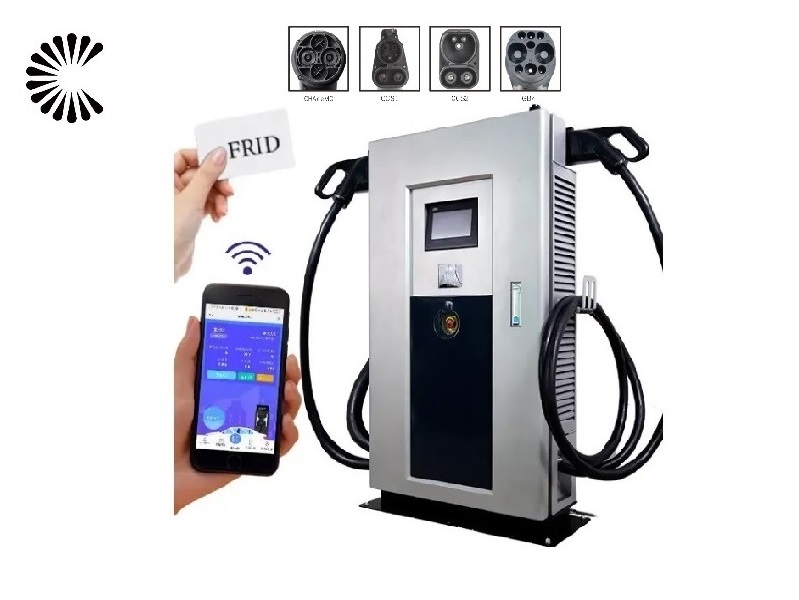
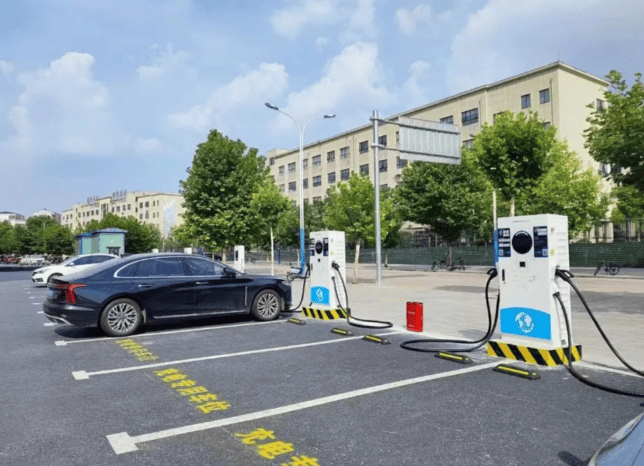
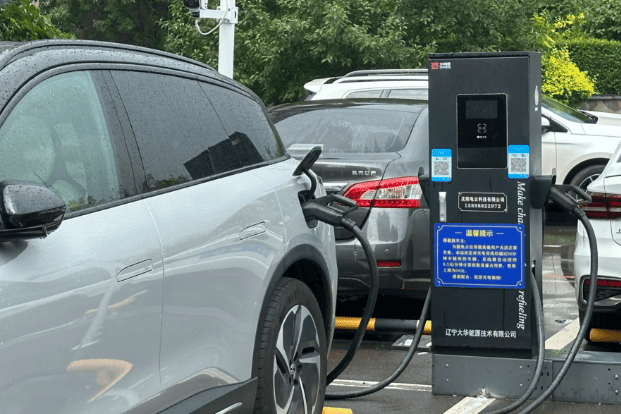
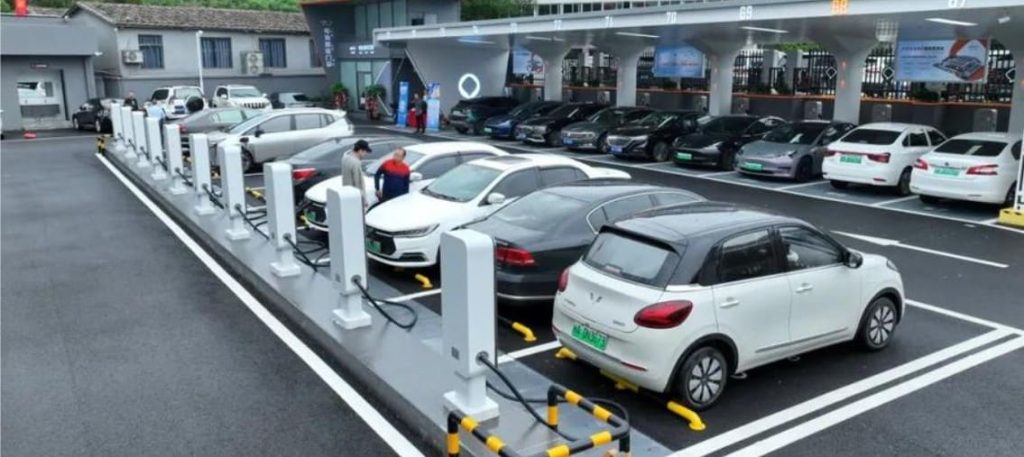
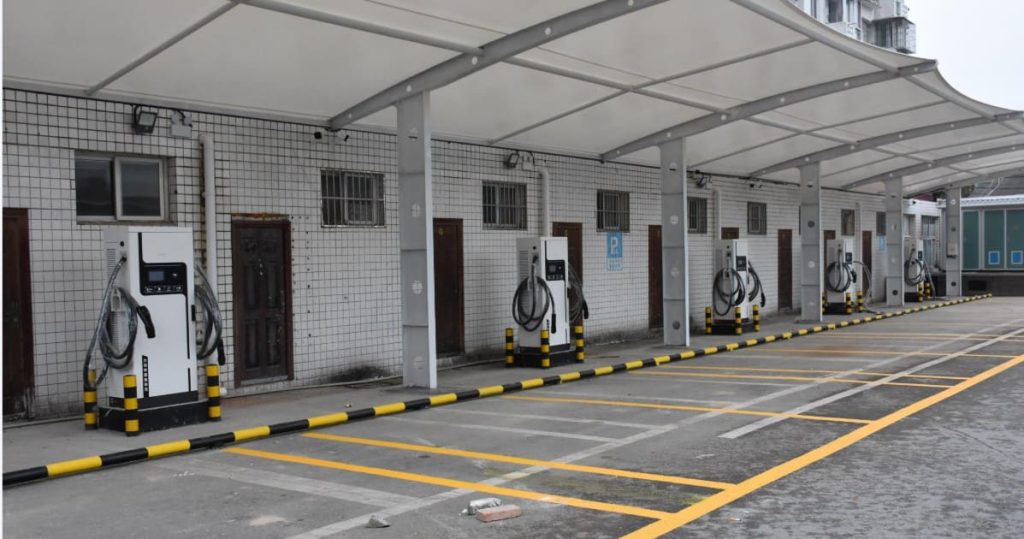
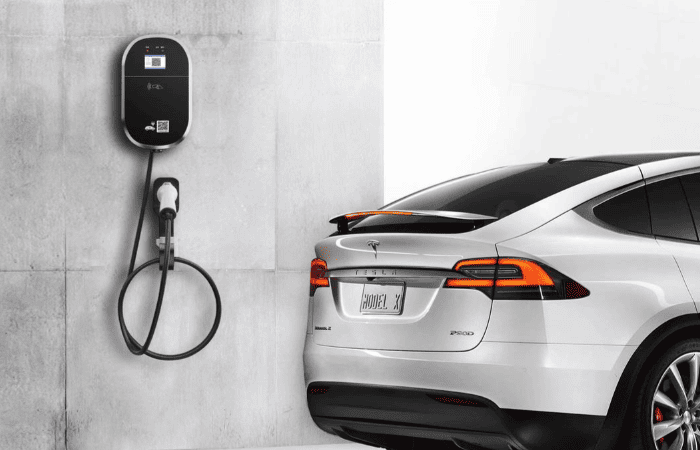
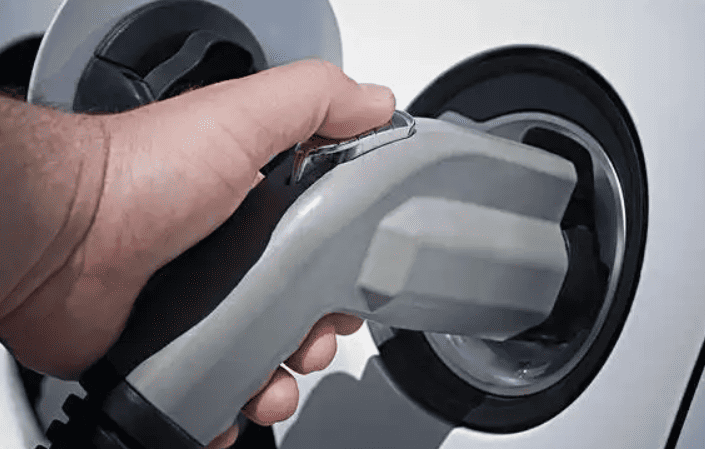
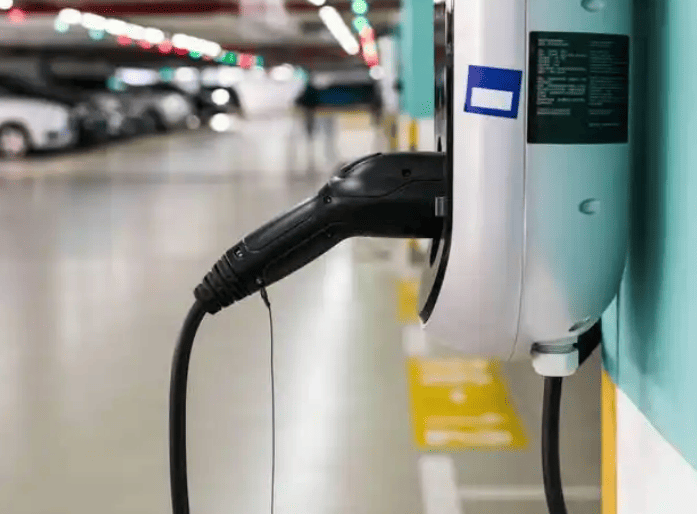
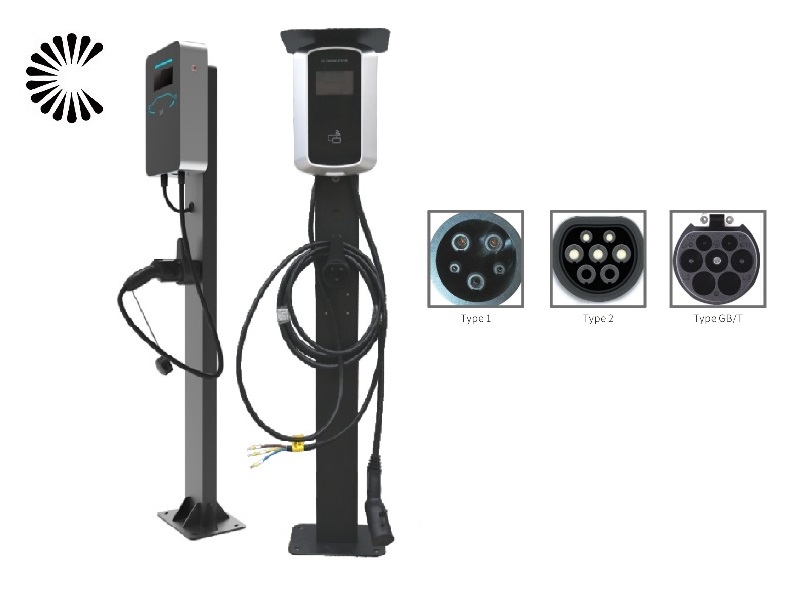
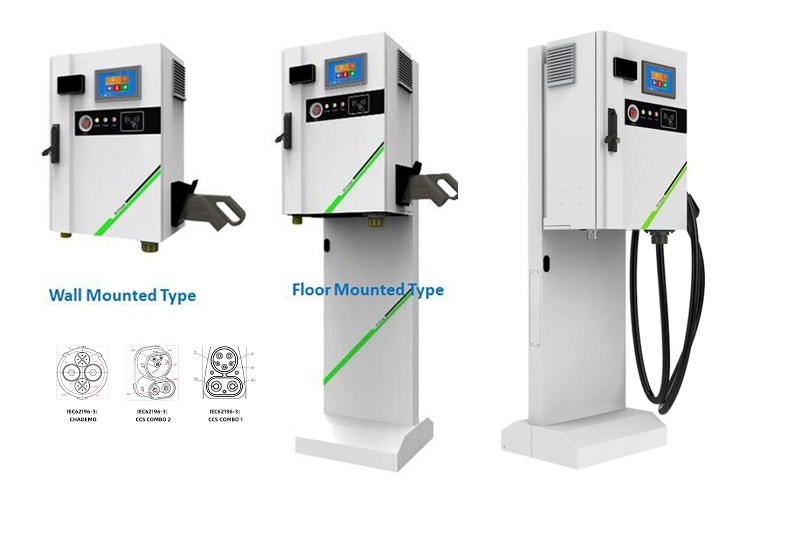
All You Want to Know about Slow EV Charger
What is a Slow EV charger?

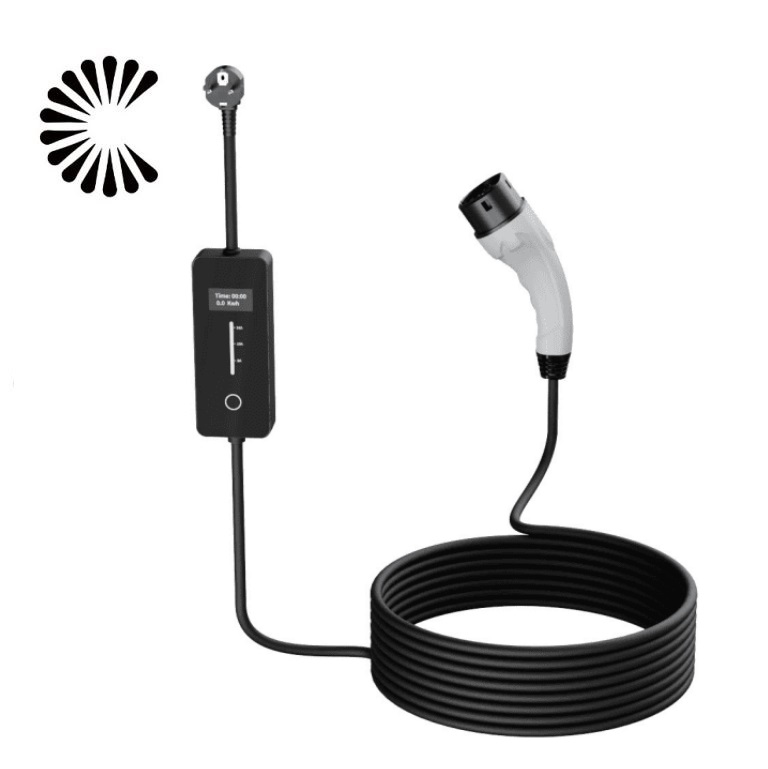
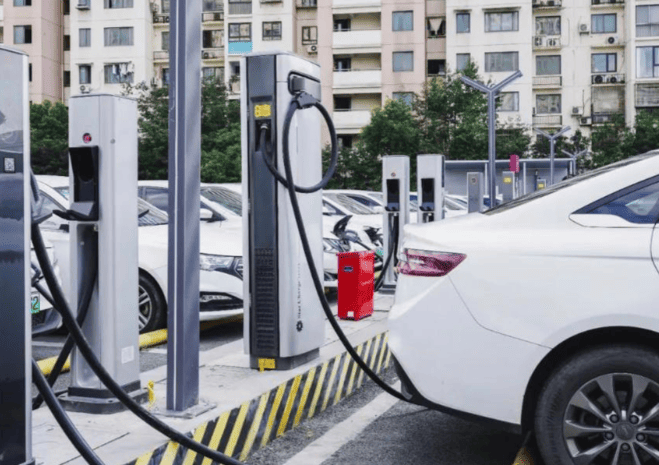
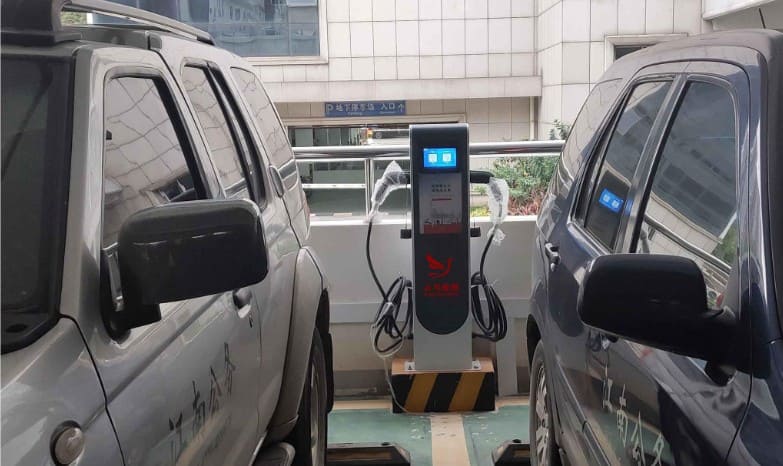
The Slow EV Charger is often the standard charger that comes with an electric vehicle when it is purchased. It is relatively simple to use, requiring only a standard electrical outlet to plug into. This makes it a convenient option for EV owners who may not have access to specialized charging infrastructure or who want a cost-effective way to charge their vehicle at home.
One of the main characteristics of a Slow EV Charger is its lower charging rate. It typically provides a charging speed of around 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. This means that for every hour the vehicle is connected to the charger, it gains an additional 3 to 5 miles of driving range. While this charging rate may be considered slow compared to other types of EV chargers, it can still be sufficient for many drivers who have limited daily driving needs or longer periods of time to charge.

The Slow EV Charger speed of these chargers is primarily due to the lower power output they provide. Level 1 chargers typically operate at 120 volts AC and draw around 12 amps of current, resulting in a power output of approximately 1.4 kilowatts. This lower power output leads to a slower charging rate compared to higher-level chargers, such as Level 2 or DC fast chargers, which can deliver significantly more power and charge the vehicle at a much faster rate.
While Slow EV Charger may not be suitable for everyone, they have several advantages. First and foremost, they are widely accessible since they can be plugged into a standard electrical outlet found in most homes. This makes them a convenient option for residential charging, especially for those who do not have access to dedicated charging stations in their area.
Additionally, Slow EV Charger is generally less expensive compared to higher-level chargers. They require minimal installation or infrastructure modifications, as they can be directly plugged into existing electrical outlets. This affordability makes them an attractive choice for EV owners on a budget or for those who have limited charging needs and can rely on overnight charging.
Moreover, Slow EV Charger is generally less demanding on electrical circuits. Since they draw lower amounts of current, they have a lower risk of overloading electrical systems or causing voltage drops. This can be advantageous in older buildings or areas with limited electrical infrastructure, where higher-level chargers may not be feasible due to potential electrical limitations.
However, it is important to note that Slow EV Charger may not be suitable for all situations. Their lower charging rate can be a disadvantage for drivers who require more frequent or faster charging, such as those with longer commutes or who need to quickly top up their vehicle’s battery during the day. In such cases, higher-level chargers like Level 2 or DC fast chargers, which provide faster charging speeds, would be more appropriate.
In conclusion, a Slow EV Charger, or Level 1 charger, is a type of electric vehicle charger that offers a lower charging rate compared to higher-level chargers. It is commonly used for residential charging or in locations where faster charging speeds are not necessary. While it may have a slower charging rate, slow EV chargers are widely accessible, affordable, and less demanding on electrical circuits. They provide a convenient and cost-effective option for EV owners with limited charging needs or who primarily charge their vehicles overnight.
What is the difference between slow EV Charger, fast EV Charger?
The difference between a slow EV charger and a fast EV charger lies in the charging speed and power output they provide. These two types of chargers are designed to cater to different charging needs and scenarios.

A slow EV charger, also known as a Level 1 charger, offers a lower charging rate compared to fast chargers. It is typically used in residential settings or places where faster charging is not crucial. Slow EV Charger are commonly included as standard equipment when purchasing an electric vehicle. They are designed for convenience and accessibility, allowing EV owners to charge their vehicles overnight or during extended periods of parking.
Slow EV Charger operate at 120 volts AC and draw around 12 amps of current, resulting in a power output of approximately 1.4 kilowatts. This lower power output translates to a relatively slow charging speed. On average, a slow charger provides a range of about 3 to 5 miles per hour of charging. This means that for every hour the vehicle is connected to a slow charger, it gains an additional 3 to 5 miles of driving range.
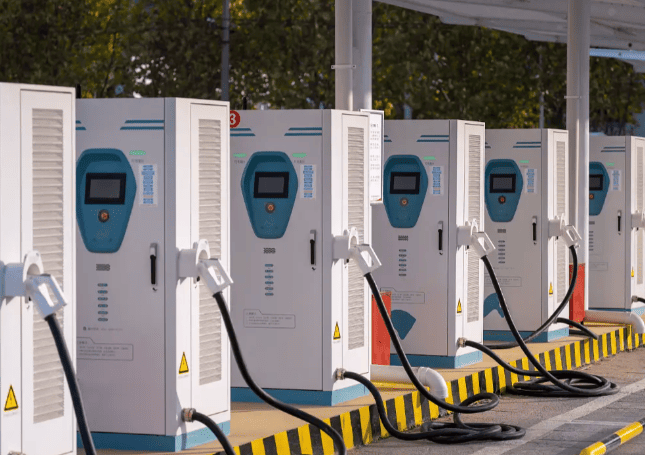
In contrast, fast EV chargers, such as Level 2 chargers or DC fast chargers, offer a significantly higher charging speed and power output. These chargers are commonly found in public charging stations, workplaces, and commercial areas. They are designed to accommodate drivers who require quicker charging times or who have higher daily driving demands.
Level 2 chargers operate at 240 volts AC and draw around 30 to 40 amps of current, resulting in a power output of approximately 7 to 10 kilowatts. This increased power output enables them to charge an electric vehicle at a faster rate compared to Slow EV Charger. With a Level 2 charger, the charging speed can reach approximately 10 to 20 miles of range per hour, depending on the specific vehicle and charger capabilities.
DC fast chargers, also known as Level 3 chargers, provide even higher power outputs. They operate at much higher voltages, typically ranging from 200 to 600 volts DC, and can deliver charging speeds of several hundred miles of range per hour. DC fast chargers are mainly installed along highways or at specific locations where drivers may need to quickly top up their vehicle’s battery during long-distance travel. They are capable of charging an electric vehicle from 0 to 80% in under an hour, depending on the vehicle’s battery capacity and charging capabilities.
The choice between a Slow EV Charger and a fast charger depends on various factors, including the driver’s charging needs, available charging infrastructure, and time constraints. Slow EV Charger is suitable for EV owners with limited daily driving needs or who primarily charge their vehicles overnight at home. Fast chargers, on the other hand, are more appropriate for drivers who require quicker charging times, longer daily driving distances, or the ability to recharge their vehicle during the day.
In conclusion, the main difference between slow and fast EV chargers lies in the charging speed and power output they provide. Slow EV Charger offers a lower charging rate, typically providing around 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. They are commonly used for residential charging. Fast chargers, such as Level 2 chargers or DC fast chargers, offer significantly higher charging speeds and power outputs, allowing for faster charging times and accommodating drivers with higher daily driving demands. The choice between slow and fast chargers depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the EV owner.
What are the disadvantages of slow charging?
While Slow EV Charger, also known as Level 1 charging, offers convenience and accessibility for electric vehicle (EV) owners, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered. These drawbacks mainly revolve around the slower charging speed and limitations associated with the lower power output of slow chargers.
The primary disadvantage of Slow EV Charger is the time it takes to fully charge an electric vehicle. Slow chargers typically provide a charging rate of around 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. This means that it can take a significant amount of time to recharge an EV, especially if the battery is deeply depleted. For example, if you have an EV with a 200-mile range and the battery is completely empty, it could take approximately 40 to 66 hours of continuous charging to fully replenish the battery using a slow charger. This lengthy charging time can be inconvenient for EV owners who have higher daily driving distances or need to quickly top up their vehicle’s battery.
Another disadvantage of Slow EV Charger is its limited suitability for certain situations. If you have a long commute or frequently drive long distances, relying solely on a slow charger might not be practical. Slow charging is best suited for EV owners with limited daily driving needs or who have longer periods of time available for charging, such as overnight charging at home. If you rely heavily on your EV throughout the day or require faster charging, a slow charger may not meet your requirements, and opting for a faster charger, such as a Level 2 or DC fast charger, would be more suitable.
Additionally, Slow EV Charger may not be ideal for situations where you need to top up your vehicle’s battery quickly during the day. For example, if you’re on a road trip or need to run multiple errands in a limited timeframe, the slow charging speed of a Level 1 charger might hinder your ability to charge your vehicle efficiently. In such cases, having access to faster charging options, like Level 2 or DC fast chargers, would be more beneficial.
The lower power output of slow chargers can also be a limiting factor. Slow EV Charger typically operates at 120 volts AC and draw around 12 amps of current, resulting in a power output of approximately 1.4 kilowatts. This lower power output may not be able to fully utilize the charging capabilities of certain EV models. Some EVs have larger battery capacities or are capable of accepting higher charging rates, and a slow ev charger might not provide the optimal charging speed for these vehicles. Using a higher-level charger, such as a Level 2 charger, would allow for faster charging times and a more efficient use of the vehicle’s charging capabilities.
Furthermore, the slower charging speed of a slow ev charger can impact the overall convenience and flexibility of EV ownership. If you have a sudden need to use your EV for an unplanned trip or emergency, relying solely on a Slow EV Charger might limit your ability to quickly charge the vehicle and meet your immediate requirements. Faster charging options, like Level 2 chargers or DC fast chargers, offer greater flexibility and allow for more rapid recharging, ensuring your EV is ready for unexpected situations.
In conclusion, slow charging has its disadvantages due to the slower charging speed and limitations associated with the lower power output of Level 1 chargers. The lengthy charging times and limited suitability for higher daily driving distances can be inconvenient for some EV owners. Additionally, the slower charging speed and lower power output may not fully utilize the charging capabilities of certain EV models, and it may not be ideal for situations where quick top-ups are needed. Considering these drawbacks, it is important to assess your specific charging needs and circumstances to determine whether a slow ev charger will adequately meet your requirements or if a faster charging option would be more suitable.
Why is EV charging so slow?
EV charging can be perceived as slow due to several factors related to the charging infrastructure, battery technology, and electrical limitations. While advancements have been made to improve charging speeds, there are inherent constraints that contribute to the perceived slowness of EV charging.
One of the primary factors affecting EV charging speed is the capacity of the charging infrastructure. Charging stations are typically designed to handle a certain amount of power, which determines the charging speed they can provide. Residential charging, often done with Level 1 chargers, relies on standard electrical outlets, which are limited in the amount of power they can deliver. Level 1 chargers typically operate at 120 volts AC and draw around 12 amps of current, resulting in a power output of approximately 1.4 kilowatts. This lower power output translates into slower charging speeds.
Another factor is the capacity of the electric vehicle’s battery itself. EV batteries have a specific charging rate that dictates how quickly they can accept energy. While advancements in battery technology have improved charging rates, there are still limitations. Rapid charging can generate more heat and potentially degrade the battery’s lifespan. To protect the battery and ensure its longevity, charging rates are often controlled to prevent overheating or other detrimental effects. As a result, the charging speed is intentionally limited to maintain the health and safety of the battery.
Furthermore, charging speeds can be affected by the electrical grid’s limitations. The power grid has a certain capacity and is designed to handle the average electricity demand. When multiple EVs are charging simultaneously, it can strain the grid, potentially leading to voltage drops or overloading. To avoid these issues and ensure grid stability, charging speeds may be limited. This is particularly relevant for public charging stations, where multiple vehicles may be charging simultaneously.
Another consideration is the safety aspect of charging. EV charging involves high-voltage electrical systems, and safety measures are in place to protect users from electrical hazards. The charging process is regulated to ensure proper grounding, fault detection, and safety protocols. These safety measures may add complexity to the charging process, resulting in slower charging speeds.
It is important to note that not all EV charging is slow. Higher-level chargers, such as Level 2 chargers or DC fast chargers, offer significantly faster charging speeds compared to slow ev charger. Level 2 chargers, operating at 240 volts AC, can deliver power outputs of approximately 7 to 10 kilowatts, charging at rates of 10 to 20 miles of range per hour. DC fast chargers, operating at even higher voltages and currents, can provide charging speeds of several hundred miles of range per hour, allowing for quick charging sessions.
Efforts are being made to enhance charging infrastructure and improve charging speeds. The deployment of higher-power charging stations, advancements in battery technology, and upgrades to the electrical grid are all contributing to faster charging options. Additionally, research and development in areas like solid-state batteries and ultra-fast charging technologies aim to further improve charging speeds in the future.
In conclusion, several factors contribute to the perceived slowness of EV charging. Limitations in charging infrastructure, battery technology, electrical grid capacity, and safety considerations all play a role. However, advancements are being made to increase charging speeds, and higher-level chargers are available for faster charging. As technology and infrastructure continue to evolve, charging speeds are expected to improve, enhancing the convenience and usability of electric vehicles.
Our EV Charger Factory Introduction:
| Business Type: | Manufacturer/Factory | Main Products: | EV Charger |
| Number of Employees: | 100 | Year of Establishment: | 2014.05 |
| Production Capacity | 5000Set/Year | After-sales Service: | Technical Support; on-line teach lessons |
| R&D Capacity: | ODM, OEM | Annual Output Value: | US$5 Million – US$10 Million |
| No. of R&D Staff: | 5 | No. of Production Lines: | 6 |
ChargersGO Factory is a reputable manufacturer specializing in Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers. Our extensive product range includes slow chargers, fast chargers, DC EV Chargers, AC EV Chargers, commercial EV Chargers, home chargers, and EV chargers of various levels, including level 1, level 2, and level 3. All our products adhere to strict China GMP design standards, ensuring top-notch quality and performance. Additionally, we take pride in securing various certifications to ensure the reliability and safety of our chargers.
Business Philosophy
“Quality is the main policy of sales” and “integrity is the principle of success” are the business philosophy of our people. We carry out one-year warranty, lifelong maintenance service, with technical consultation and other services, and long-term supply of equipment. Welcome new and old customers to negotiate cooperation!
Production Process:
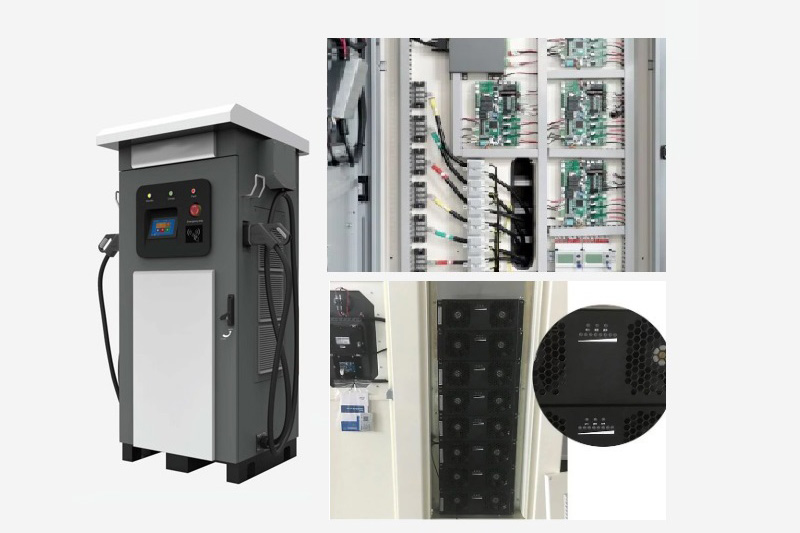
The production of an Electric Vehicle (EV) charger entails a meticulous process aimed at delivering top-notch quality, safety, and performance. It involves several essential stages:
By adhering to this comprehensive production process, EV charger manufacturers ensure that their products are efficient, reliable, and safe, contributing to the broader adoption of electric vehicles and sustainable transportation.
By following a well-structured production process and adhering to strict quality standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality EV chargers that contribute to the growth of electric mobility and a greener, sustainable future.

Certifications:

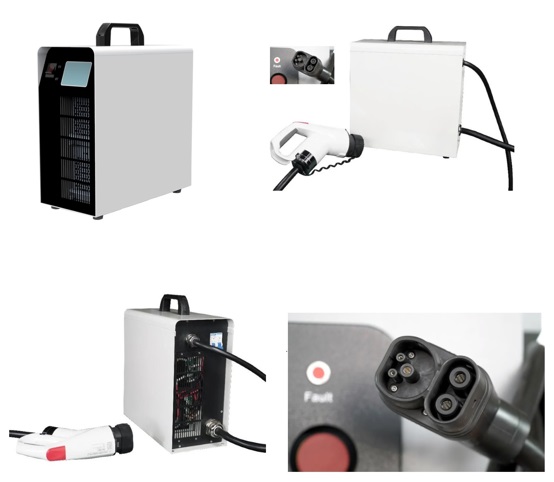
Small EV Charger Packing:
Retail and Wholesale Packaging of Small EV Chargers for Shipment
Retail Small EV Charger Shipment:
For retail orders, Small EV Chargers are shipped using express shipping methods.
Wholesale Small EV Charger Shipment:
For wholesale orders, Small EV Chargers are carefully packed in export fumigation-free wooden cases, suitable for bulk shipments or container transportation.
The primary objective of these packing measures is to safeguard the Small EV Chargers from any potential damage during sea shipment, ensuring they arrive at their destination in optimal condition. Employing correct packing procedures and utilizing high-quality materials minimizes the risk of harm during the journey.
Packing a Large EV Charger for Sea Shipment: Ensuring a Safe Voyage
Packing a large EV charger for sea shipment is a meticulous and demanding process, but with meticulous planning and precision, it can be done effectively to guarantee its safe arrival at the destination. Below are the essential steps a manufacturer may undertake when preparing a large machine for sea shipment:
Overall, packing a large EV charger for sea shipment demands precision and adherence to proper procedures. Employing high-quality materials and meticulous attention to detail ensures the machine’s safe and intact arrival at its intended destination. For added assurance, consulting a professional packing and shipping company can guarantee the machine is expertly packed and ready for its sea journey.


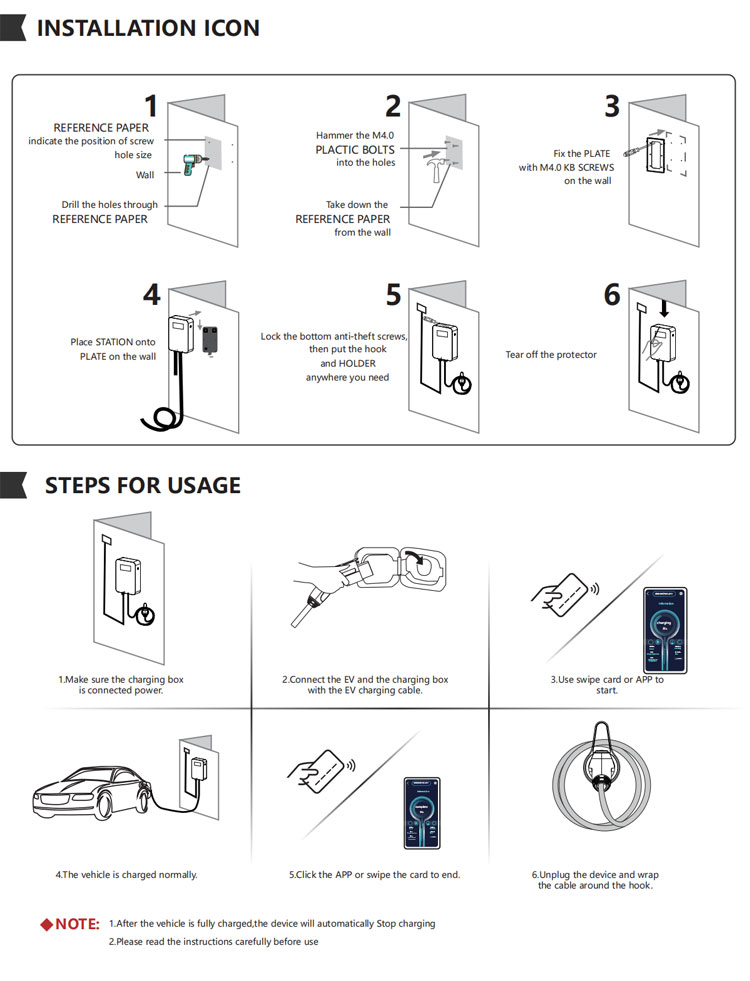
Installing an Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger requires careful planning and consideration to ensure a safe and efficient charging experience. Here is a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
It is crucial to have a licensed electrician perform the installation to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards. Additionally, some EV charger manufacturers offer professional installation services, which can provide peace of mind and ensure a smooth and trouble-free installation process.
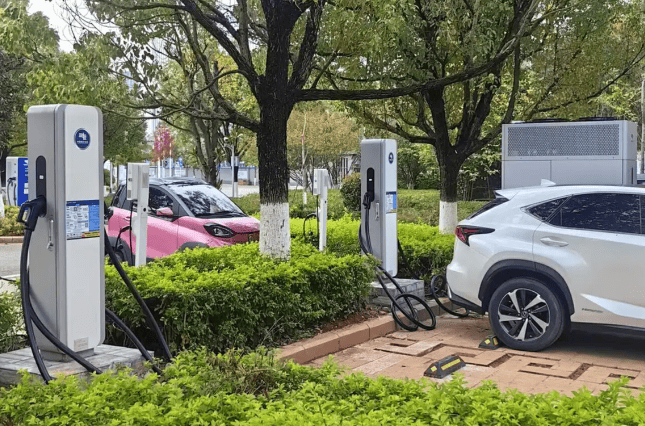
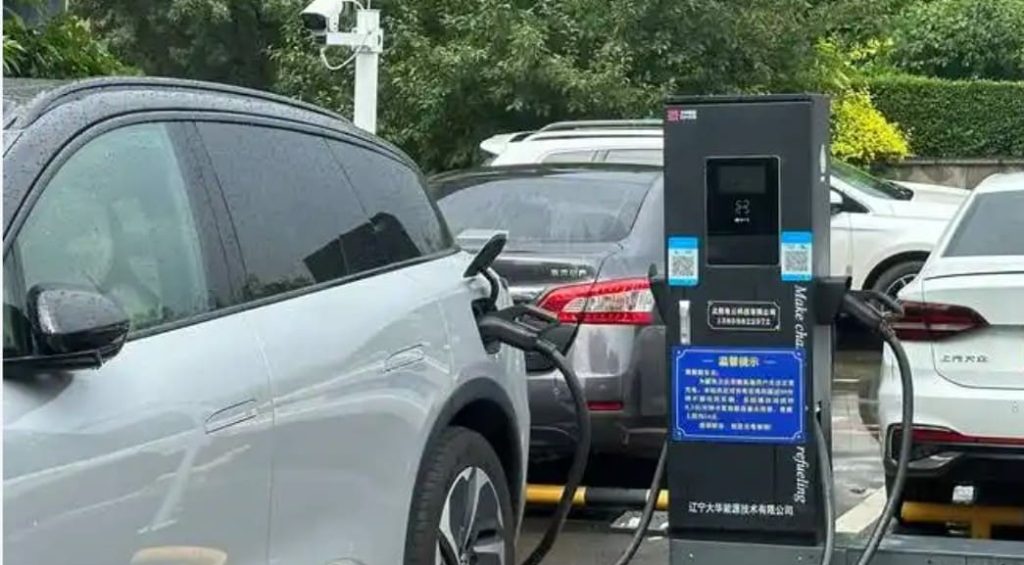
Applications of slow ev charger
Slow EV chargers, also known as Level 1 chargers, offer a lower charging power compared to fast chargers (Level 2 and DC fast chargers). Despite their lower speed, slow EV chargers serve essential applications:
While slow EV chargers may take longer to charge a vehicle fully, they play a crucial role in expanding the charging network and encouraging electric vehicle usage in various settings.
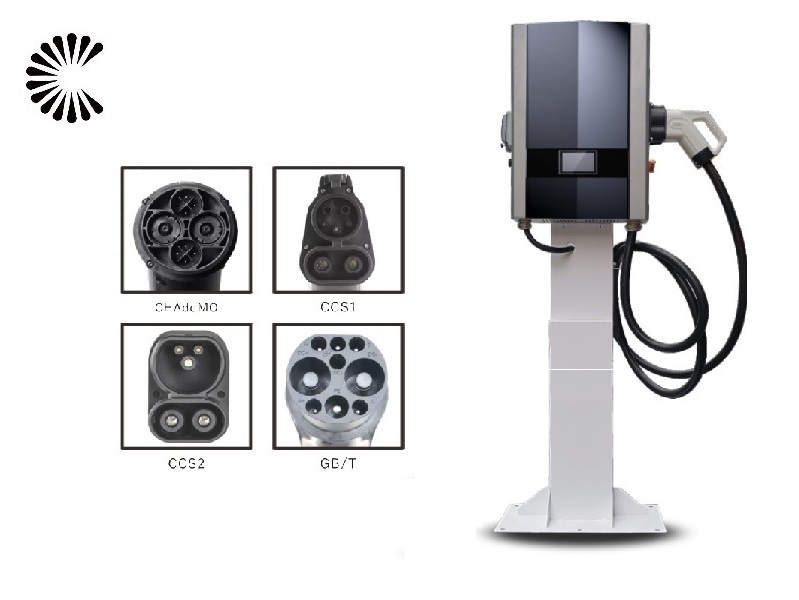
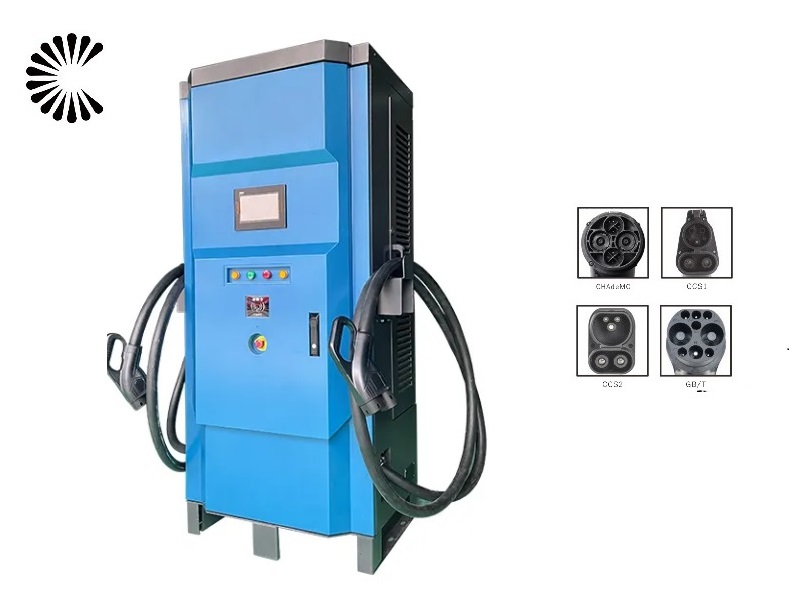
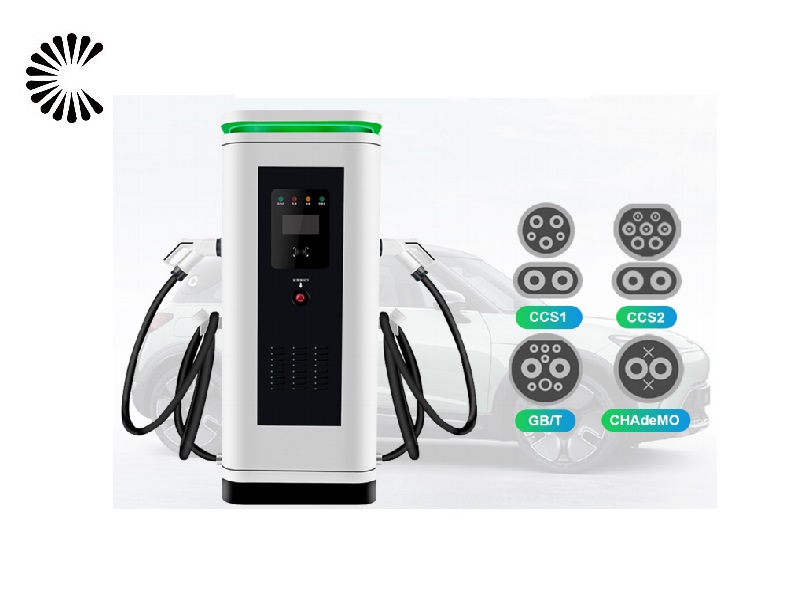
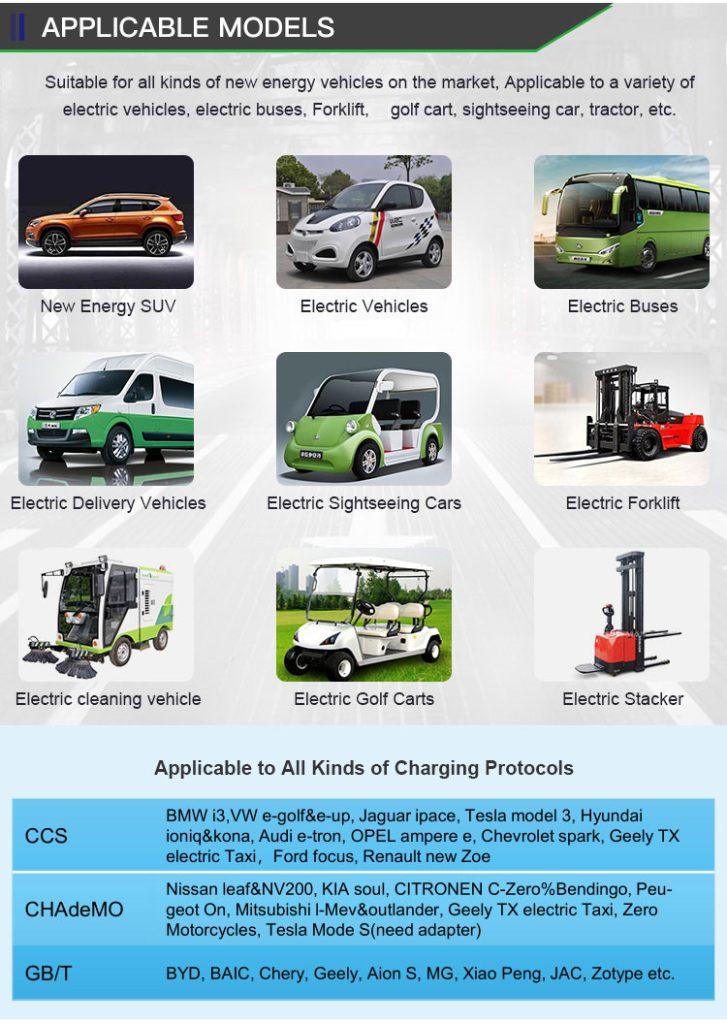
It is appplicable for all kinds of charing protocols, Suitable for all kinds of new energy vehicles on the market,Applicable to a variety of electric vehicles, electric buses,Forklift,golf cartsightseeing cartractor, etc.
| CHAdeMO | Nissan leaf&NV200, KIA soul, CITRONEN C-Zero%Bendingo, Peu geot On, Mitsubishi l-Mev&outlander, Geely TX electric Taxi,Zero Motorcycles, Tesla Mode S(need adapter) |
| CCS | BMW i3,VW e-golf&e-up, Jaguar ipace, Tesla model 3, Hyundai ioniq&kona, Audi e-tron, OPEL ampere e, Chevrolet spark, Geely TX electric Taxi,Ford focus, Renault new Zoe |
| GB/T | BYD, BAIC,Chery, Geely, Aion S, MG, Xiao Peng, JAC, Zotype etc. |
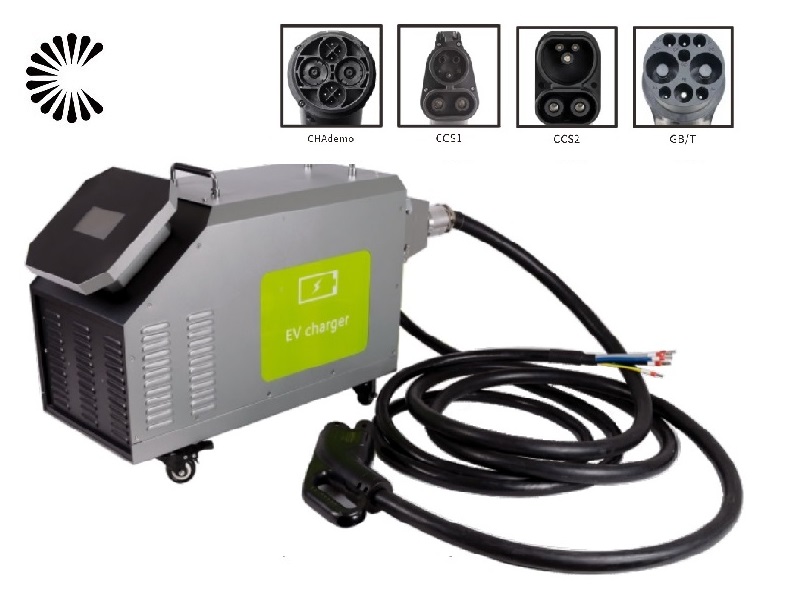
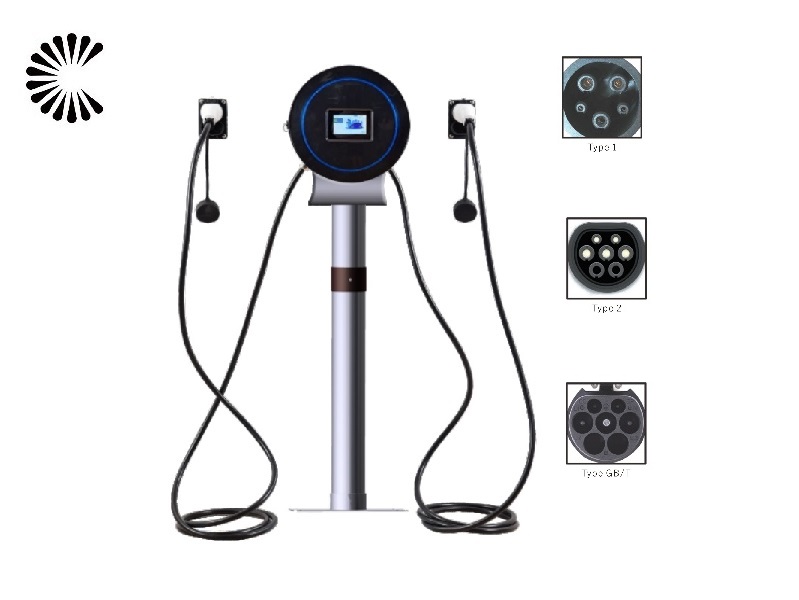
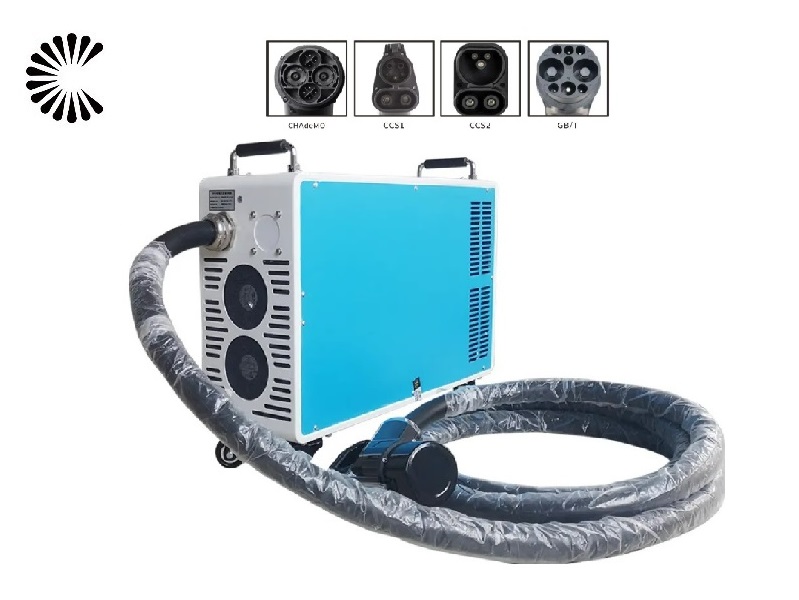
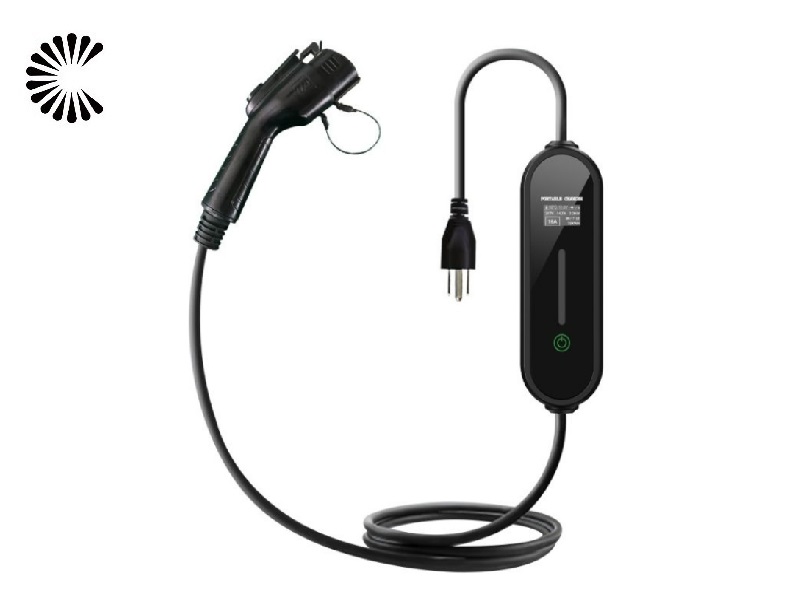
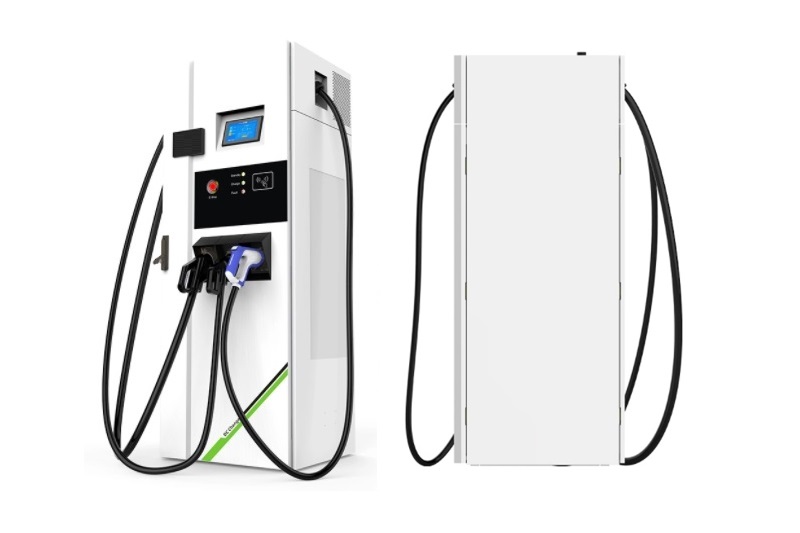
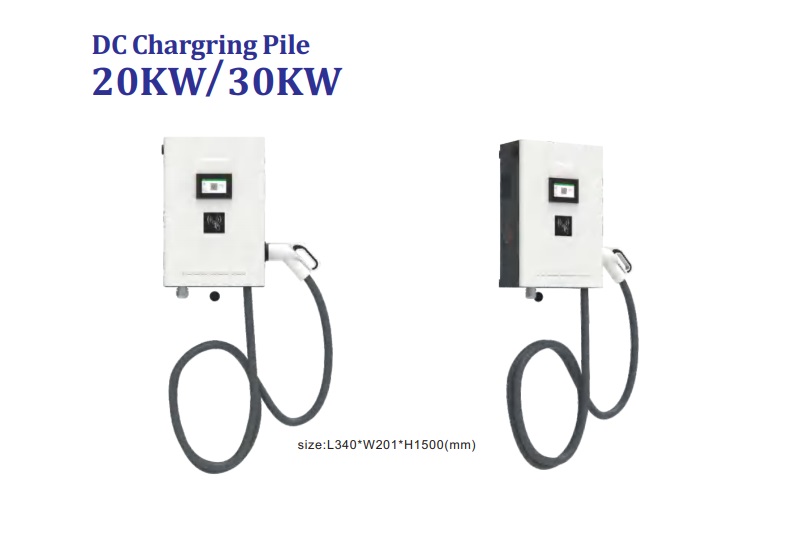
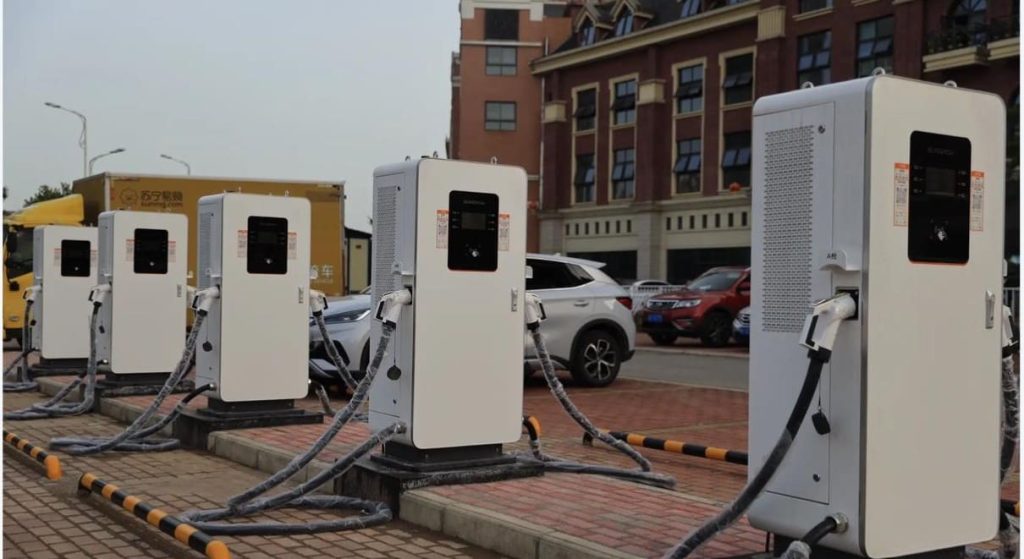
Slow EV Charger Wholesale Manufacturer In China
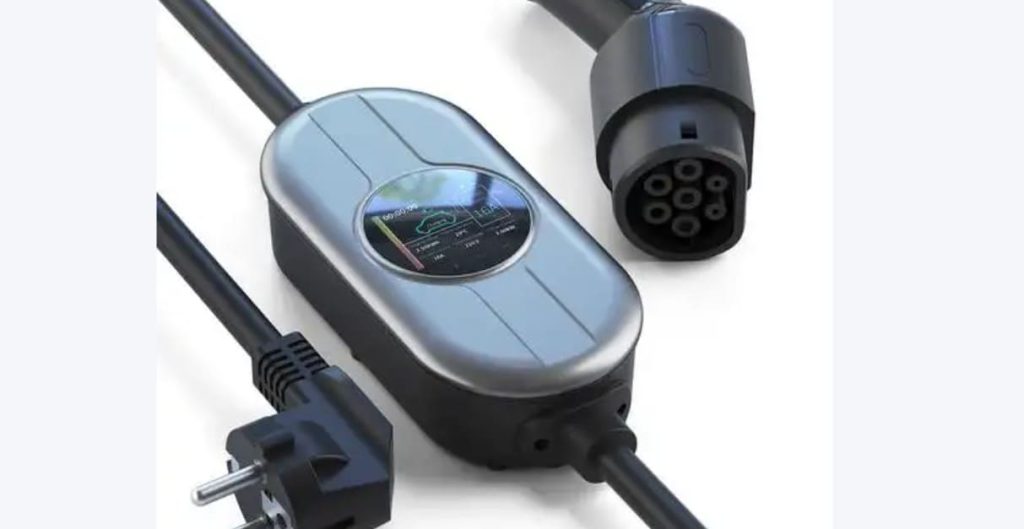
A slow EV charger, also known as a Level 1 charger, is a type of electric vehicle (EV) charger that provides a lower charging rate compared to other chargers. It is typically used in residential settings or locations where a faster charging speed is not necessary or readily available. Slow EV Charger is designed to be convenient and accessible for EV owners who primarily charge their vehicles overnight or during extended periods of parking
Slow EV Charger for Sale (Click to Get the Price List):
Contact Us
Frequently Asked Questions (Click for More RFQ)
-
Are you a factory or trading company?
For over two decades, we have proudly served as a leading and reputable manufacturer specializing in innovative and sustainable energy applications. With our expertise and commitment to excellence, we have been at the forefront of the industry, delivering cutting-edge solutions to meet the ever-evolving needs of our customers. Our extensive experience in this field enables us to provide you with the highest quality products and services. We are dedicated to creating a positive impact on the environment through our sustainable energy solutions, and we look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and success in the years to come.
-
What is the warranty?
Our products are covered by a comprehensive 12-month warranty period. During this time, we are dedicated to providing exceptional technical support and will replace any faulty parts at no cost to you. However, please note that while we take care of the replacement parts, customers are responsible for the delivery charges. Rest assured, we stand by the quality of our products and are committed to ensuring your satisfaction throughout the warranty period. If you encounter any issues or have any warranty-related inquiries, our dedicated team is ready to assist you promptly. Your trust in us is paramount, and we look forward to providing you with a reliable and hassle-free warranty service.
-
What is the packing method?
As a standard practice, our goods are carefully packed in brown cartons to ensure their safety during transit. However, if you hold a legally registered patent, we are delighted to accommodate your branding requirements. Upon receiving your authorization letters, we will be more than happy to pack the goods in your branded boxes. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we are committed to providing a customized packaging solution that aligns with your brand’s identity. Should you have any further questions or special requests regarding packaging, please feel free to share them with us. We look forward to meeting your packaging needs and delivering a seamless experience.
-
What is your terms of payment?
For your convenience, our payment terms are as follows: 50% deposit via T/T (Telegraphic Transfer) before production begins, and the remaining 50% is due before delivery. To ensure transparency and your complete satisfaction, we will provide you with photos of the products and packaging once the order is ready. This way, you can review the items before making the final payment. If you have any queries or require further information about our payment process, our dedicated team is here to assist you. Your trust in us is essential, and we are committed to delivering a seamless and reliable payment experience.
-
What is your terms of trade?
We offer a comprehensive range of trade terms to cater to your specific needs. Our available trade terms include EXW (Ex Works), FOB (Free on Board), CFR (Cost and Freight), CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), DAP (Delivered at Place), DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid), and DDP (Delivered Duty Paid). Each option is designed to provide flexibility and convenience for our valued customers. If you have any questions or require further clarification regarding our trade terms, please don’t hesitate to reach out to our dedicated team. We are committed to providing you with a seamless and satisfying trading experience.
-
How about your delivery time?
Typically, our standard delivery time ranges from 3 to 7 working days after receiving your advance payment. However, please note that the specific delivery schedule may vary depending on the items you’ve ordered and the quantity of your order. Rest assured, we are committed to processing your order efficiently and ensuring a prompt delivery. Should you have any further inquiries or need more precise delivery information, our dedicated team is here to assist you every step of the way. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we look forward to fulfilling your order with utmost care and timeliness.
-
Can you produce according to the samples?
Yes, whether you provide us with samples or technical drawings, we have the capability to produce the desired product. Our skilled team can build custom molds and fixtures to meet your specific requirements. Rest assured, we are fully equipped to bring your vision to life with precision and quality. If you have any specific details or special requests, feel free to share them with us. We take pride in our ability to deliver exceptional results, and we are excited to work with you on this project.
-
What is your sample policy?
We are pleased to offer samples for products with ready parts in stock. Please note that while we provide the samples, customers are kindly requested to cover both the sample cost and the courier cost. This ensures that you can evaluate the product’s quality and suitability before making a purchase. If you have any further questions or require assistance, our dedicated team is ready to help. Your satisfaction is our priority, and we look forward to providing you with the best possible service.
-
Do you test all your goods before delivery?
Absolutely!, we have 100% test before delivery. We ensuring the quality and reliability of our goods is our top priority. Before delivery, each product undergoes rigorous testing and quality checks to meet our high standards. We take pride in delivering only the best products to our valued customers. You can rest assured that your purchase will be thoroughly inspected and meet all necessary requirements before it reaches your hands. If you ever encounter any issues with our product, our dedicated customer support team is here to assist you promptly. Your satisfaction is essential to us, and we stand behind the quality of our goods wholeheartedly.
-
How does a car wall charger work?
A car wall charger, also known as an electric vehicle (EV) charger or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), is used to charge the battery of an electric vehicle when it is parked at a location with access to an electrical power source. Here’s how a typical car wall charger works:
Electricity Supply: The car wall charger is connected to an electrical power source, usually a household outlet (Level 1 charger) or a dedicated circuit or charging station (Level 2 charger). Level 1 chargers typically plug into a standard 120-volt household outlet, while Level 2 chargers require a 240-volt circuit, which can charge the vehicle faster.
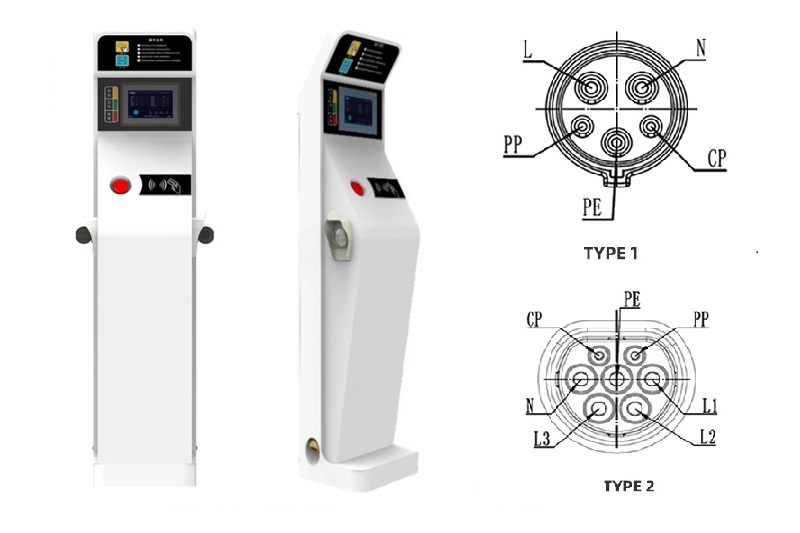
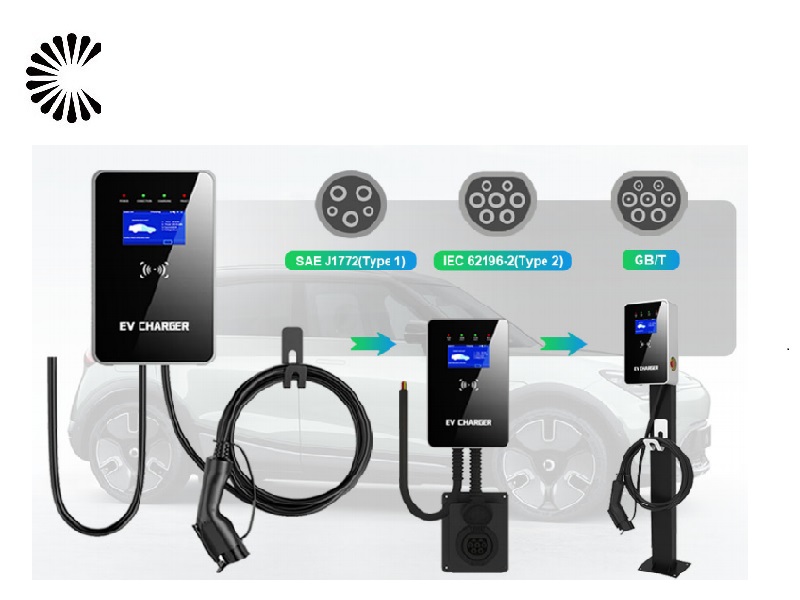
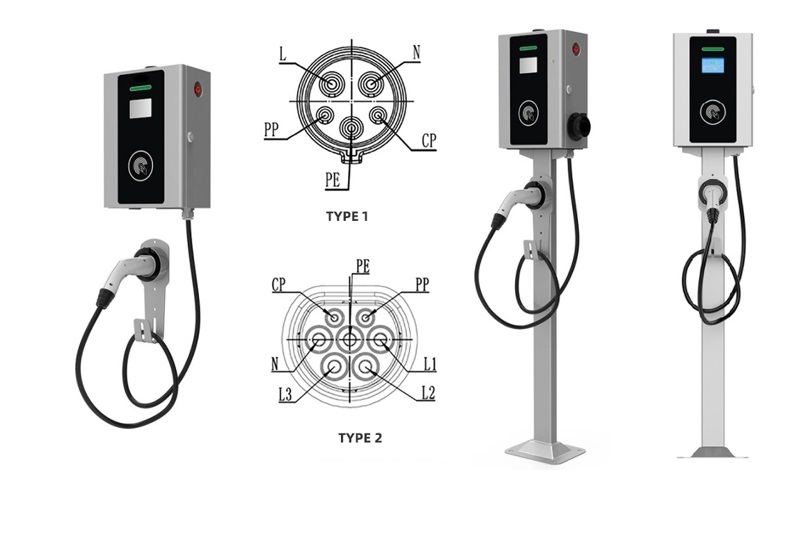
Charging Cable: The car wall charger is equipped with a charging cable that connects to the electric vehicle’s charging port. The cable has connectors that match the specific charging port type of the vehicle, such as Type 1 (J1772) or Type 2 (Mennekes).
Communication Protocol: The charger communicates with the electric vehicle through a standardized communication protocol like the J1772 or Combined Charging System (CCS) protocol. This communication allows the charger to negotiate the charging rate and ensure the safety and compatibility of the charging process.
Safety Measures: Car wall chargers have safety features built in to protect both the vehicle and the charger. These may include ground fault protection, overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and thermal protection to prevent overheating.
Charging Process: Once the car wall charger is connected and communication is established between the charger and the vehicle, the charging process begins. The charger supplies the appropriate electrical current to the vehicle’s battery to charge it.
Charging Level: The charging level depends on the capacity of the charger and the capabilities of the vehicle. Level 1 chargers generally provide slower charging rates, while Level 2 chargers offer faster charging. Level 3 chargers (DC fast chargers) are even faster but require specialized charging infrastructure.
Charging Status: Some car wall chargers have LED indicators or displays to show the charging status, including whether the vehicle is charging, fully charged, or if there are any issues during the charging process.
Completion and Disconnect: Once the vehicle’s battery is fully charged or reaches the desired charge level, the charger stops the flow of electricity, and the charging session is completed. The user can then disconnect the charging cable from the vehicle’s charging port.
Overall, car wall chargers provide a convenient and safe way to charge electric vehicles, helping to promote the adoption of electric mobility and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. -
What does a wallbox charger do?
A wallbox charger is a device that you can install on your home’s wall or garage to charge an electric car. It works like a special power outlet specifically designed for electric vehicles. When you plug your electric car into the wallbox charger, it provides the electricity needed to charge the car’s battery.
Imagine it like plugging your phone into a charger, but instead of a small phone, you’re connecting a big electric car. The wallbox charger is faster and more efficient than charging your car from a regular household outlet. It helps make sure your car’s battery is ready to go for your next drive, just like how you charge your phone overnight to have it fully charged in the morning. It’s a convenient and practical way to charge your electric vehicle at home, so you can enjoy the benefits of electric driving without worrying about finding public charging stations. -
What is the car charging plug called?
The car charging plug is commonly referred to as an “EV charging connector” or simply a “charging plug.” It is the part of the electric vehicle charging cable that connects to the car’s charging port. The specific name of the plug can vary depending on the type of connector used by the vehicle and the charging station. Some common names for different types of charging plugs include Type 1 (J1772), Type 2 (Mennekes), CHAdeMO, and CCS (Combined Charging System). Each of these connectors is designed to fit different electric vehicle models and specific charging infrastructure standards.
-
What is a slow EV charger?
A slow EV charger is a type of electric vehicle (EV) charging station that takes a longer time to fully charge an electric car compared to other types of chargers. When you plug in your EV to a slow charger, it will deliver a lower amount of electric power to your vehicle’s battery, resulting in a slower charging rate.
Unlike faster chargers, such as fast chargers or rapid chargers, which can charge an EV relatively quickly, slow chargers are designed for more convenient and slower charging sessions, typically ideal for overnight charging at home or in places where the car will be parked for an extended period.
While slow chargers may not be as quick as faster options, they can still be useful for EV owners who don’t need an immediate full charge and want to charge their vehicles over an extended period, avoiding the need for more powerful and expensive charging infrastructure. -
Why is EV charger so slow?
EV chargers can be slow for several reasons, using human language to explain at an English Level 6:
Power limitations: Some charging stations, especially slow chargers found in homes or public areas, may have limited power capacity. They are designed to handle lower amounts of electric power, which means they cannot deliver a higher rate of charging to the electric vehicle’s battery. Faster chargers, on the other hand, are built with more substantial power capabilities, allowing for quicker charging.
Safety concerns: Slower charging can be implemented to minimize the risk of overheating or damaging the EV’s battery. Faster charging generates more heat, and if not managed properly, it could lead to safety issues. Slow chargers prioritize safety and ensure a more controlled and stable charging process.
Cost and infrastructure: Building fast-charging infrastructure can be more expensive and requires more advanced technology. Slow chargers are more cost-effective and easier to install, making them a more viable option for homes, small businesses, and areas with limited resources.
Battery health: Some electric vehicle batteries can handle faster charging, while others may experience increased wear and tear with rapid charging. Slow chargers are gentler on the battery, which can help prolong its overall lifespan and maintain better long-term performance.
Usage patterns: Slow chargers are commonly found in places where cars are parked for more extended periods, such as residential areas or workplaces. Since the vehicles are not expected to be fully charged quickly, the slower charging rate is sufficient for these situations.
It’s essential to have a variety of charging options available, including both slow and fast chargers, to cater to different EV owners’ needs and make charging convenient for everyone. As technology advances and electric vehicle adoption grows, we can expect to see more improvements in charging speed and efficiency. -
Is slower charging better for EV?
Slower charging can be better for an electric vehicle (EV) in certain situations, using human language to explain at an English Level 6:
Battery health: Slower charging tends to be gentler on the EV’s battery. Rapid charging generates more heat, which can put additional stress on the battery cells. Slower charging allows the battery to stay cooler, which can help extend its overall lifespan and maintain better long-term performance.
Safer charging: Slow charging is generally considered safer as it reduces the risk of overheating or damaging the battery. Faster charging requires sophisticated thermal management systems to handle the increased heat generated during the charging process. Slower charging provides a more controlled and stable charging experience, minimizing potential safety concerns.
Charging at home: For many EV owners who charge their vehicles at home overnight, slower charging is more than sufficient. Since they don’t need a quick full charge while they sleep, slow charging offers a convenient and practical way to keep their EVs charged without placing unnecessary stress on the battery.
Cost-effective: Slow chargers are typically less expensive to install and operate than fast chargers. They require less complex technology and infrastructure, making them a more economical option for homes, workplaces, and places where vehicles are parked for extended periods.
However, it’s essential to note that slower charging may not always be ideal for every situation. In some instances where drivers need to charge their EV quickly for a long journey or in busy public charging stations, faster chargers like rapid chargers or fast chargers are more appropriate.
Ultimately, the choice between slower or faster charging depends on individual needs and preferences. Having a mix of charging options available allows EV owners to choose the best charging solution based on their specific circumstances and requirements. -
How long does it take to charge an EV with a slow charger?
The time it takes to charge an electric vehicle (EV) with a slow charger can vary depending on the size of the EV’s battery, the charging rate of the specific charger, and how much charge the battery needs. Generally, slow chargers have a charging rate of around 3 to 6 kilowatts (kW), which is slower than fast or rapid chargers.
To give you an idea, let’s consider an example: If we assume a typical electric car has a battery capacity of 40 kilowatt-hours (kWh) and we’re using a 6 kW slow charger:
Charging from 0% to 80%: It might take approximately 6 to 7 hours to charge the battery from completely empty to 80% full. During this time, the charging rate gradually slows down as the battery approaches 80% to protect its health.
Charging from 80% to 100%: The last 20% of the battery might take an additional 2 to 3 hours, as charging slows down further when nearing 100%.
So, in total, using a slow charger, it could take around 8 to 10 hours to fully charge the battery from 0% to 100%.
It’s important to remember that these times are approximate estimates, and actual charging times may vary based on the EV model, battery condition, and other factors. Additionally, some newer EV models may have larger batteries, which could take longer to charge using a slow charger.
For faster charging times, drivers can opt for fast chargers or rapid chargers, which deliver higher power and can charge an EV more quickly.