ev charger vs 240v outlet
EV Charger vs. 240V Outlet: Powering Your Electric Journey
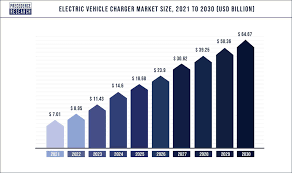
Central Thesis: Dedicated EV charging stations and standard 240V outlets differ significantly in charging speed, safety, cost-effectiveness, and ideal use cases, making the charger superior for most EV owners despite higher upfront costs.

Power and Charging Speed: The Race Against Time
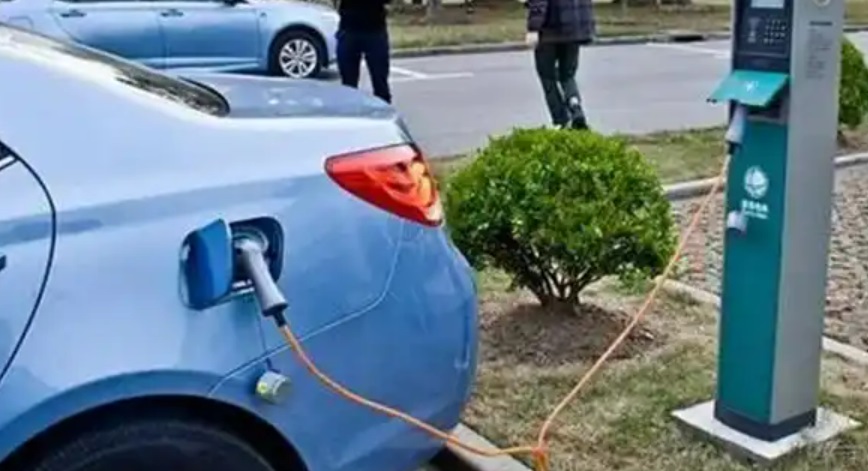
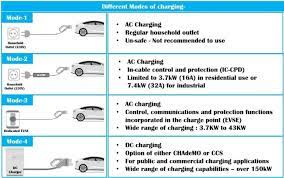
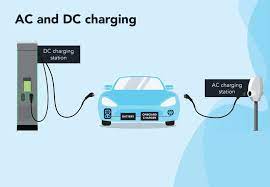
A standard 240V outlet (Level 2 charging) typically delivers 3.7–7.7 kW of power using a single-phase 32-amp circuit. This translates to adding 30–50 km (19–31 miles) of range per hour. For a common 60 kWh EV battery, a full charge can take 8–16 hours. This speed limitation exists because the car’s onboard charger must convert AC power from the outlet to DC power for the battery—a slower, less efficient process constrained by the vehicle’s internal hardware.
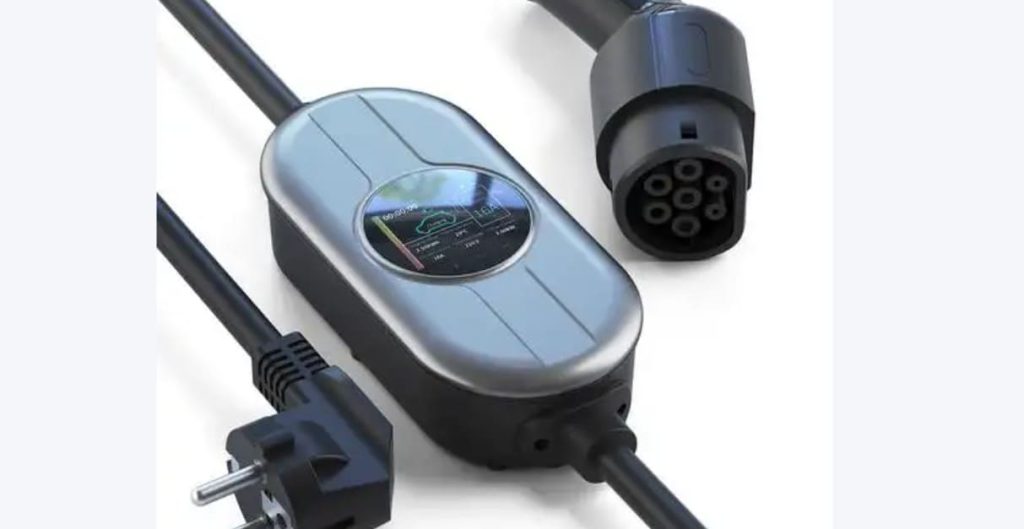
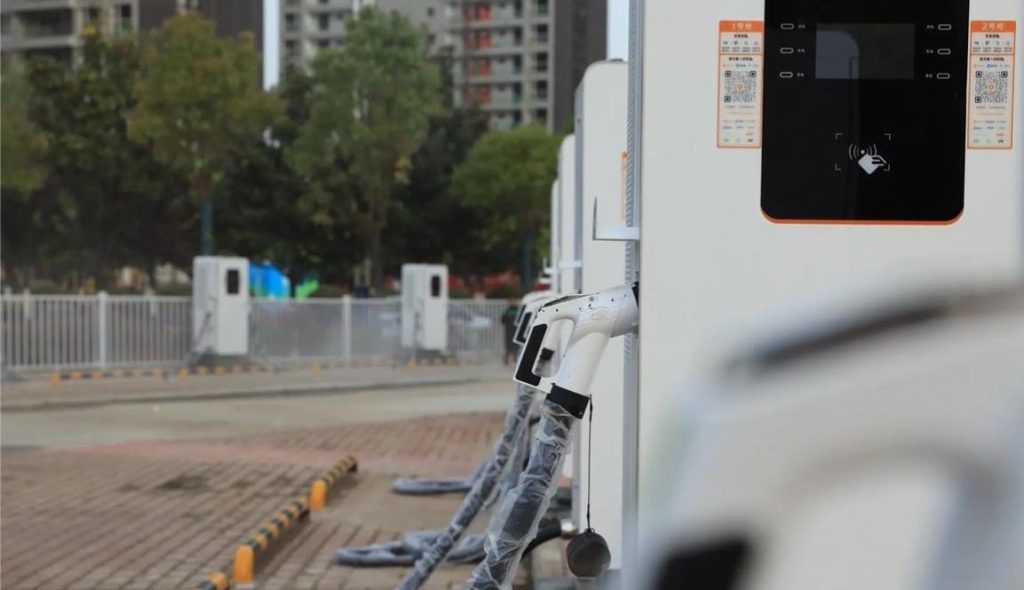
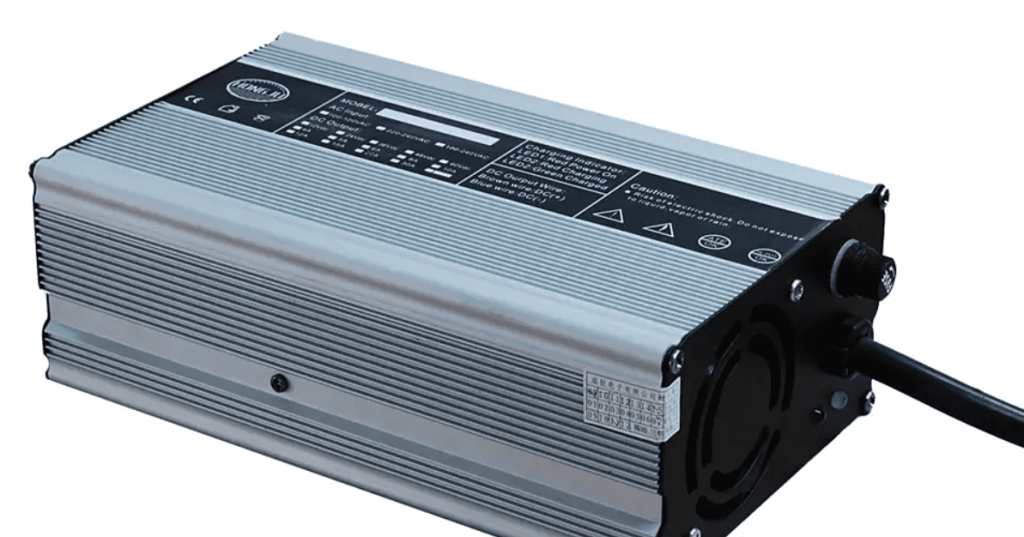
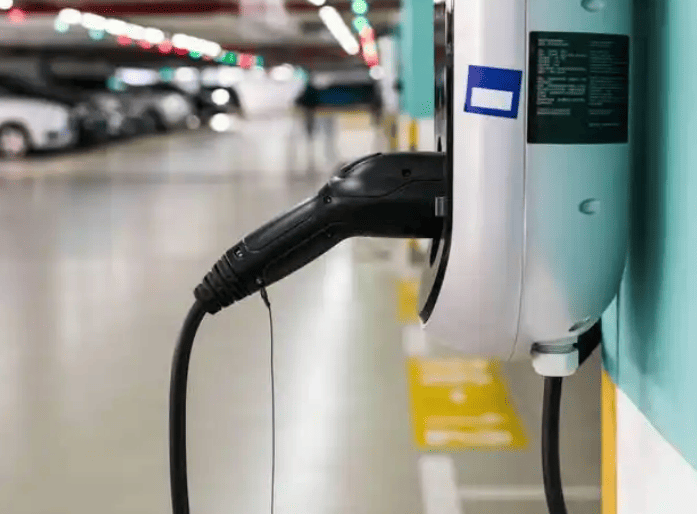
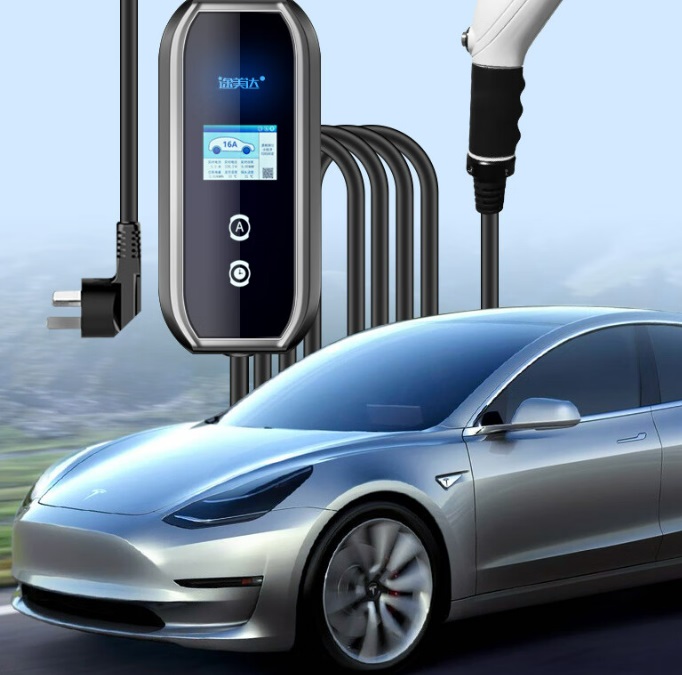
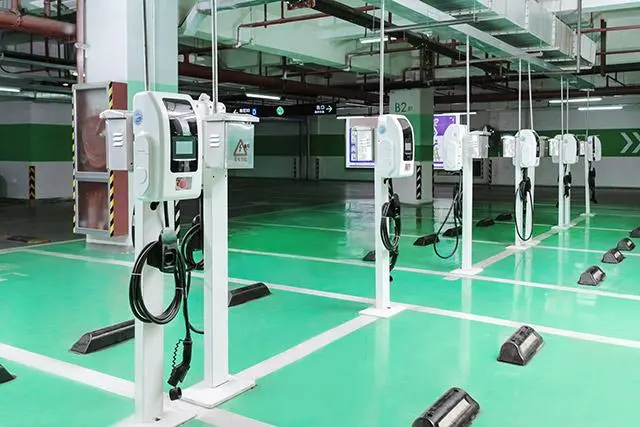
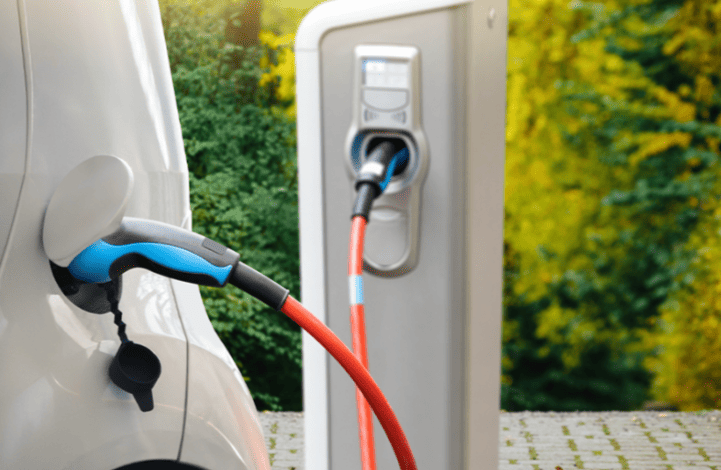
In contrast, dedicated EV charging stations unlock substantially higher power. AC chargers support up to 21 kW (three-phase 380V), cutting charging times by half compared to outlets. More crucially, DC fast chargers (public stations) operate at 50–350 kW, bypassing the car’s onboard converter to feed DC power directly to the battery. This enables rapid “refueling”—reaching 80% charge in just 30 minutes, ideal for road trips or urgent top-ups. While home DC chargers are rare due to grid demands, robust AC wallboxes drastically outperform standard outlets.
Safety and Durability: Built for the Long Haul
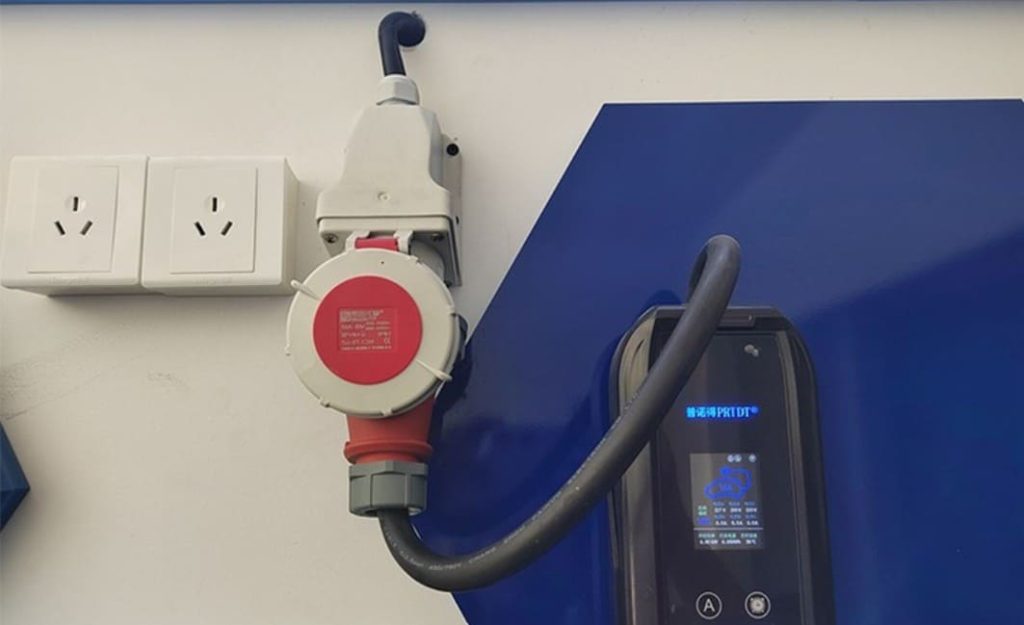
Regular EV charging at a 240V outlet comes with unstated risks. Although NEMA 14-50 plugs are frequently found in garages, they were not made to withstand the high loads (8+ hours) required for daily EV charging. Particularly in older homes with inadequate wiring, this can eventually result in overheating, melted sockets, or even electrical fires. To ensure safe use, a qualified electrician must check the circuit’s capacity and verify proper grounding, which is sometimes a neglected step.
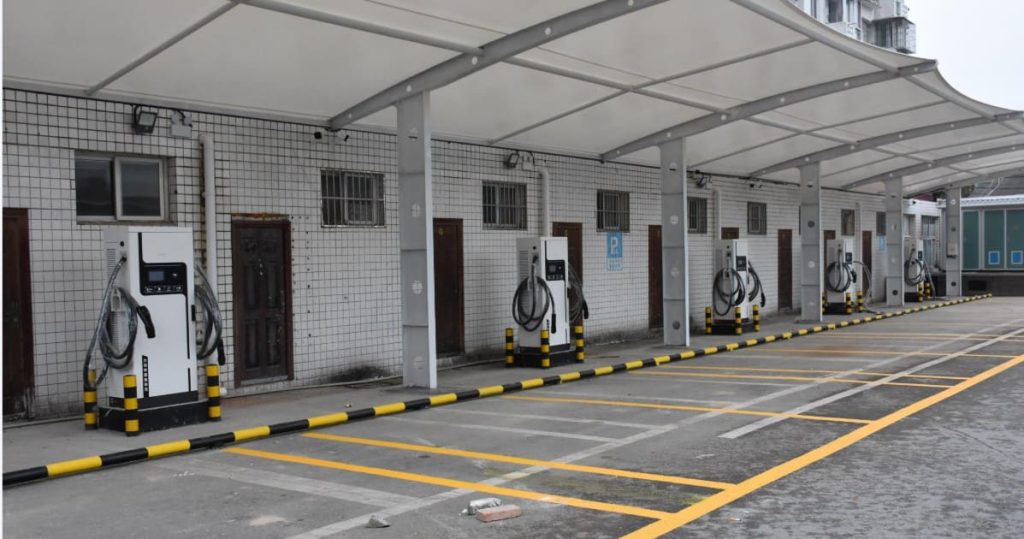
Using engineering of the highest caliber, EV charging stations put safety first. They have ground-fault protection, integrated temperature sensors to prevent charging if overheating happens, weatherproof enclosures (IP54 or higher for outdoor use), and automatic shutoffs during voltage fluctuations. Proper wiring, dedicated circuit breakers, and adherence to regional electrical codes are guaranteed by certified installers. For worry-free overnight charging, this “set-and-forget” dependability is essential.
Cost Analysis: Paying More Now to Save Later
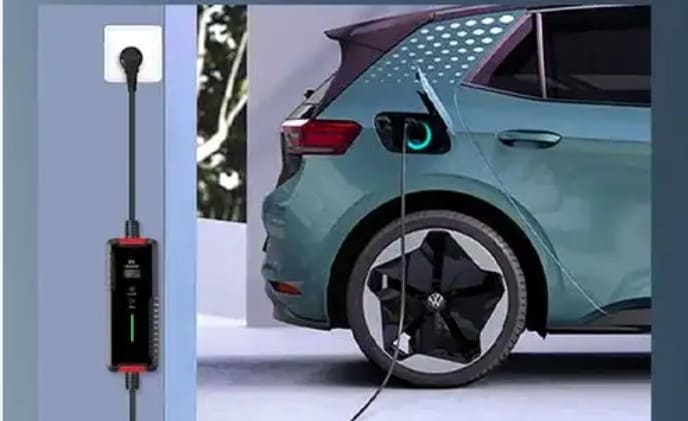
At first glance, a 240V outlet seems cheaper. If your home already has compatible wiring, you only need a $200–$500 portable charging cable. However, hidden expenses accumulate: public charging costs 2–3x more per kWh than home electricity, and slower charging wastes valuable time. For a driver covering 24,000 km annually, relying on public outlets can cost $1,200+ more per year compared to home charging.
Installing a dedicated charger involves higher upfront investment—typically $500–$2,000 for hardware and professional installation (including permits and wiring). Yet this pays dividends. Home chargers access off-peak electricity rates (as low as $0.03–$0.05/kWh overnight), slashing energy costs. As real-world cases show:
- Tesla owners save ~$1,280 annually
- BYD owners save ~$1,125 annually
With reduced public charging fees and battery longevity benefits (discussed later), most users recoup installation costs within 2–3 years.
Matching Chargers to Your Lifestyle
Choose a 240V outlet if:
- You’re a renter unable to install permanent hardware
- You drive a plug-in hybrid (smaller batteries charge fully overnight)
- You need occasional backup charging at remote locations
Invest in a charging station if:
- You own a battery-electric vehicle (BEV) requiring frequent charging
- Your daily driving exceeds 80 km (50 miles)
- You take regular road trips needing quick top-ups
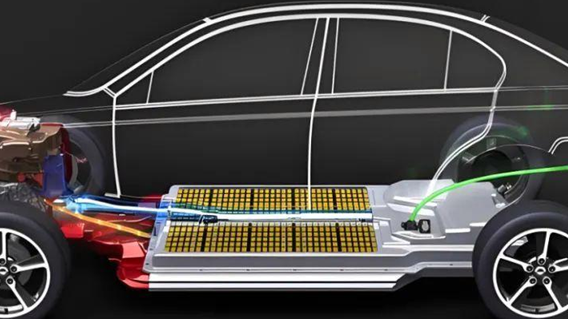
- You prioritize battery health (slow charging extends lifespan)
Compatibility and Future-Proofing
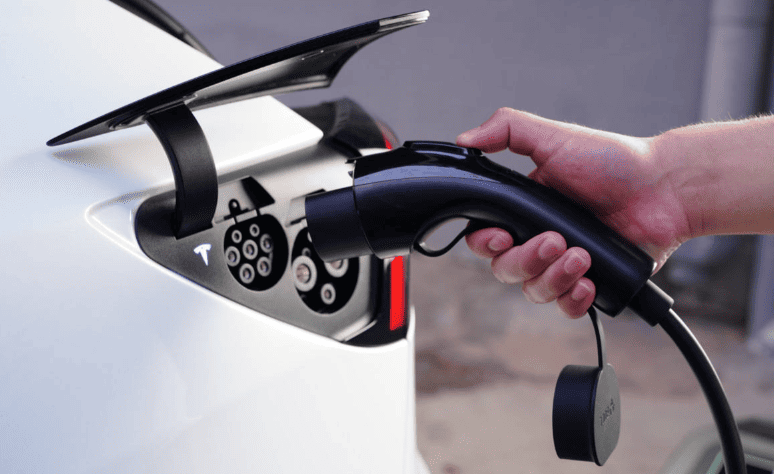
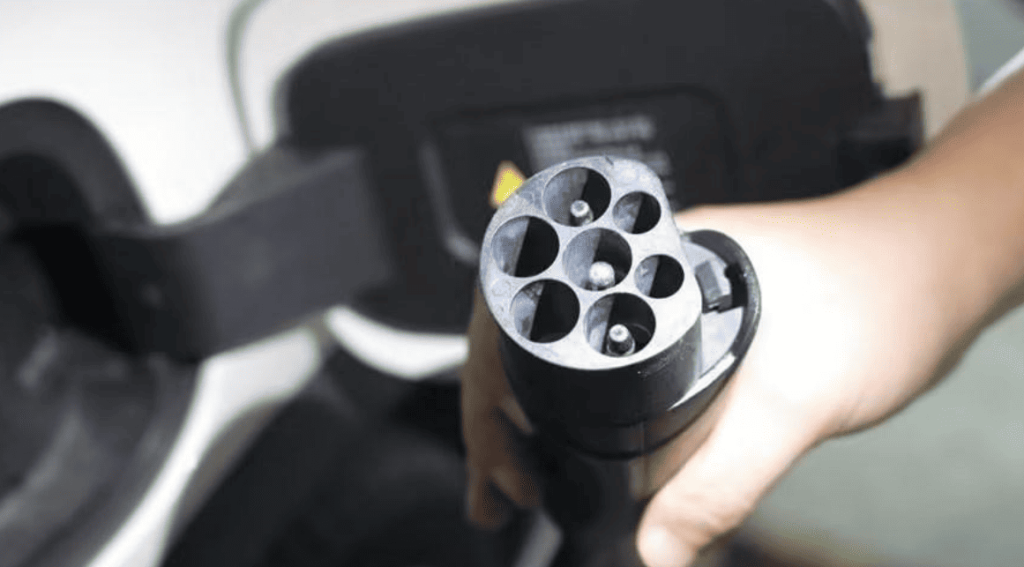
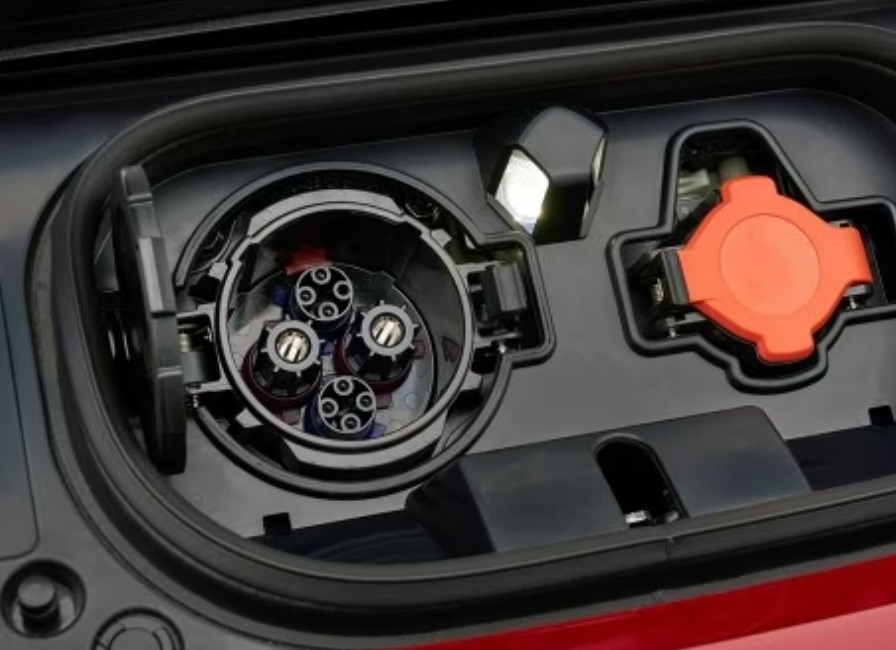
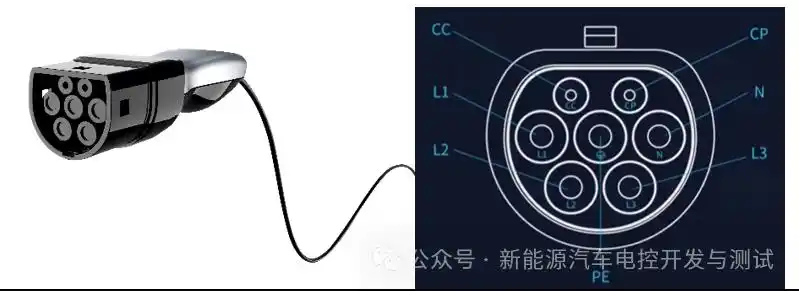
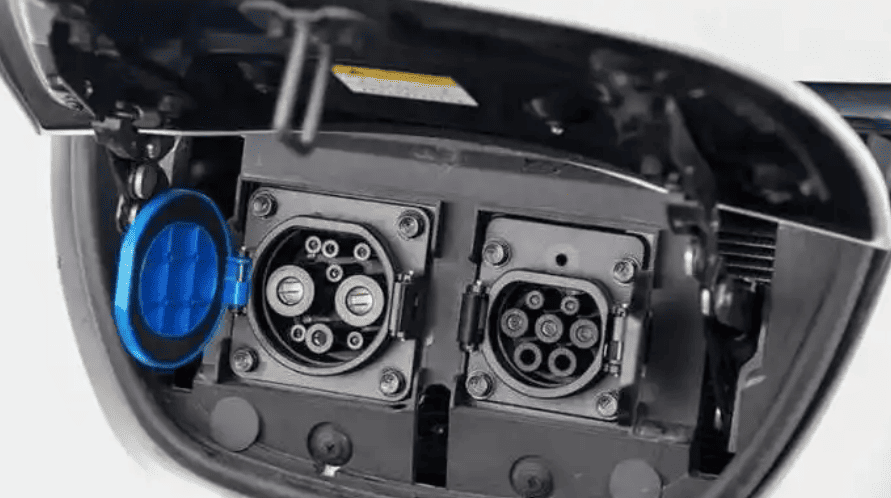
Generic sockets, such as NEMA 14-50 in North America, are used with standard 240V outlets. Despite their versatility, they are dependent on the cable that comes with your EV, which might not have any smart features. Vehicle-specific connectors such as Type 2 (Mennekes), CHAdeMO, Tesla NACS, and CCS (Combo) are used by charging stations. The role of the charging station in enabling next-generation EVs is highlighted by new standards such as China’s GB/T 20234.3-2023, which supports up to 1,000V DC charging. Before buying a charger, make sure the port type of your car is correct. For instance, Teslas frequently need adapters for third-party stations.
Conclusion: The Smart Charger Choice
Installing a specially designed home charging station is the best long-term option for committed EV owners, particularly BEV drivers. It promotes battery health while providing quicker, safer, and more cost-effective charging. Set aside 240V outlets for temporary setups or emergencies. Verify your electrical panel’s capacity (a 40–100 amp circuit is typical) and local regulations prior to installation. Purchasing a sturdy home charger guarantees that you’re ready for the electric future as EVs advance toward larger batteries and lightning-fast charging.