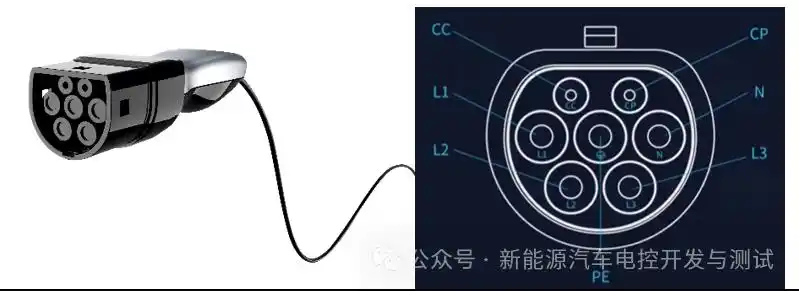
EV charging station companies

EV charging station companies. Businesses that produce equipment, run charging networks, and offer integrated energy management solutions make up the dynamic and quickly changing global electric vehicle (EV) charging station market. These businesses are all striving to construct the vital infrastructure required for the broad use of EVs.
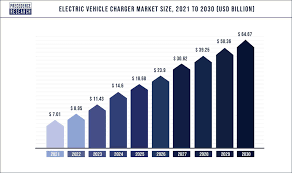
The global market for EV charging infrastructure is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.6%, from USD 29.4 billion in 2024 to USD 266.7 billion by 2034. This increase is primarily due to the growing global adoption of EVs, robust government backing for clean transportation programs, and ongoing developments in fast-charging technologies that make EVs more feasible for daily use.
The Structure of the EV Charging Industry
The EV charging ecosystem has matured into a well-defined structure, typically segmented into three key layers: upstream core components, mid-stream charging station manufacturing, and downstream operational services. This organized value chain ensures specialization and efficiency, from producing essential parts like charging modules and guns to manufacturing complete charging stations and ultimately managing network operations and user interfaces.
The industry has also developed a diverse range of ownership and operational models. These include public ownership, private or commercial ownership, utility-owned infrastructure, and public-private partnerships (PPPs), each playing a distinct role in the broader charging ecosystem.
Leading Chinese Charging Companies
China has emerged as a global leader in both EV adoption and charging infrastructure development, accounting for more than 60% of global public EV chargers in 2024. Several key players dominate this market.
Telexing stands as China’s largest new energy vehicle charging network ecosystem operator. The company has achieved remarkable scale, with its charging volume (accumulating over 50 billion kilowatt-hours), covering 366 cities across China with nearly 800,000 charging terminals, contributing to carbon emission reductions exceeding 51 million tons. Beyond mere scale, Telexing has pioneered the concept of a “charging network” versus simple “charging piles,” integrating chips into each terminal and utilizing big data for comprehensive linkage and intelligent scheduling. This supports orderly charging and grid coordination, effectively connecting vehicles to form an Internet of Vehicles (IoV) and aggregating vehicle batteries to create a distributed energy storage network. The company has also innovated in safety, developing a “two-layer safety protection” system that conducts big data “cloud inspections” of vehicle batteries during each charging process, using self-learning models to accurately warn of abnormalities.
Xingxing Charging is another major player, focusing on high-power charging technology research and development. The company has actively participated in formulating national charging standards, establishing itself as a representative of private charging operators with a product line covering both AC and DC equipment, as well as power exchange facilities.
State Grid e-Charging leverages its extensive national grid resources to establish a comprehensive five-level charging network operation and maintenance system. It boasts wide coverage and ranks at the forefront of the industry in terms of the number of connected charging piles, playing a crucial role in the national infrastructure rollout.
Xiaoju Charging , the digital charging operator under Didi Chuxing, has collaborated with over 8,400 merchants and served more than 34 million users. In a significant move announced in mid-2025, Xiaoju Charging partnered with BYD to co-build 10,000 megawatt-level fast-charging stations. This collaboration aims to integrate years of accumulated technological innovation capabilities and charging network operation experience to accelerate the construction of a nationwide megawatt fast-charging network.
International Market Leaders
The EV charging market is also vibrant and competitive on the global stage, with several key companies leading the charge in different regions.
In the United States, the public DC fast charger (DCFC) segment is projected to maintain a robust 14% CAGR from 2025 through 2040, reaching 475,000 ports and generating an annual market value of $3.3 billion by 2040. This growth occurs despite periodic policy headwinds, demonstrating strong underlying market demand. Federal initiatives like the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Program, supported by over $7.5 billion in federal funding aimed at deploying 500,000 public chargers by 2030, have been instrumental in catalyzing this growth.
Europe is also demonstrating strong momentum, with public chargers growing at an 11.3% CAGR through 2040, led particularly by DC charger expansion at a 13.7% CAGR. The residential segment is expected to reach 57 million AC chargers by 2040, while commercial charging grows at a 12% CAGR. The European Union’s Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) requires member states to install thousands of fast-charging points along major highways by 2025 and 2030, providing a regulatory push to match market pull.
Globally, the number of EV charging ports is expected to increase at a CAGR of 12.3% from 2026-2040, reaching a total of 206.6 million ports. The residential charging market will continue to be the dominant segment, with an anticipated 133 million ports globally by 2040. To achieve this expansion, annual global spending on EV charging infrastructure is expected to increase at a CAGR of 8% from 2026-2040, reaching $300 billion.
Technological Innovations Driving the Industry
The evolution of charging technology is a critical aspect of the industry’s development, making charging faster, more efficient, and more integrated with the broader energy system.
High-Power and MegaWatt Charging represents a significant frontier. Companies like BYD are developing “all-scenario adaptive” megawatt fast-charging technologies. Their innovations include “intelligent boost” technology, allowing equipped vehicles to be fully compatible with existing public fast charging piles, and “dual-gun charging” technology, which reportedly reduces charging time by about 70% compared to industry standards.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Technology is playing a crucial role in efficiency gains. Leading industry companies are using SiC power devices, known for their high voltage resistance, low loss, and high-power density characteristics, to push charging equipment efficiency beyond 96%. The industry is also simultaneously focusing on enhancing protection levels, optimizing noise reduction technology, and improving heat dissipation systems.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration is perhaps one of the most transformative innovations. Companies like Telexing are upgrading charging networks into the neural center of “virtual power plants.” By linking millions of charging terminals and massive amounts of charging data, they can turn vast numbers of electric vehicles into a huge distributed energy storage system. For example, at a Qingdao industrial park, using a “photovoltaic + electric vehicle energy storage” model, electricity is stored during low demand periods at a price of 0.3 yuan/kWh and discharged back during peak periods. This approach reportedly saves over 1.7 million yuan in electricity costs annually, with employees potentially achieving “free driving and even making money” by participating in energy storage transactions.
Wireless Charging, though still an emerging segment, is included in market forecasts and represents the next frontier in charging convenience.
Business Models and Strategic Partnerships
The charging industry has developed diverse business models and seen significant partnerships formed to accelerate infrastructure deployment.
Automaker-Charging Provider Collaborations have become increasingly common. The partnership between BYD and Xiaoju Charging to build 10,000 megawatt fast-charging stations is a prime example of this trend, combining automotive innovation with charging network operational expertise.
Utility-Led Deployments continue to play a vital role. State Grid e-Charging leverages its extensive national grid resources to establish a comprehensive five-level charging network operation and maintenance system, ensuring wide coverage and reliability.
Specialized Narket Focus is another approach. Some companies are focusing on specific segments, such as heavy-duty truck ultra-charging technology, developing solutions that can deliver extreme charging speeds and operate reliably in harsh environmental conditions from -40℃ to 70℃.
Future Outlook and Challenges
Looking ahead, the EV charging industry faces both tremendous opportunities and significant challenges as it scales to meet global electrification goals.
Market Growth is expected to continue its rapid pace. By 2025, some analysts project the global charging pile market space could exceed one hundred billion yuan, representing a substantial blue-ocean market opportunity. Specifically, the markets in China, the United States, and Europe are expected to reach approximately 72.912 billion yuan, 19.034 billion yuan, and 10.383 billion yuan, respectively, by 2025, with CAGRs from 2022-2025 of 50.95%, 135.68%, and 34.87%.
Addressing Range Anxiety through improved convenience remains a priority. The vision is that with megawatt-level ultra-fast charging becoming core development trend, facilitated through high-voltage platform and high-current solutions working in parallel, the goal of making “charging as convenient as refueling” will accelerate towards reality. Charging pile technology, through dynamic power distribution, can both reduce grid expansion costs and achieve multi-vehicle compatibility.
Grid Integration and Stability will become increasingly critical. As utilization in public charging increases and infrastructure efficiency improves, the ratio of EVs to public chargers is expected to increase from 7.5 battery electric vehicles per charger in 2025 to 14.2 in 2040. This increased efficiency helps manage the grid impact of widespread EV adoption.
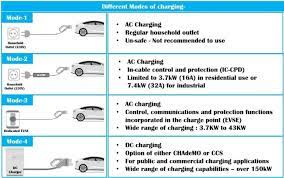
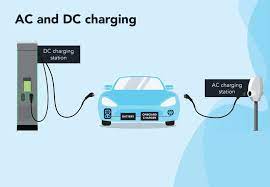
Standardization and Interoperability are essential for a seamless user experience. Charging equipment standards are the core support for the standardized development of the charging equipment industry. Mainstream global standard systems include IEC, EN, SAE, CHAdeMO, and China’s national standards. China has established a comprehensive standard system covering conductive charging, wireless charging, and battery swap technology routes, encompassing the entire process from equipment technology, interfaces, and communication protocols to construction and operation. There are ongoing calls for subsequent standards to include unified megawatt-level charging, communication protocols, charging pile coding, and QR code logic to help standardize market order, promote technological innovation, and ensure healthy and sustainable industry development.
In conclusion, EV charging station companies worldwide are not merely building infrastructure but are actively shaping an entirely new ecosystem for transportation energy. Through technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and supportive policies, these companies are overcoming challenges related to speed, convenience, and grid integration. The transition from isolated charging points to intelligent, networked systems that interact dynamically with both vehicles and the broader energy grid represents a fundamental shift. As this industry continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly vital role in enabling a sustainable transportation future, ultimately making electric vehicle charging as effortless, ubiquitous, and reliable as traditional refueling, thereby accelerating the global transition to clean transportation.