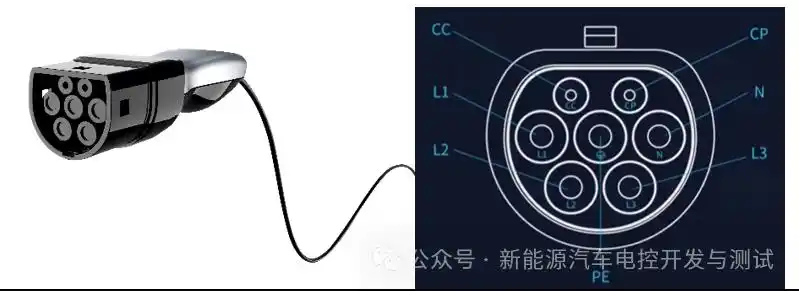
Can I have a 7kW charger at home?
Can I Have a 7kW Charger at Home? Absolutely, You Can Install a 7kW Charger at Home!
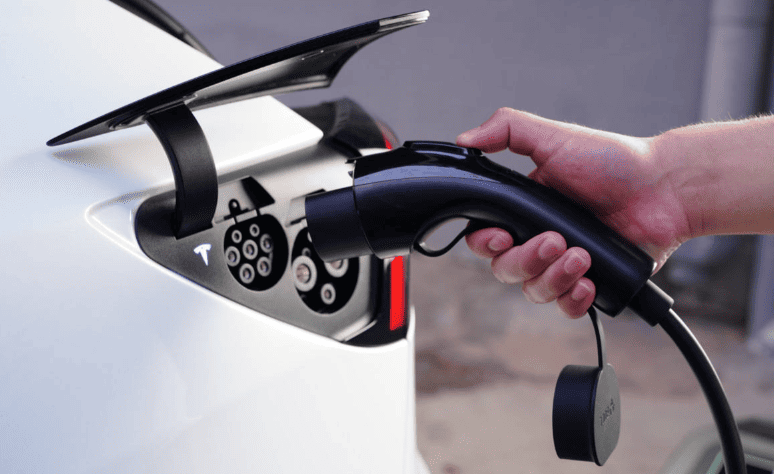
Yes, you absolutely can install a 7kW charger (also commonly called a home EV charger or EVSE) at your house. With a great balance between charging speed and compatibility with standard residential electrical systems, this power level is among the most widely used and sensible options for home charging. It makes daily driving effortless by enabling you to conveniently recharge your electric vehicle’s battery overnight, much like you would with a phone charge. However, installing one safely and successfully necessitates careful planning and preparation to make sure the electrical system and physical layout of your particular home can support it. It takes more than just purchasing a device and plugging it in; certain technical and safety requirements must be met.
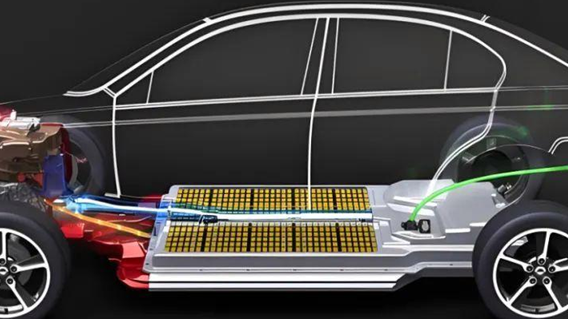
The most fundamental consideration is your home’s electrical capacity. A 7kW charger operates on a standard 240-volt single-phase AC supply, which is common in homes globally (like North America’s split-phase or Europe/UK/Asia’s single-phase). Using the power formula (Power = Voltage x Current), a 7kW charger draws approximately 32 Amps (7000W / 230V ≈ 30.4A; 7000W / 240V ≈ 29.2A – commonly referred to as a 32A charger). Your main household electrical panel and service must have sufficient spare capacity to accommodate this significant new load without overloading the system. If your total household electrical service is relatively low (e.g., 60A or 100A), adding a continuous 32A load, especially when combined with other high-power appliances like air conditioners, electric ovens, or clothes dryers running simultaneously, can easily trip the main breaker. An electrician needs to assess your panel’s current load and total capacity. You might need to upgrade your main service panel or rearrange circuits to free up capacity. Crucially, the dedicated circuit for the charger itself must be correctly sized. This means installing a new circuit breaker in your panel rated appropriately for the charger (typically 40A for a continuous 32A load, following electrical codes like the 80% rule) and running new wiring from the panel directly to the charger location. This wiring must be of the correct gauge to handle 32A safely over the distance; typically, this requires at least 6mm² (or 10 AWG in North America) high-quality copper cable. Using undersized or poor-quality wire creates significant fire hazards due to overheating. Furthermore, this dedicated circuit must include proper grounding and ideally, residual-current protection (RCD/GFCI) for safety, mandated in many regions. Ensuring your home’s wiring is modern and capable is the non-negotiable first step.
Beyond the main panel capacity, the physical installation location and space requirements are vital for safety, convenience, and longevity of the charger. You need a suitable spot, most commonly on a wall in your garage or mounted on an external wall near your driveway or dedicated parking spot. This location must be within reach of your vehicle’s charging port when parked normally, considering the length of the charging cable (typically 5-7 meters). Adequate clearance around the unit is essential: allow at least 1-2 meters in front for easy access to the connector and maneuvering, plus sufficient space on the sides and rear (often 30-50cm minimum) for ventilation and potential maintenance access. Chargers generate heat during operation, so good airflow is critical. Installing one in a tightly enclosed, unventilated space is a serious fire risk and can cause the charger to malfunction or shut down. For outdoor installations, which are very common, the charger unit must have a suitable weatherproof rating – look for an IP (Ingress Protection) rating of at least IP54, which signifies protection against dust ingress and water splashes from any direction. Avoid locations prone to flooding, deep standing water, or areas where heavy rain or snow directly impacts the unit. The mounting surface needs to be sturdy enough to support the weight of the charger and the occasional force applied when plugging/unplugging the cable. Planning this location carefully, considering both daily use and environmental factors, prevents future headaches and hazards.
Proper grounding is not optional; it’s a critical safety lifeline for any electrical equipment, especially high-power devices like EV chargers. A robust grounding system provides a safe path for fault currents to travel directly to the earth if something goes wrong internally within the charger or the vehicle (like a live wire touching the casing). This prevents the metal parts of the charger or your car from becoming dangerously energized, protecting you from severe or fatal electric shock. The electrical regulations in your area will specify the exact requirements, but a common standard is that the grounding resistance should be 4 ohms or less. Achieving this often requires driving a dedicated grounding rod near the charger location and connecting it to the charger’s grounding terminal with appropriately sized copper wire. Crucially, this grounding connection must be extremely secure – loose or corroded connections are ineffective and dangerous. A qualified electrician will verify the grounding resistance using specialized test equipment as part of the installation. If you are installing in a location like an apartment car park or a detached garage with a sub-panel, ensuring a proper grounding path back to the main panel and/or local earth is essential. Never assume an existing pipe or structure provides adequate grounding; a dedicated, verified ground is mandatory for safe EV charging.
The type of electricity meter you use can significantly impact your charging costs. You can technically plug a 7kW charger into your existing household electricity supply using your standard residential meter. However, this is often the least economical way to charge your EV, especially if your utility uses tiered (increasing block) or time-of-use (TOU) pricing. Charging an EV adds a substantial amount of electricity consumption. On a standard residential tariff, charging overnight might push your total monthly consumption into higher, more expensive pricing tiers, inflating the cost of all your household electricity, not just the EV portion. Many utility companies now offer specific EV charging tariffs or dedicated EV meters. These meters are separate from your main household meter and are specifically for measuring the electricity used by your EV charger. The key advantage is that they typically offer significantly cheaper rates, especially during off-peak hours (like overnight). This separation ensures your high EV consumption doesn’t push your household usage into expensive tiers, and allows you to take full advantage of cheaper overnight rates solely for your car. Applying for a dedicated EV meter usually involves contacting your utility provider; there might be a small installation cost, but the long-term savings on your electricity bills are usually substantial and make it highly worthwhile. Using your existing meter is possible, but opting for a dedicated EV meter is a smarter financial decision.
Finally, don’t overlook the crucial step of obtaining necessary permissions before proceeding with installation. If you live in a single-family home with your own driveway/garage, this primarily involves checking local building codes or homeowner association (HOA) rules, if applicable. However, if you live in an apartment, condominium, or townhouse with shared parking, or even if your dedicated parking is part of a managed complex, obtaining permission from the property management company, landlord, or homeowners’ association (HOA/Strata) is essential. Some older buildings may have electrical systems with insufficient spare capacity to support adding EV chargers without significant (and expensive) upgrades. Management bodies might have rules concerning alterations to common property, aesthetic concerns, or liability issues. They may require specific installation standards, approved contractors, or proof of adequate insurance. Starting this conversation early is vital. Present a clear plan, potentially involving your chosen electrician, to address any concerns about safety, capacity, and installation methods. Be prepared to provide documentation and potentially involve the utility company in discussions about capacity. Securing written permission before purchasing equipment or scheduling installation prevents costly delays or rejections later.
In conclusion, installing a 7kW home charger is not only feasible but highly recommended for the convenience and speed it offers EV owners. A thorough preparation is essential for a successful installation. This includes carefully evaluating and possibly upgrading your home’s electrical capacity (panel, dedicated circuit, wiring), selecting a safe and practical installation location with enough space and ventilation, making sure your grounding system is reliable and verified, choosing a dedicated EV electricity meter for maximum cost savings, and obtaining all required permissions from property managers or appropriate authorities. When these requirements are satisfied, a professionally installed 7kW charger turns your house into your main refueling station and offers a safe, effective, and incredibly convenient way to keep your electric car ready for your daily trips.Remember, investing in a proper, certified installation by a qualified electrician is paramount for safety, reliability, and peace of mind for years to come.