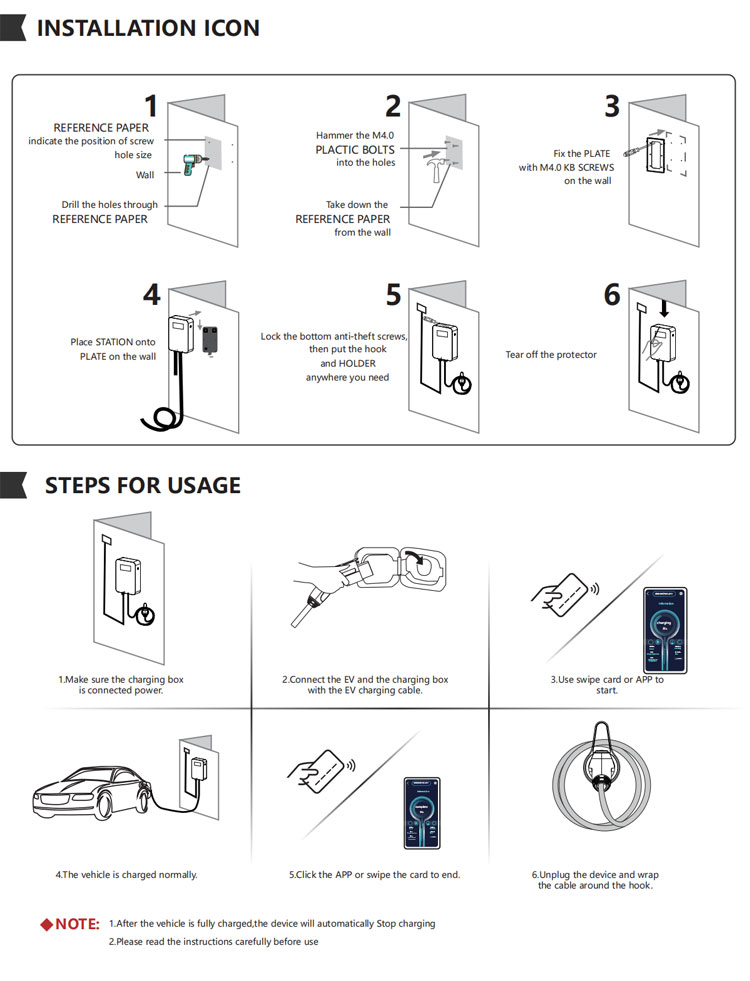
Installing an Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger requires careful planning and consideration to ensure a safe and efficient charging experience. Here is a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
It is crucial to have a licensed electrician perform the installation to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards. Additionally, some EV charger manufacturers offer professional installation services, which can provide peace of mind and ensure a smooth and trouble-free installation process.
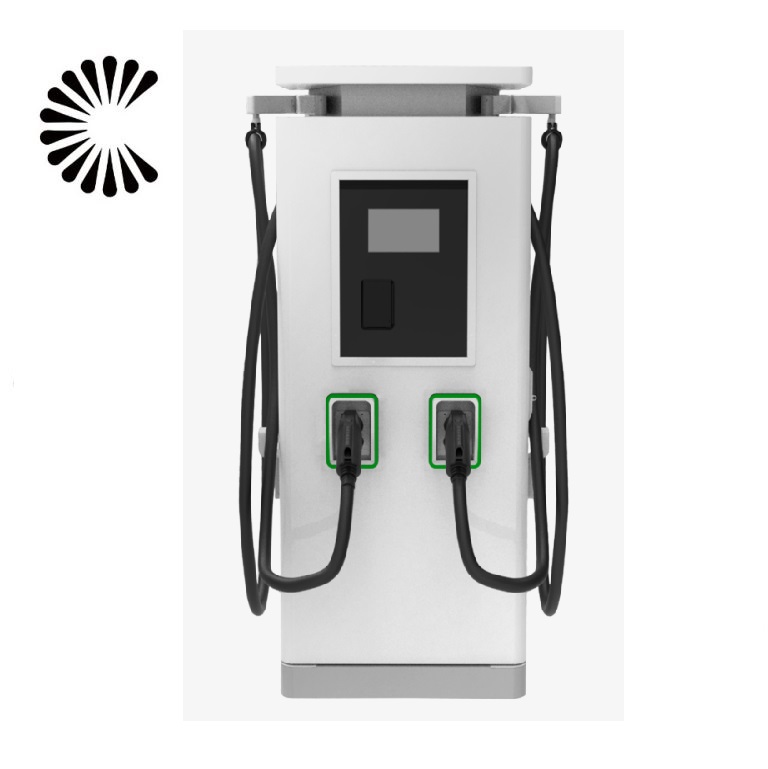
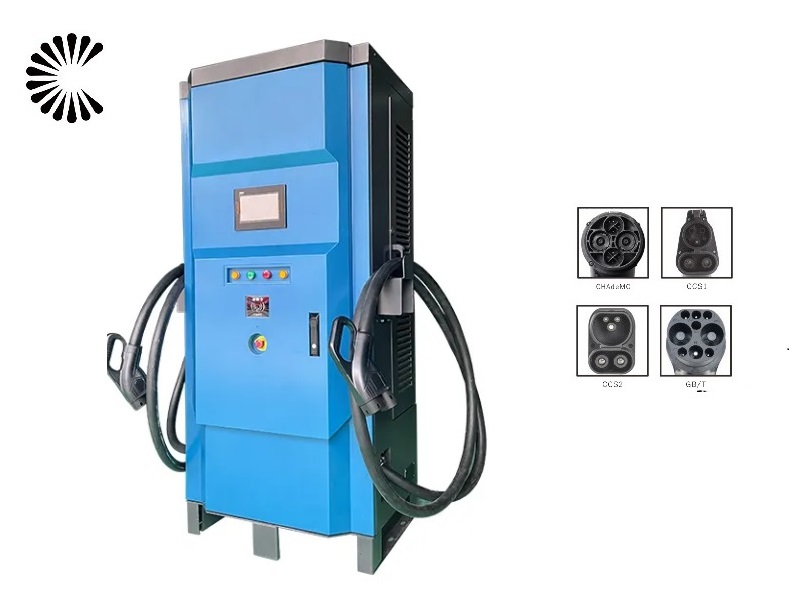
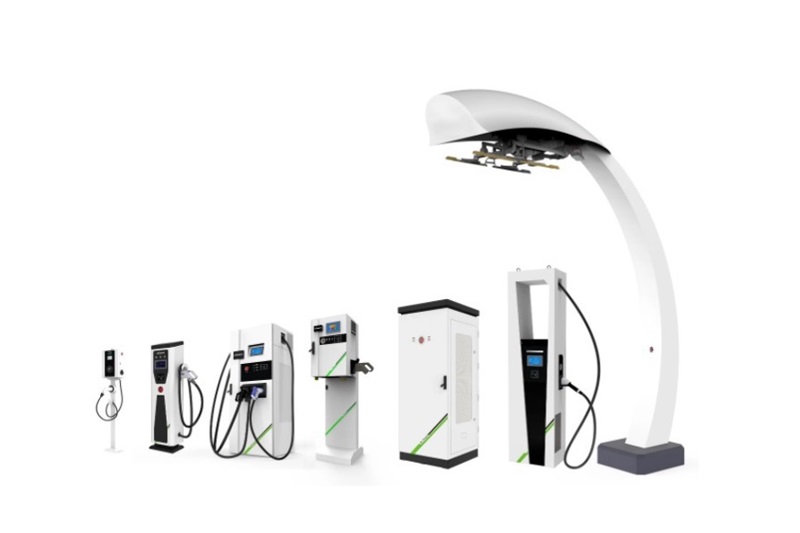
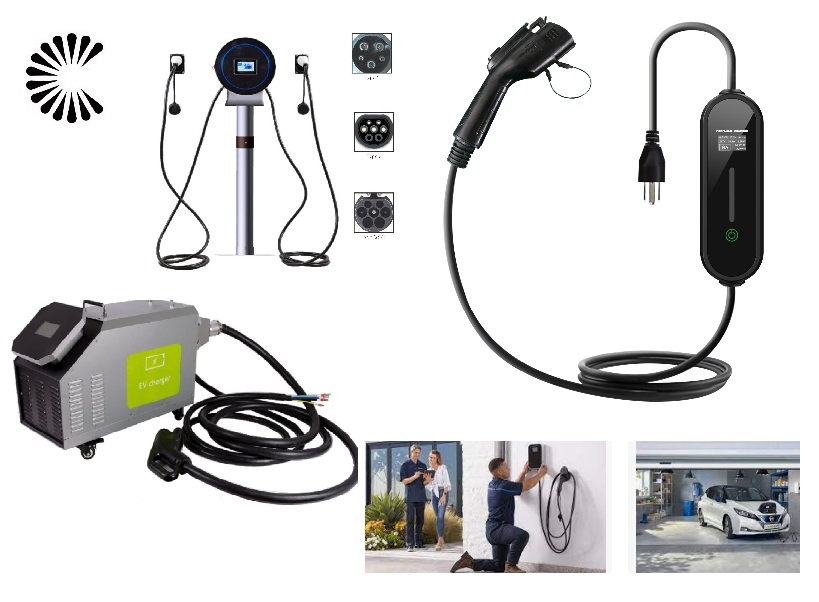
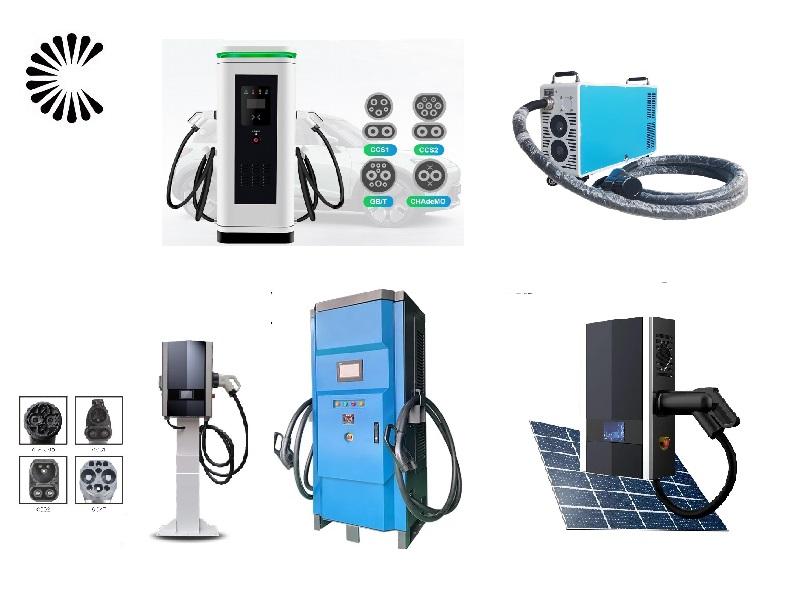
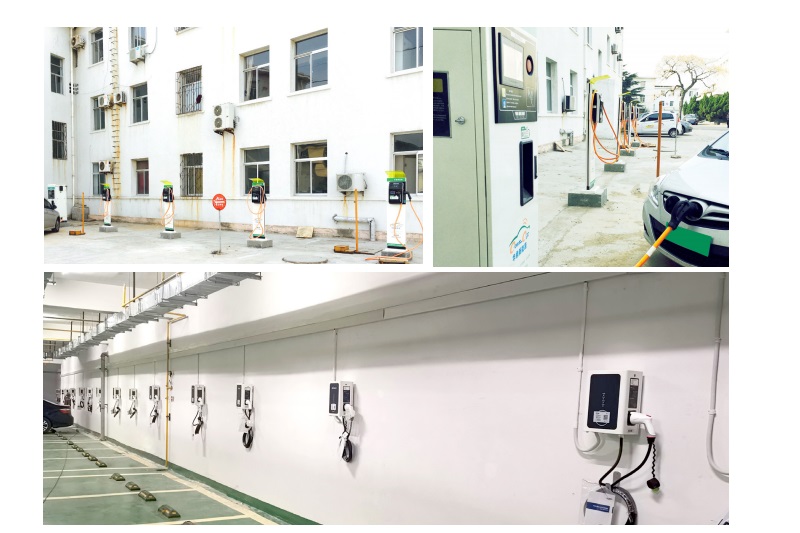
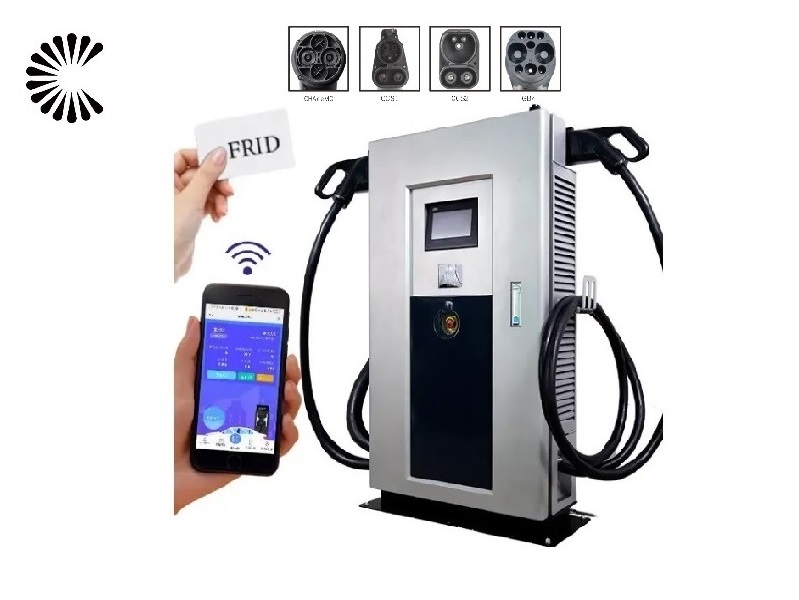
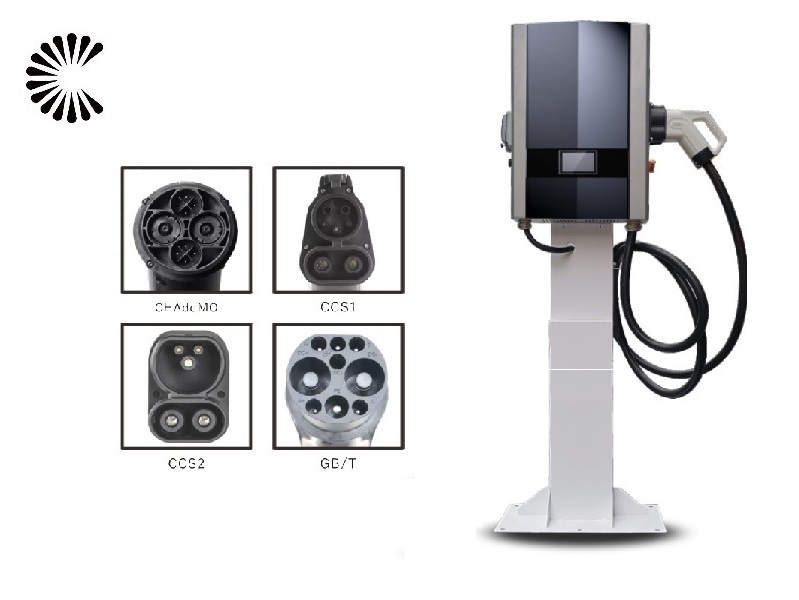
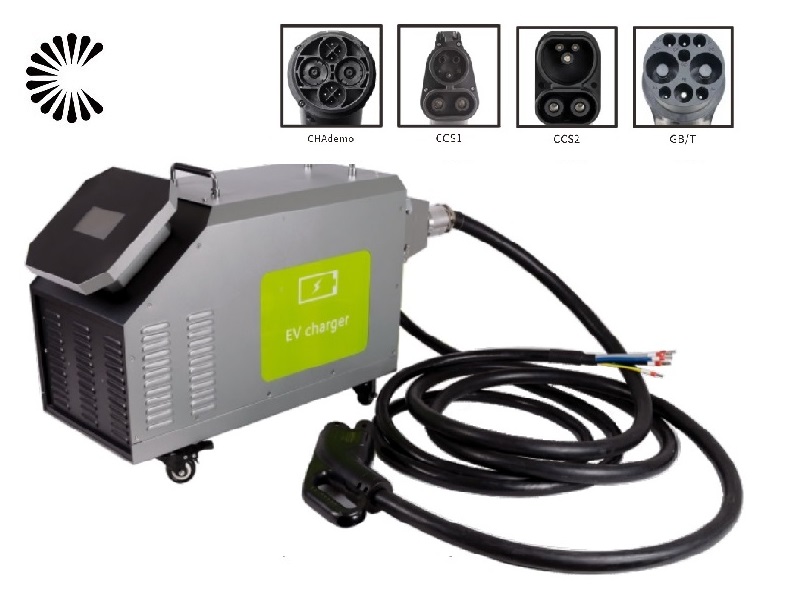
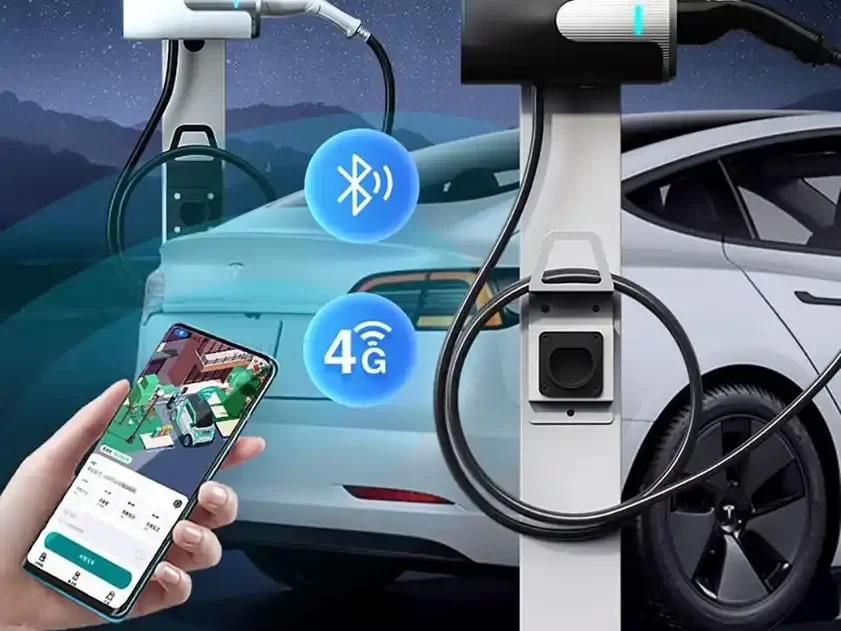
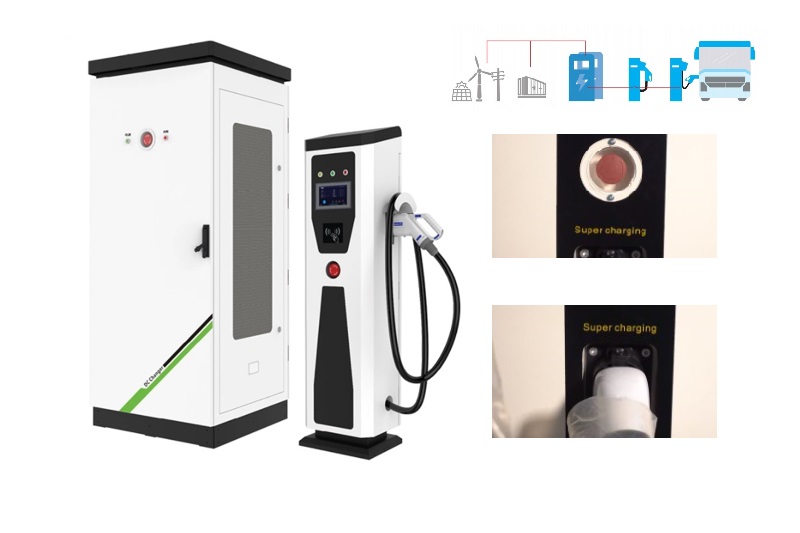
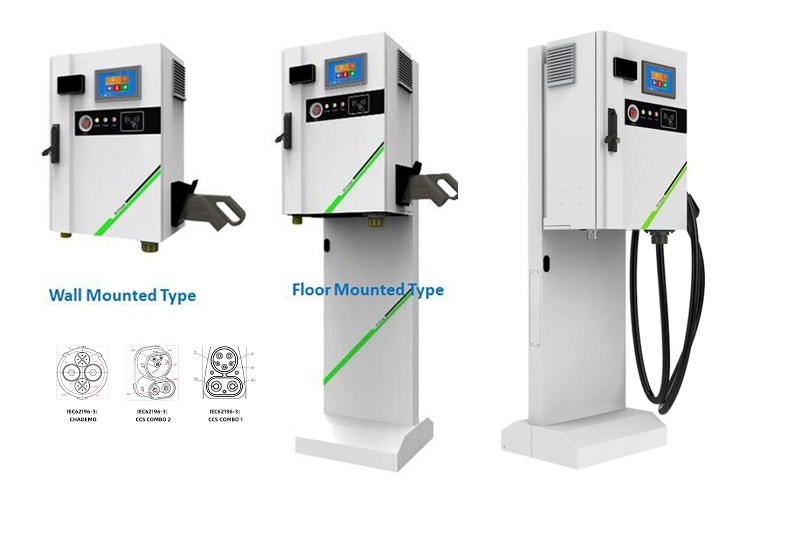
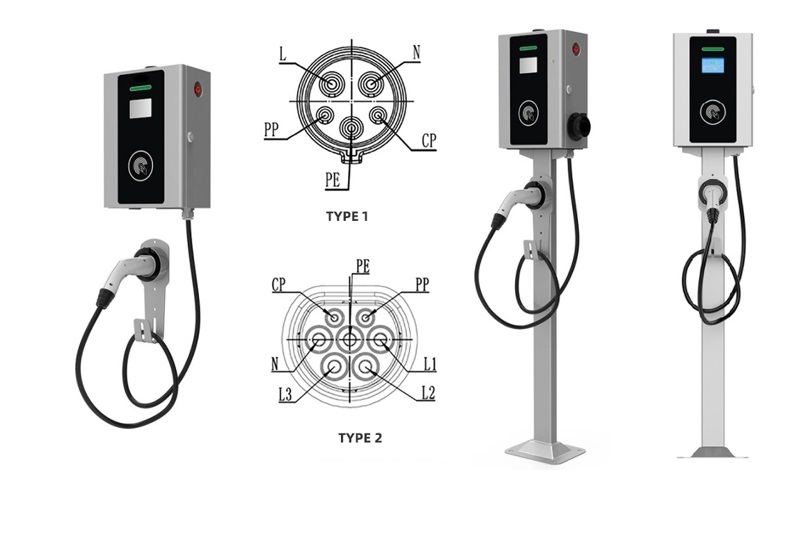
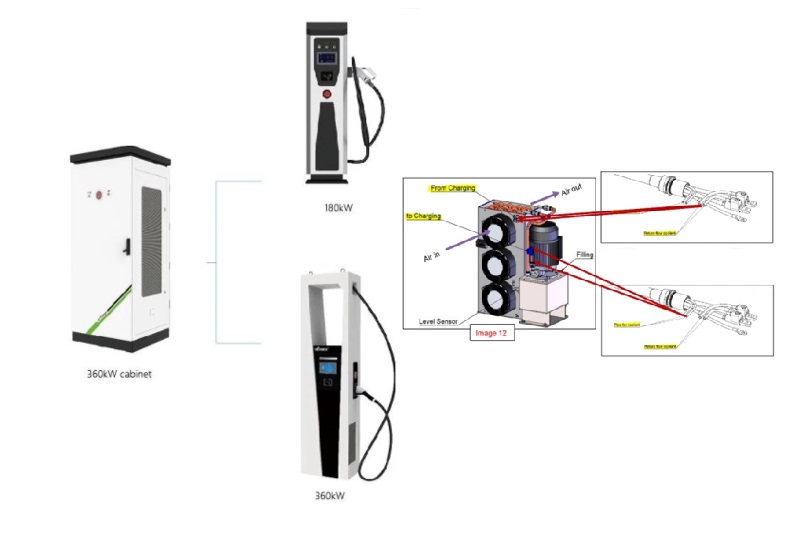
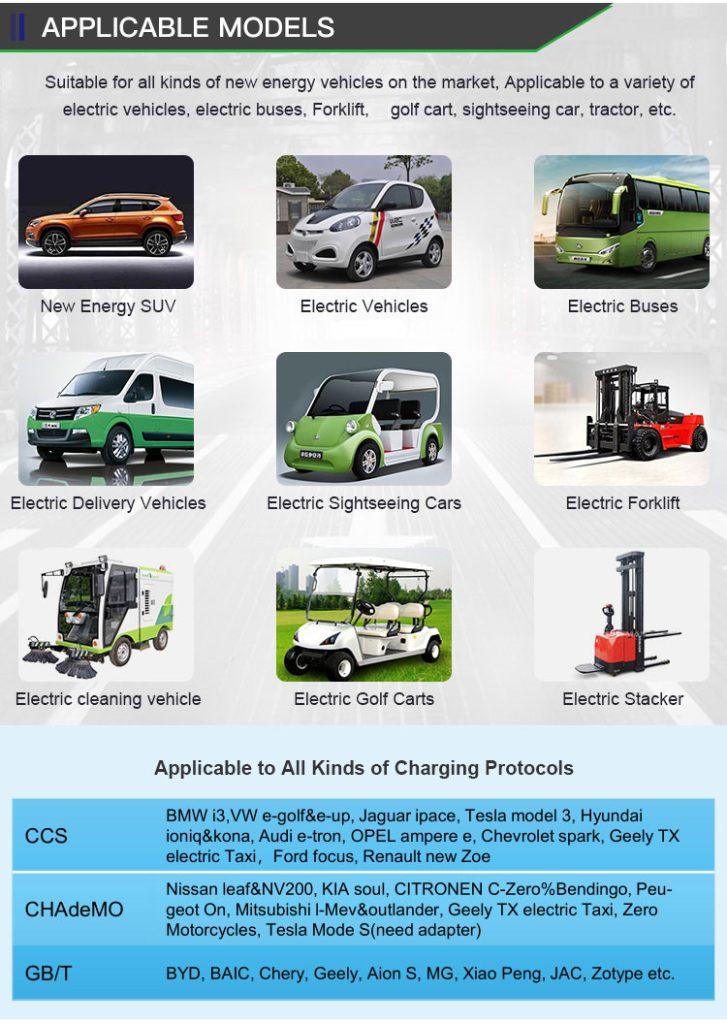
Applications of EV Charger:
In essence, Level 3 EV chargers are vital for scenarios where EVs need to be charged quickly and efficiently to meet the demands of busy individuals, travelers, commercial operators, and public transportation services.
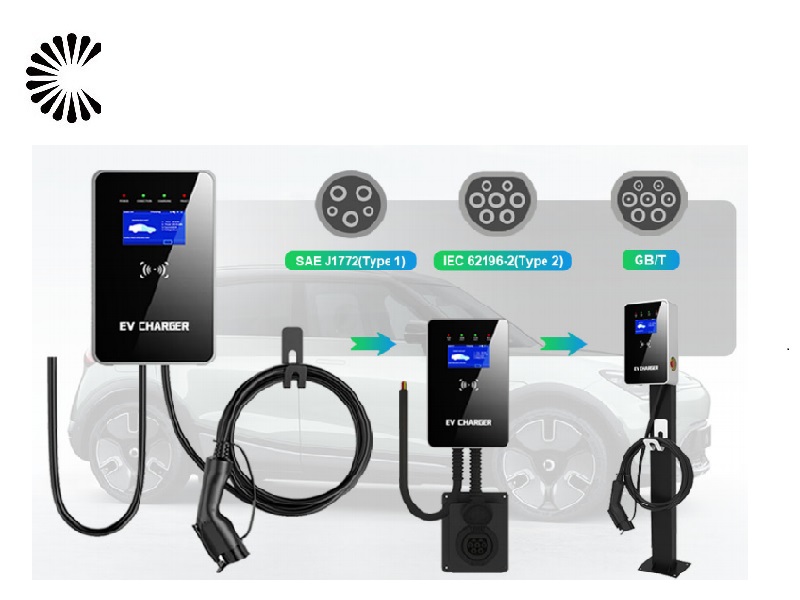
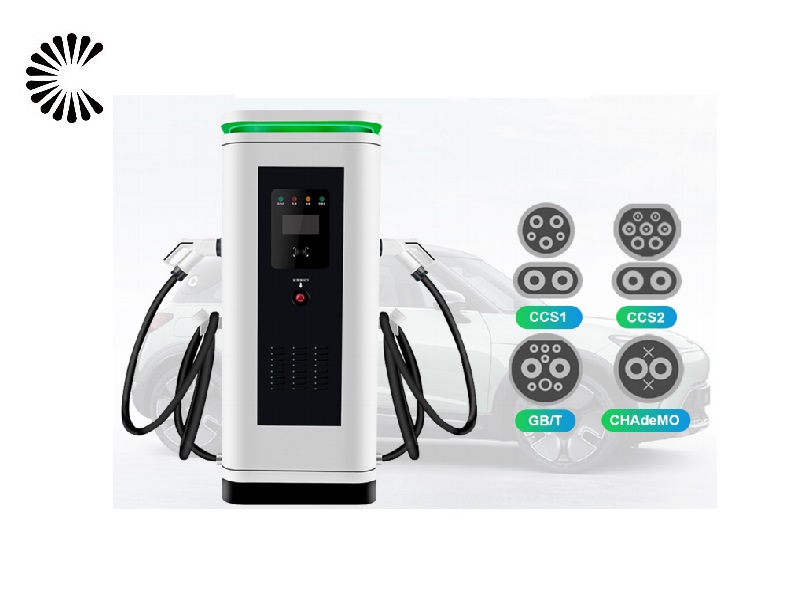
It is appplicable for all kinds of charing protocols, Suitable for all kinds of new energy vehicles on the market,Applicable to a variety of electric vehicles, electric buses,Forklift,golf cartsightseeing cartractor, etc.
| CHAdeMO | Nissan leaf&NV200, KIA soul, CITRONEN C-Zero%Bendingo, Peu geot On, Mitsubishi l-Mev&outlander, Geely TX electric Taxi,Zero Motorcycles, Tesla Mode S(need adapter) |
| CCS | BMW i3,VW e-golf&e-up, Jaguar ipace, Tesla model 3, Hyundai ioniq&kona, Audi e-tron, OPEL ampere e, Chevrolet spark, Geely TX electric Taxi,Ford focus, Renault new Zoe |
| GB/T | BYD, BAIC,Chery, Geely, Aion S, MG, Xiao Peng, JAC, Zotype etc. |
EV Charger Wholesale Manufacturer In China
Charging an Electric Vehicle (EV) involves refilling the energy stored in the EV’s battery. This is done by connecting the EV to a charging station or charger. ChargersGO is the manufacturer and wholesaler for EV Charger. Please feel free to contact with us.