Should i charge my ev to 100? does charging ev to 100 damage battery?

Should i charge my ev to 100? does charging ev to 100 damage battery? Because of the chemical characteristics of lithium-ion batteries, it is generally not advised to charge your EV to 100% for daily use as this can hasten battery degradation over time. However, because of the Battery Management System’s (BMS) protective function, occasionally charging to full capacity for lengthy trips is acceptable and won’t result in immediate damage. The key is to balance your charging habits to maximize battery health and longevity.
Understanding Lithium-ion Battery Chemistry
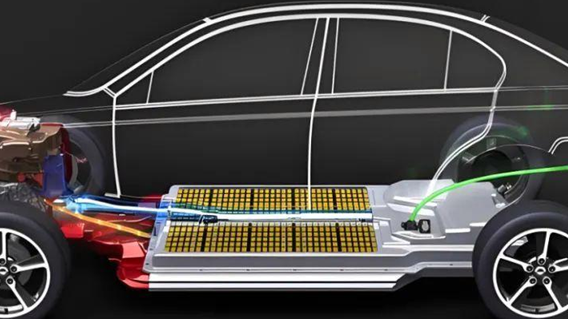
Lithium-ion batteries, which power most modern EVs, are sensitive to extreme states of charge. When a battery is charged to 100%, the lithium ions are densely packed into the anode (negative electrode), creating high stress on the electrode materials. This stress leads to accelerated degradation through mechanisms like cathode cracking, lithium plating, and solid electrolyte interface (SEI) growth. Over time, these processes reduce the battery’s ability to hold a charge, resulting in diminished range. While occasional full charges won’t cause immediate harm, consistently charging to 100% can reduce the battery’s lifespan by 10-20% over several years. This is why manufacturers often recommend limiting daily charging to 80-90%.
The Role of the Battery Management System (BMS)
Modern EVs are equipped with an advanced BMS that safeguards the battery against overcharging and other harmful conditions. When you charge to 100%, the BMS doesn’t actually allow the battery to reach a true “full” state; instead, it maintains a buffer to prevent overcharging. For example, even when the display shows 100%, the BMS may have reserved 2-3% of the capacity to reduce stress. Additionally, the BMS regulates charging speed, especially above 80%, by reducing the current to minimize heat generation and electrode strain. It also manages temperature through cooling systems to prevent thermal damage. Despite these protections, frequent full charges still contribute to long-term wear because the BMS cannot entirely eliminate the chemical stressors associated with high states of charge.
Daily Use vs. Long-Distance Travel
For daily commuting and short trips, charging to 80-90% is ideal. This practice keeps the battery in a moderate voltage range, reducing stress on the electrodes and slowing down degradation. Most EVs allow you to set charging limits via the infotainment system or mobile app, making it easy to adopt this habit. For instance, Tesla’s daily charging recommendation is 80-90%, while Nissan Leaf owners are advised to avoid frequent full charges. On the other hand, for long-distance travel, charging to 100% is acceptable and sometimes necessary to maximize range. The critical point is to avoid letting the vehicle sit at 100% for extended periods. If you charge to full, plan to drive soon afterward to prevent the battery from remaining at high voltage for too long.
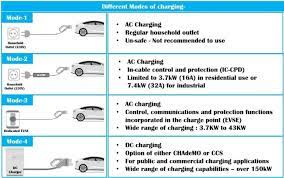
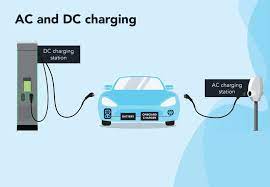
Impact of Fast Charging vs. Slow Charging
Fast charging (DC charging) is convenient but places additional strain on the battery due to high current and heat generation. When you fast charge to 100%, the combined effects of high temperature and high state of charge can accelerate degradation. Studies show that frequent DC charging to full capacity can reduce battery life by up to 10% compared to AC slow charging. Slow charging (AC charging) is gentler on the battery because it operates at lower power levels, generating less heat. If you need to charge to 100%, using a slow charger is preferable. For example, charging overnight at home to 100% occasionally is less harmful than doing so regularly at a DC fast charger.
Regional Recommendations and User Practices
In regions like North America and Europe, manufacturers often emphasize battery longevity, advising users to charge to 80-90% for daily use. Tesla, BMW, and Audi explicitly recommend this in their manuals. In contrast, some users in emerging markets, where charging infrastructure is less developed, may prefer charging to 100% for peace of mind. However, with the global push toward battery sustainability, educating users about optimal charging practices is becoming increasingly important. Companies are also integrating features like scheduled charging and adaptive limits to help users maintain battery health effortlessly.
Practical Tips for Extending Battery Life
- Set Charging Limits: Use your EV’s built-in features to cap charging at 80-90% for daily use.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Park in shaded or covered areas to reduce thermal stress on the battery.
- Use Timers: Schedule charging to finish just before you depart, minimizing the time the battery spends at high charge levels.
- Balance Occasional Full Charges: If you charge to 100%, try to do it only when necessary and drive shortly after.
- Prefer Slow Charging: Whenever possible, use AC slow charging for overnight sessions.
Conclusion
While charging your EV to 100% once in a while won’t harm it right away, charging it frequently can shorten the battery’s lifespan. The best course of action is to charge to 80–90% for daily use and save full charges for long trips. By using your vehicle’s BMS and implementing smart charging techniques, you can take advantage of your EV’s benefits while protecting the battery for years to come. For manufacturers worldwide, customizing recommendations to local preferences—for example, emphasizing longevity in mature markets and range assurance in emerging markets—can improve user satisfaction and product reliability.