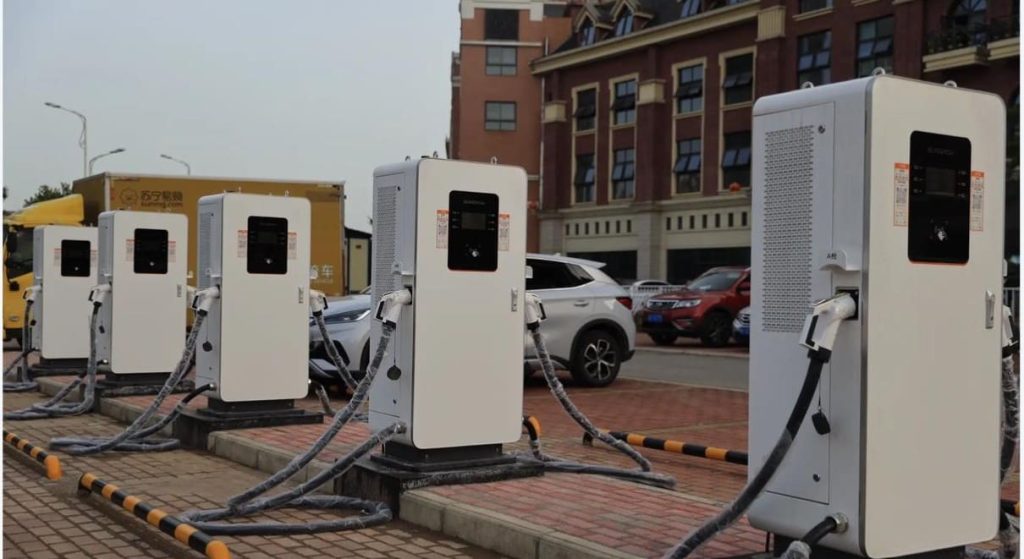
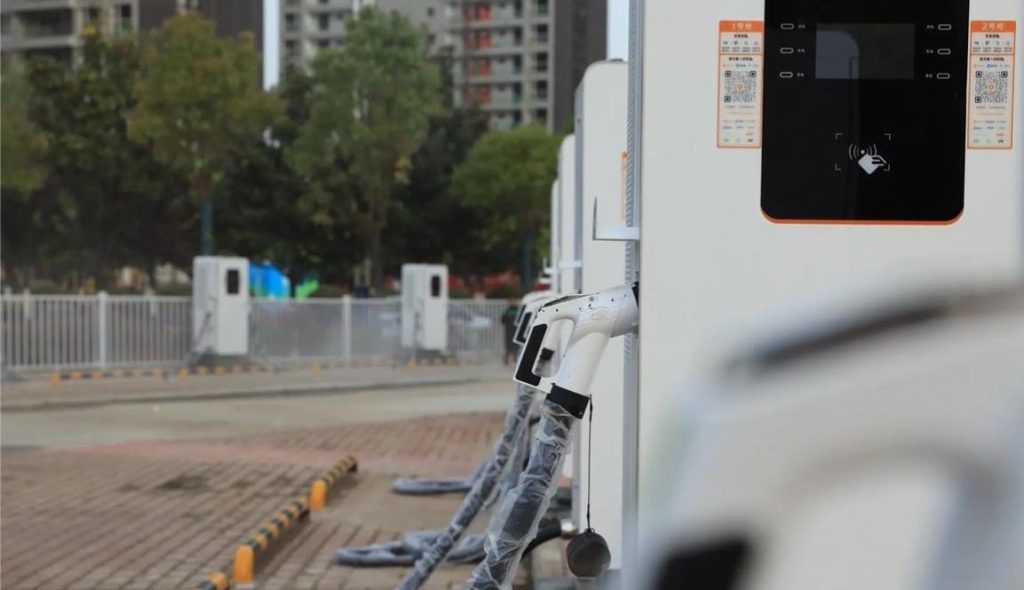
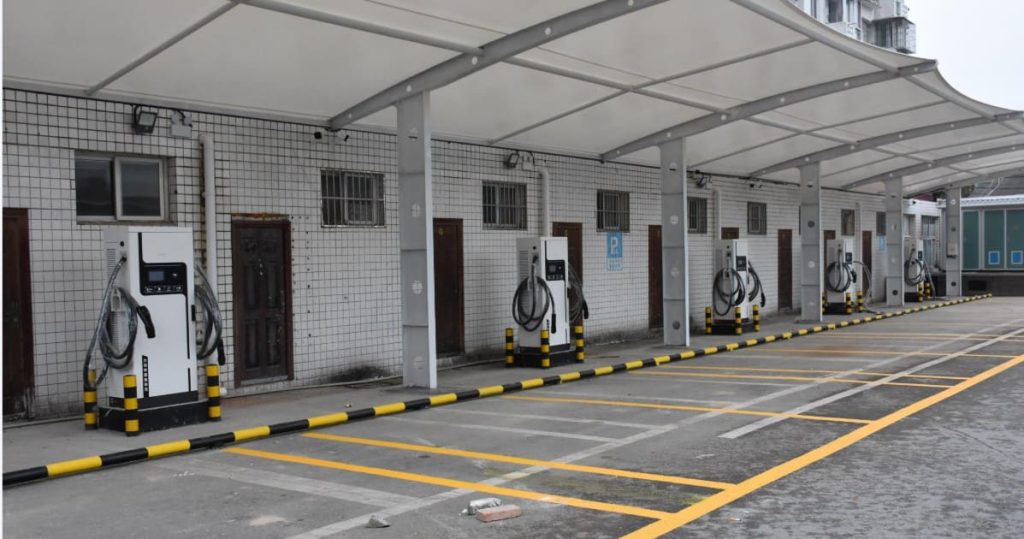
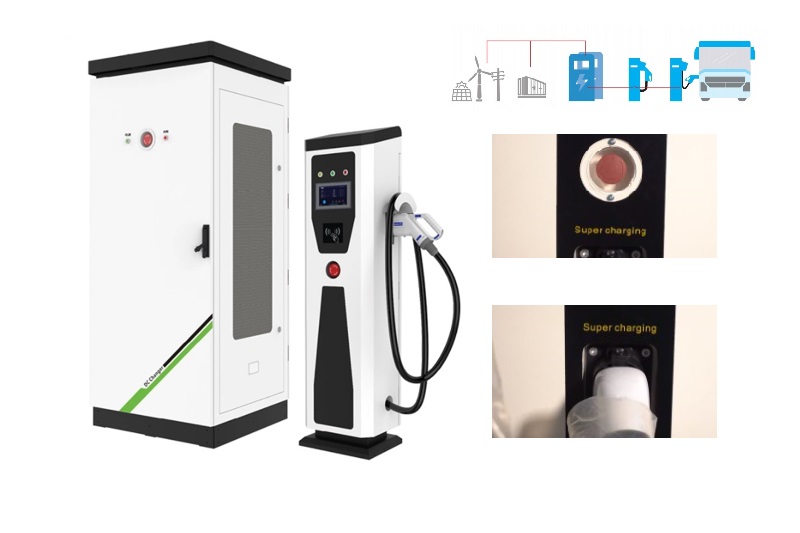
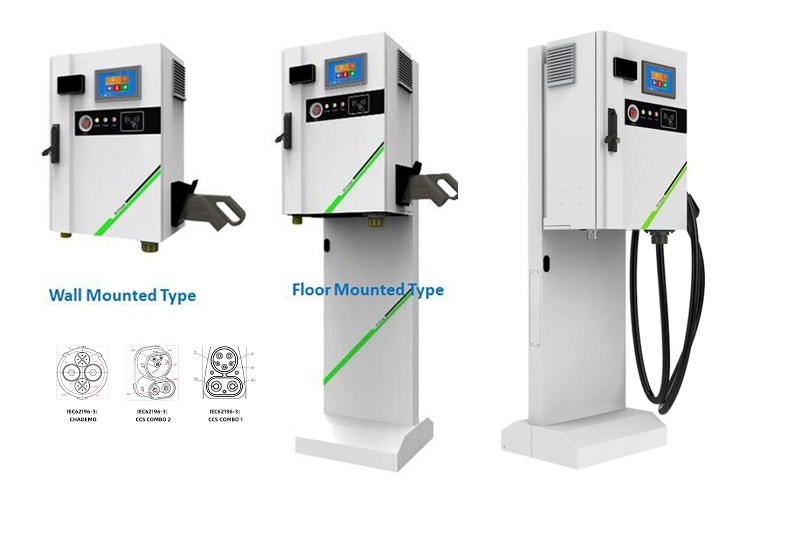
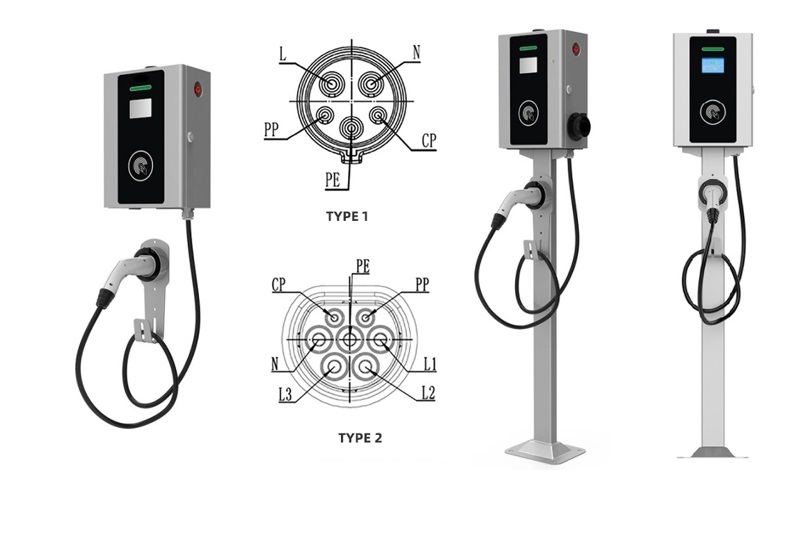
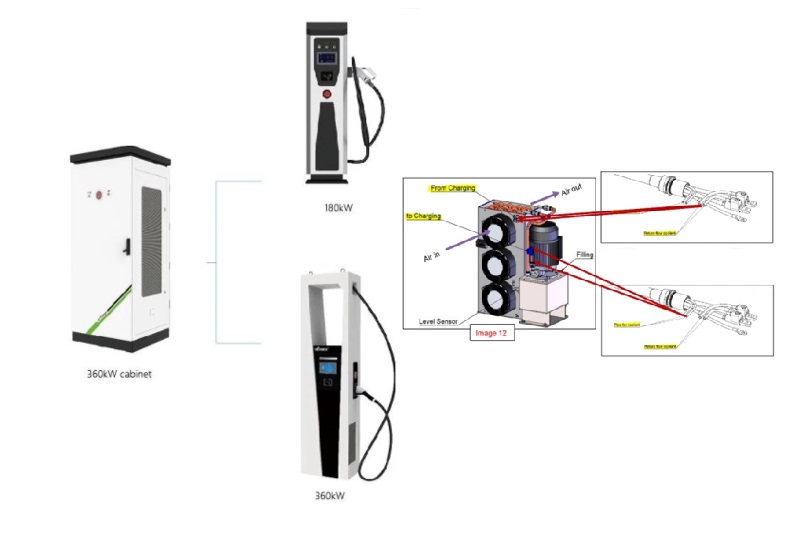
Who Has the Most EV Charging Stations
[ez-toc]
Who Has the Most EV Charging Stations? Over the past decade, the electric vehicle charging industry has undergone a remarkable transformation, fueled by innovative enterprises that have pushed the boundaries of infrastructure. Their efforts have birthed expansive charging networks spanning the globe. Collaborating with an EV charging company can serve as a gateway to leadership within this rapidly expanding sector. However, it’s important to note that the market has experienced an influx of companies vying for attention. Amid this buzz, knowing the major players and their endeavors becomes pivotal for those already in the industry or considering entry. We’ve distilled the options to the prime contenders, presenting a compilation of the foremost electric vehicle charging companies currently making waves in the market.
Biggest EV Charging Companies in 2023:
1. Electrify America: The Leading Fast Charging Network for EVs
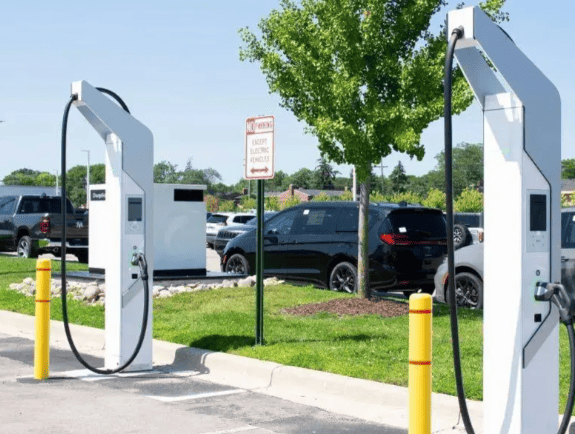
When it comes to DC fast charging networks, Electrify America takes the crown, catering to a wide array of EV models. They embrace all EVs equipped with a CCS charging connection, which is the industry standard. Even the few vehicles like the Nissan Leaf that still rely on CHAdeMO can utilize Electrify America for now. Tesla vehicles, sporting their own unique connector in the US, can tap into Electrify America and other DC fast charging networks through a CCS adapter.
For rapid charging, Electrify America stations are the cream of the crop in the nation, doling out a generous 350 kW of electricity in an hour. This speed outpaces the capacity of any current vehicle on the market, albeit not by much. A notable exception is the Lucid Air, which can gulp up to 300 kW.
If your vehicle can handle more than 100 kW of charging power, you’re in for a treat at an Electrify America station – charge times often hover around half an hour or less. And with the imminent arrival of vehicles capable of handling over 200 kW, the charging experience will edge closer to what we’re used to at gas stations.
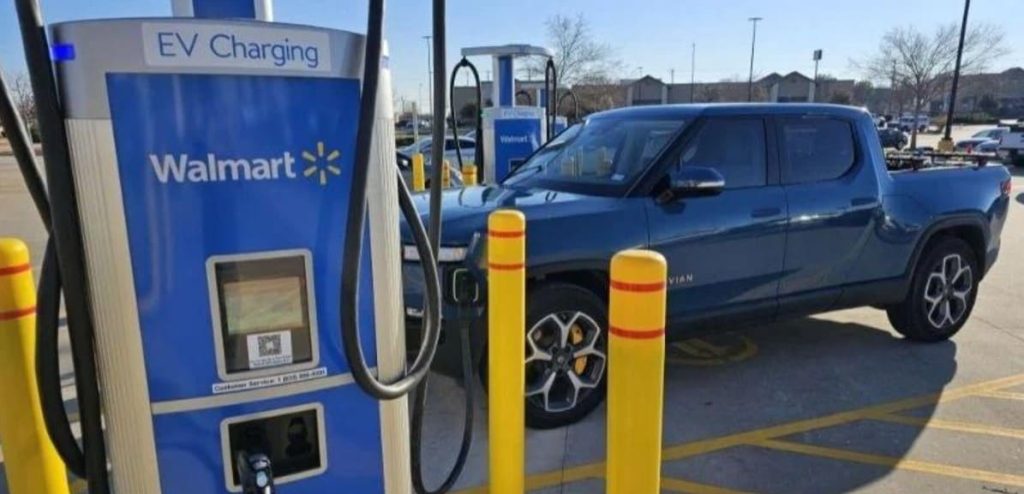
These charging stations are strategically situated near highway exits, frequently nestled in partner store parking lots like Walmart or Sheetz. You have the option to kickstart and settle your charging session using their app, or simply swipe your credit card.
For Nissan Leaf owners, there’s a tad bit of a gamble with Electrify America. While multiple stations usually grace each location, only one boasts a CHAdeMO port. If another car is occupying that station – even if they’re not utilizing the CHAdeMO port – patience becomes your ally until they move on.
2. Tesla Superchargers
When it comes to charging infrastructure, Tesla’s Supercharger network claims the throne as the largest in the country. Notably, the stations are spaced closer together compared to Electrify America’s. The hitch, however, is that currently, only Tesla vehicles can tap into this network. Nevertheless, given Tesla’s dominant position in the EV market, a significant chunk of electric cars cruising the roads can conveniently recharge at Supercharger stations.
The hallmark of the Supercharger network is the seamless and hassle-free charging experience it offers. Since Tesla already possesses your payment details, all you need to do is plug the charger into your car, and the charging dance commences automatically. In fact, this process flows even smoother than a traditional gas pump. The flip side? If you don’t sport a Tesla account, you’re out of luck regarding charging at Supercharger stations – a scenario some privacy-conscious individuals might lean toward.
Tesla Superchargers boast a slightly lower maximum speed compared to Electrify America’s, but this discrepancy remains mostly a theoretical restraint for now. The swiftest Superchargers theoretically hit the 300 kW mark, although they are currently capped at 250 kW. This pace outstrips the capabilities of the majority of vehicles on the road, regardless of whether they’re Tesla or another brand.
In a bid to foster inclusivity, Tesla is currently toying with the notion of opening up the Supercharger network to non-Tesla vehicles. This ambitious endeavor is undergoing testing beyond US borders. Should this come to fruition, it would mark a significant stride toward a future where any fast-charging-capable EV could seamlessly charge at any DC fast charging station, ushering in a new era of EV accessibility.
3. EVgo:
The realm of DC fast charging stretches far beyond road trips – consider those of us who reside in areas where home charging isn’t feasible. In such scenarios, the necessity for conveniently placed fast chargers within our towns becomes evident. This is precisely where EVgo steps in, reigning as the largest DC fast charging network in the United States, catering precisely to this demand.
EVgo’s charging stations typically operate at around 50 kW. This translates to an approximately one-hour charge time to reach the 80% mark. While this might seem lengthy for multi-stop road journeys, it’s actually quite reasonable when you’re juicing up while running errands, shopping, or indulging in a restaurant meal. Interestingly, for certain vehicles, EVgo matches their charging speed to the vehicle’s capability – the Chevy Bolt is a prime example. For Bolt owners, the charging experience remains consistent, whether they’re at an Electrify America station or utilizing EVgo.
Naturally, EVgo provides an app to streamline the charging process, but they also extend the courtesy of accepting credit card swipes. One standout feature is that EVgo is exceptionally friendly for cars equipped with a CHAdeMO port. At every EVgo station, there’s a carefully balanced provision of one CCS and one CHAdeMO plug. This ingenious arrangement signifies that, at a charging location with four stations, there are a grand total of four potential spots for charging – a boon, particularly for Nissan Leaf owners or any CHAdeMO-enabled vehicle users.

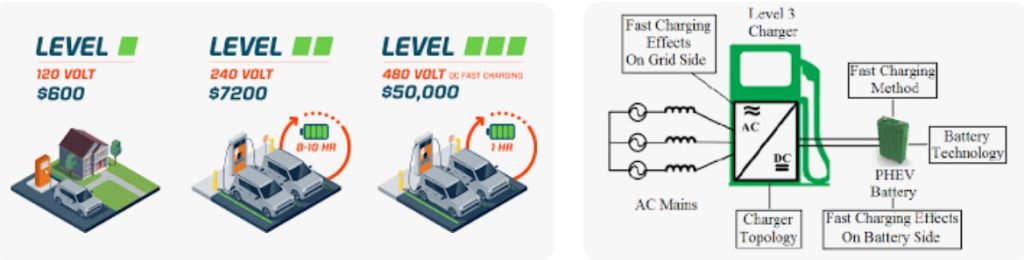
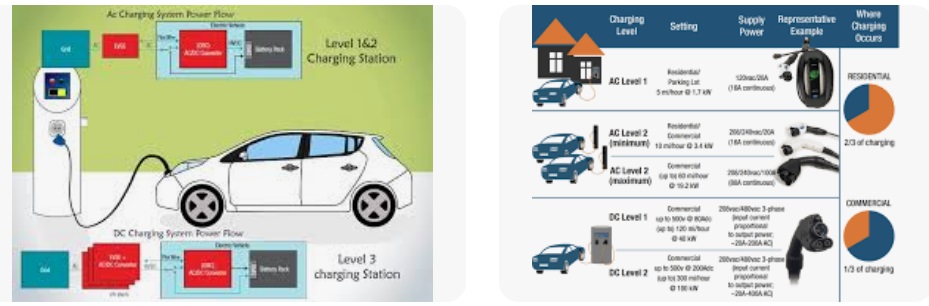
4. ChargePoint: A Diverse Charging Network Tailored for Longer Stays
When it comes to the scale of charging networks in the US, ChargePoint takes the lead, yet its landscape is distinct in its approach. While it boasts an expansive network, it’s worth noting that a sizable portion of these are not DC fast charging stations. Instead, ChargePoint stations lean toward offering approximately 6.6 kW of electricity per hour, falling within the realm of Level 2 charging achievable through a 240V outlet or a home charging station. This translates to roughly 25 miles of driving range added per hour.
ChargePoint adopts a unique business model that distinguishes it from the aforementioned examples. You’ll stumble upon these stations at various locations such as apartment complexes, hotels, retail stores, and other commercial establishments. They might also pop up at places like public libraries or parks. These are destinations where you tend to spend several hours, allowing your vehicle ample time to recharge significantly during your stay.
While ChargePoint’s emphasis leans toward Level 2 charging, it does feature a subset of DC fast chargers within its network. While they might not reach the swiftness of Electrify America or Tesla chargers, some of these stations do come relatively close. While you might stumble upon the occasional 125 kW fast charger, more commonly, you’ll encounter ones capable of 24 kW to 62 kW. To locate these speedier options through the app or website, you’ll need to sift through the majority of Level 2 chargers that make up the ChargePoint network.
5. Blink: A Noteworthy Network with a Lean towards Level 2 Charging
While not reaching the scale of ChargePoint, Blink stands as another significant charging network, predominantly centered around supplying Level 2 chargers. These chargers are commonly found at hotels, various businesses, and similar locales. A notable development came about when Blink acquired SemaConnect, a similarly sized charging network, substantially expanding their coverage nationwide. While such consolidation might not appeal to everyone, it does mean you’re dealing with one less charging app to clutter your device.
Similar to ChargePoint, the Blink network does include a handful of DC fast chargers. However, the selection here is quite modest. The availability of Blink fast chargers is limited, and those that do exist usually deliver around 50 kW of power.
Blink is the sort of charging network you’re less likely to actively seek out. Instead, you’re more apt to stumble upon it, finding it as the sole charger available at a place you’ve decided to visit. Of course, if you’ve already got the Blink app installed, you’re all set to take advantage of their charging offerings.
6. Wallbox: Melding Style and Function for EV Charging Excellence
In the world of EV charging solutions, Wallbox stands out not only for its sleek and refined design but also for its innovative approach that bridges the gap between EV drivers and energy management. This dynamic approach not only facilitates charging but also nurtures a more harmonious connection between homeowners and the energy grid.
The company’s ingenuity lies in its lateral thinking about how customers wish to engage with EV chargers. This innovative mindset translates into Wallbox’s distinctive blend of style and performance, resulting in a charging solution that’s not only efficient but also seamlessly integrates with the modern driver’s needs.
7.Allego: Allego‘s Drive to Expand Charging Availability
The central focus revolves around ensuring that charging solutions are accessible to everyone. Enter Allego, the Dutch enterprise at the forefront of propelling the widespread availability of public charging. With operations spanning across 16 countries, Allego has managed to blanket 1.5 billion kilometers of roadways with its expansive network. This network comprises over 40,000 sockets, providing EV drivers with the opportunity to charge their vehicles in an array of locations.
8. ChargersGO: Pioneering Charging Excellence
Hailing from Shanghai, this Chinese charging trailblazer is resolute in its quest to lead the way in this dynamic industry. ChargersGO stands out as one of China’s swiftest-growing service providers, offering a range of options that seamlessly blend both online and offline accessibility.
9. ADS-TEC Energy
Nestled in Ireland, ADS-TEC Energy is leading the charge towards a future less reliant on fossil fuels. Their focus is on embracing electrified solutions, decentralizing energy systems, and orchestrating intelligent, cross-sectoral systems that capitalize on the power of renewable energy sources.
At the core of their offerings, ADS-TEC Energy provides ingenious smart grid solutions and a robust storage-based platform. These innovations play a pivotal role in driving the broader adoption of sustainable energy and propelling the evolution of environmentally friendly transportation.
10.BP Pulse
A familiar presence along UK roadways, BP Pulse emerges from a legacy rooted in petroleum-related endeavors. Drawing upon this rich history in the energy sector, the company has embarked on a transformative journey towards a more sustainable future, powered by renewable energy sources.
This transformation translates into an imminent offering of home and public installations spanning the UK. With plans encompassing over 50,000 home wall chargers and an extensive network of public charge points, including rapid and ultra-fast charging alternatives, BP Pulse is paving the way for a greener and more efficient driving landscape in the UK.
11. Compleo Charging Solutions AG
Following in the footsteps of renowned automotive manufacturers, Compleo Charging Solutions emerges as a German powerhouse, ushering in a range of charging solutions for public, commercial, and residential needs.
Yet, their contribution goes beyond just hardware. The company takes on the mantle of educating both EV drivers and enterprises interested in setting up charging points. This role is fulfilled through their Compleo Academy, imparting comprehensive knowledge about the intricate world of EV charging. With a mission to be a comprehensive destination, Compleo positions itself as a ‘one-stop-shop’ for an array of esteemed businesses, offering cutting-edge solutions for their diverse charging requirements.
12. ABB
ABB, a company hailing from Sweden and Switzerland, has established a significant presence in the electric vehicle (EV) charging domain. With a global reach, the company offers charging solutions for homes, businesses, and vehicle fleets. This widespread availability has been a key driving force behind ABB’s remarkable expansion. One of ABB’s notable strengths lies in its extensive experience across various technological domains, which has provided it with a substantial repository of knowledge to draw upon.
During the nascent stages of the EV charging industry, ABB gained prominence as the foremost producer of DC fast chargers. Today, their product portfolio has expanded to encompass a comprehensive array of offerings, including Level 2 chargers.
13. Key Points:
ABB’s origins trace back to 1988 when it emerged from a merger. However, both of the merging entities had their inception in the late 1800s as manufacturers of electrical equipment.
ABB boasts a workforce of over 105,000 employees, according to the company’s own records.
In January 2023, a significant milestone was achieved as ABB celebrated the sale of its one-millionth EV charger. Additionally, the company revealed plans for a new manufacturing facility in the United States, geared towards producing an impressive 10,000 DC fast chargers annually.
14.Eaton
Eaton, a significant player in the realm of electric vehicle charging, boasts a workforce of over 85,000 individuals worldwide. Impressively, the company achieved sales totaling $20.8 billion in the year 2022. With its origins dating back to 1911, Eaton has progressively evolved into a prominent force in the electric vehicle charging sector. However, the company’s interests extend beyond just electric vehicle charging, encompassing a broader engagement with the advancement of vehicle electrification technologies.
15. Key Points:
Although Eaton was established in the United States, its global headquarters are now situated in Dublin, Ireland.
Eaton is engaged in producing various components for the aerospace industry, serving both military and commercial aviation.
In 2012, Eaton initially introduced its line of electric vehicle chargers. After a hiatus from the electric vehicle charging industry in the late 2010s, the company re-entered the scene in 2022 with an all-new range of EV chargers, featuring software developed in collaboration with ChargeLab.
16.Siemens
Siemens, a major player in the electric vehicle charging sector, has garnered its substantial reputation through user-friendly installation procedures and solutions tailored for both homes and businesses. This success comes as no surprise, given the company’s steadfast commitment to providing scalable and user-intuitive charging networks that prioritize efficient charging rates.
17. Key Points:
Founder Werner von Siemens laid the groundwork for the company back in 1847 when he created the pointer telegraph.
The Siemens brand functions through three distinct entities: Siemens AG, Siemens Energy, and Siemens Healthineers. This organizational approach aims to empower each company to establish itself as a leading entity within its specific domain.
Notably, during the period when Siemens Energy became an independent entity, roughly one-sixth of global electricity generation relied on technologies developed by Siemens Energy.
18. Greenlots
Based in Los Angeles, Greenlots became a part of Royal Dutch Shell in 2019, yet retained its original name for a period. However, in November 2021, Greenlots disclosed its plans to adopt the new identity of Shell Recharge Solutions, a transformation set to take effect in early 2022. Operating with a footprint of approximately 550 fast-charging ports in the United States, the company has made significant strides.
Several Shell fuel stations have introduced Shell Recharge charging ports into their infrastructure. Additionally, an interesting development was the complete conversion of a gas station into a Shell Recharge station, although this occurred in the UK. Looking forward, it’s likely that Shell will eventually carry out similar conversions at some of its U.S. fuel stations, transitioning them into EV fast-charging hubs.
19.Francis Energy:
Francis Energy possesses and manages approximately 530 DC Fast Charging ports across the country. The company’s journey commenced with an EV fast-charging network that spanned the state of Oklahoma. Presently, it is actively engaged in various fast-charging initiatives across 24 states within the United States. The overarching objective of the company is to persistently extend its reach throughout the heartland of America, with the aim of alleviating concerns about limited driving range (range anxiety) and propelling the adoption of electric vehicles in regions where the charging infrastructure for EVs remains insufficient.
Amidst the rapid growth of the EV industry and the expansion of charging networks, a select few are making the most substantial impact in terms of public charging accessibility. This drive to facilitate more EV drivers is spurring accelerated innovation in charging solutions – not only in terms of quantity but also in the swiftness of power delivery.
These ten publicly-traded organizations stand as the driving force behind this transformative movement. Their contributions enable EV manufacturers to showcase their latest innovations while enticing consumers to increasingly embrace electric mobility.
US EV Charging Market
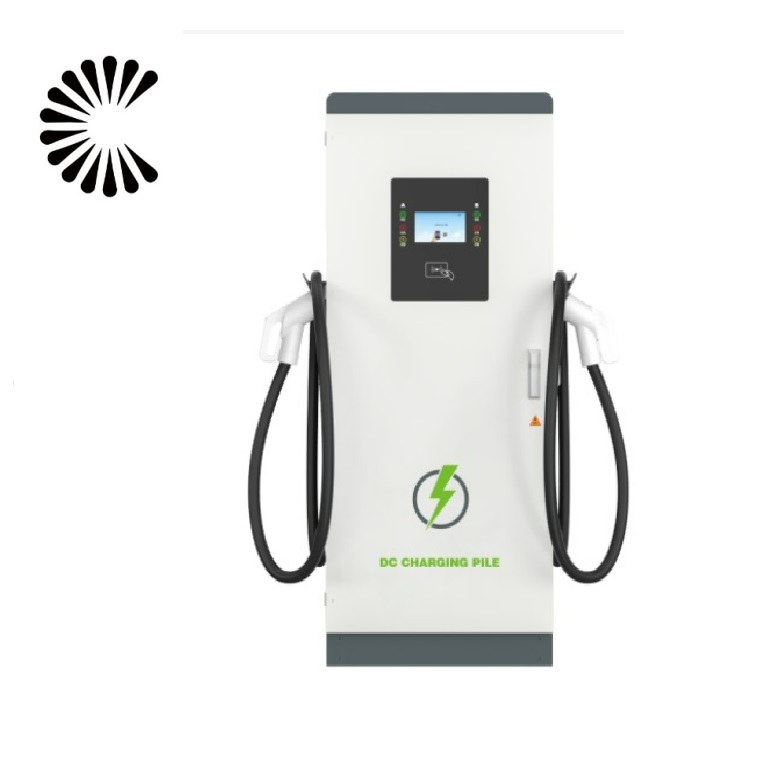
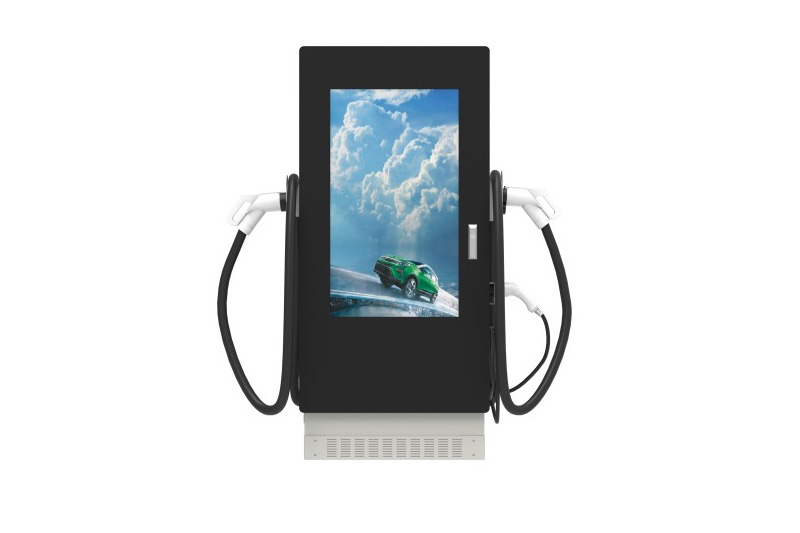
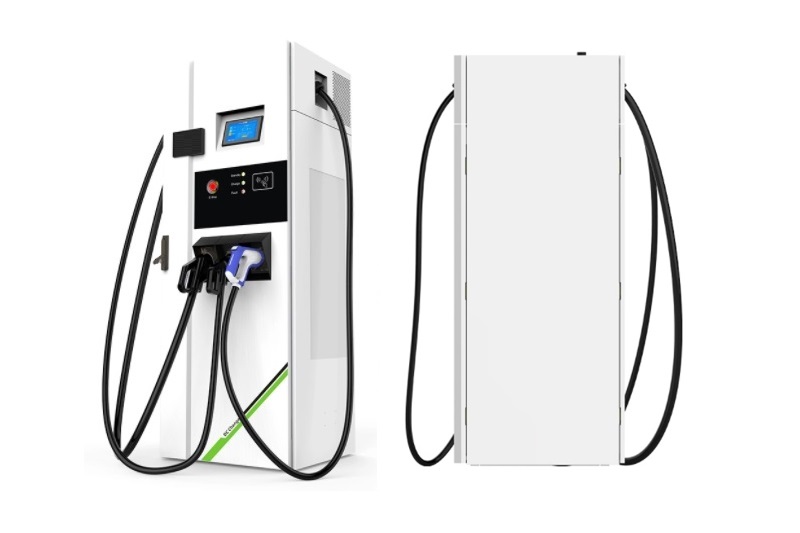
EV Chargers for Sale:
ChargersGO Factory Informations
Our EV Charger Factory Introduction:
| Business Type: | Manufacturer/Factory | Main Products: | EV Charger |
| Number of Employees: | 100 | Year of Establishment: | 2014.05 |
| Production Capacity | 5000Set/Year | After-sales Service: | Technical Support; on-line teach lessons |
| R&D Capacity: | ODM, OEM | Annual Output Value: | US$5 Million – US$10 Million |
| No. of R&D Staff: | 5 | No. of Production Lines: | 6 |
ChargersGO Factory is a reputable manufacturer specializing in Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers. Our extensive product range includes slow chargers, fast chargers, DC EV Chargers, AC EV Chargers, commercial EV Chargers, home chargers, and EV chargers of various levels, including level 1, level 2, and level 3. All our products adhere to strict China GMP design standards, ensuring top-notch quality and performance. Additionally, we take pride in securing various certifications to ensure the reliability and safety of our chargers.
Business Philosophy:
“Quality is the main policy of sales” and “integrity is the principle of success” are the business philosophy of our people. We carry out one-year warranty, lifelong maintenance service, with technical consultation and other services, and long-term supply of equipment. Welcome new and old customers to negotiate cooperation!
Production Process:
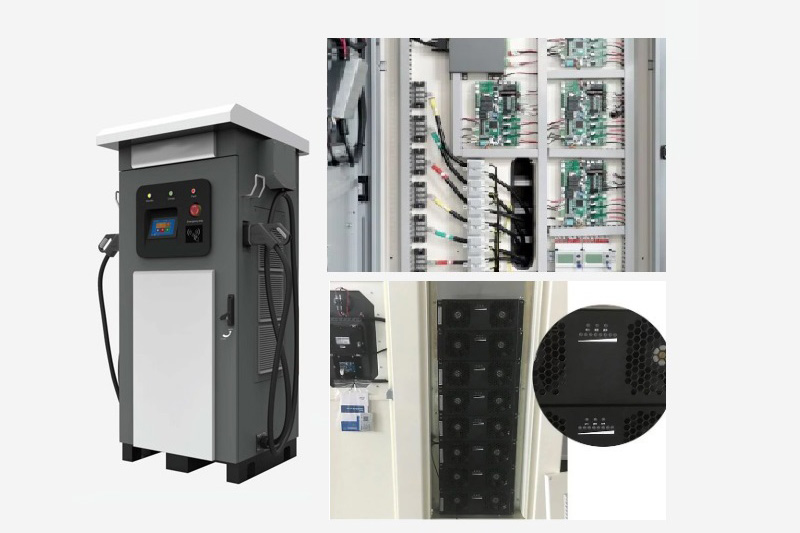
The production of an Electric Vehicle (EV) charger entails a meticulous process aimed at delivering top-notch quality, safety, and performance. It involves several essential stages:
By adhering to this comprehensive production process, EV charger manufacturers ensure that their products are efficient, reliable, and safe, contributing to the broader adoption of electric vehicles and sustainable transportation.
By following a well-structured production process and adhering to strict quality standards, manufacturers can produce high-quality EV chargers that contribute to the growth of electric mobility and a greener, sustainable future.

Certifications:

Small EV Charger Packing:
Retail and Wholesale Packaging of Small EV Chargers for Shipment
Retail Small EV Charger Shipment:
For retail orders, Small EV Chargers are shipped using express shipping methods.
Wholesale Small EV Charger Shipment:
For wholesale orders, Small EV Chargers are carefully packed in export fumigation-free wooden cases, suitable for bulk shipments or container transportation.
The primary objective of these packing measures is to safeguard the Small EV Chargers from any potential damage during sea shipment, ensuring they arrive at their destination in optimal condition. Employing correct packing procedures and utilizing high-quality materials minimizes the risk of harm during the journey.
Packing a Large EV Charger for Sea Shipment: Ensuring a Safe Voyage
Packing a large EV charger for sea shipment is a meticulous and demanding process, but with meticulous planning and precision, it can be done effectively to guarantee its safe arrival at the destination. Below are the essential steps a manufacturer may undertake when preparing a large machine for sea shipment:
Overall, packing a large EV charger for sea shipment demands precision and adherence to proper procedures. Employing high-quality materials and meticulous attention to detail ensures the machine’s safe and intact arrival at its intended destination. For added assurance, consulting a professional packing and shipping company can guarantee the machine is expertly packed and ready for its sea journey.


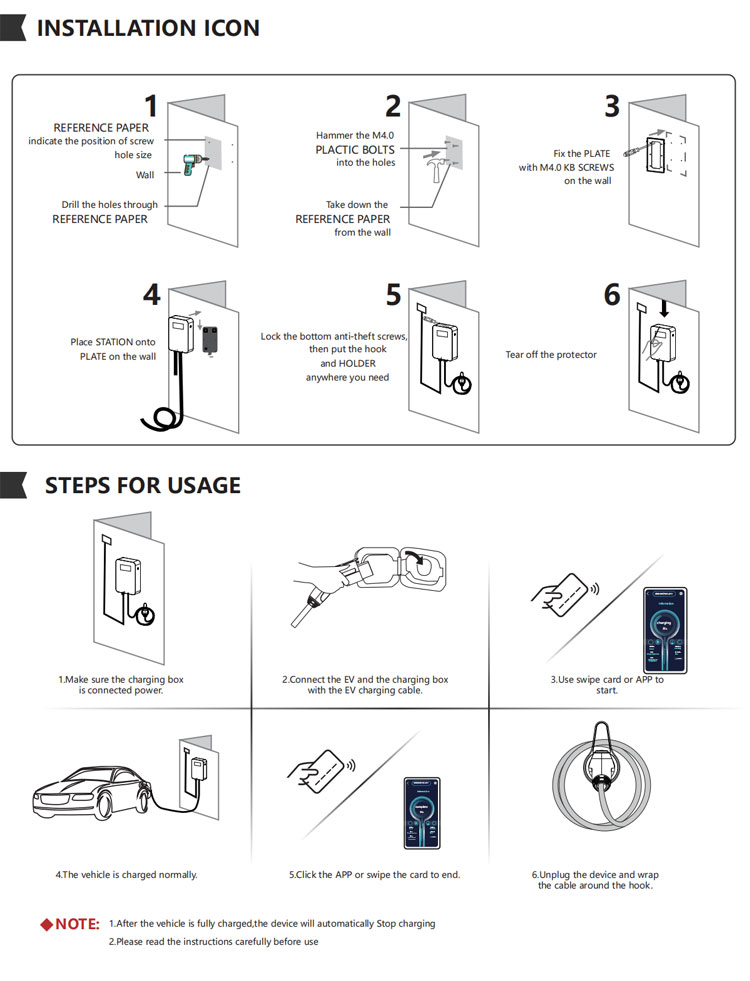
Installing an Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger requires careful planning and consideration to ensure a safe and efficient charging experience. Here is a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
It is crucial to have a licensed electrician perform the installation to ensure compliance with electrical codes and safety standards. Additionally, some EV charger manufacturers offer professional installation services, which can provide peace of mind and ensure a smooth and trouble-free installation process.
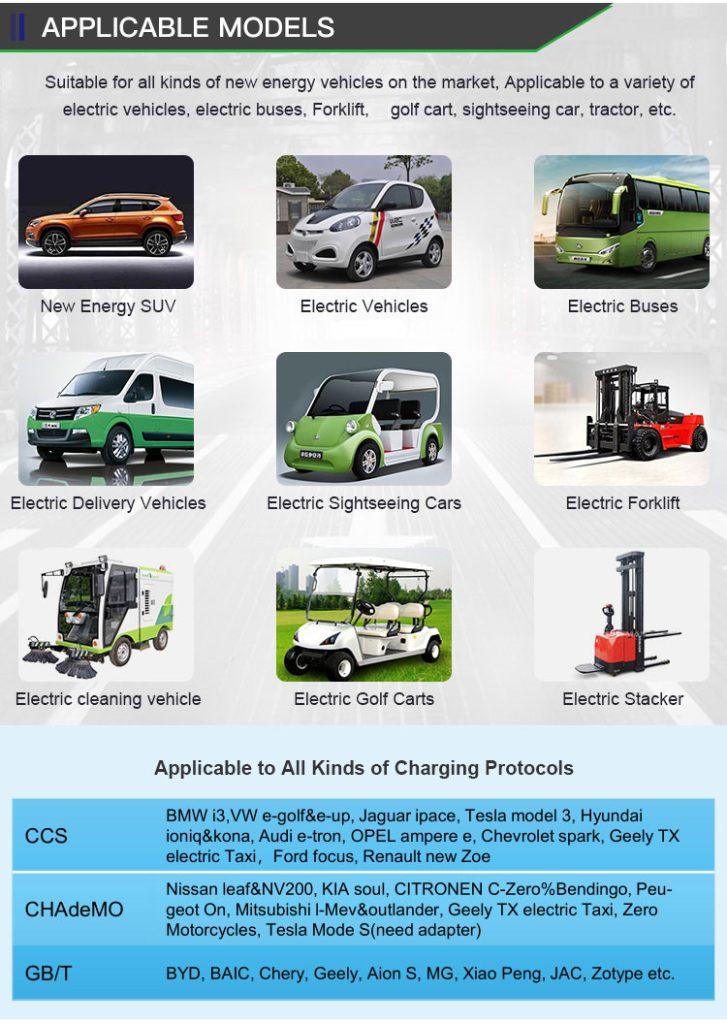
Applications of EV Charger:
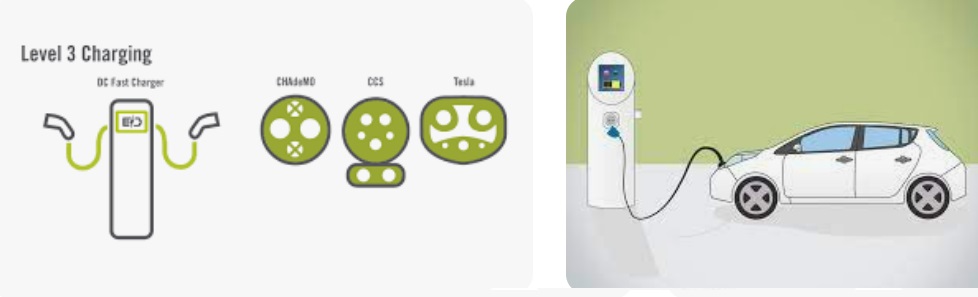
In essence, Level 3 EV chargers are vital for scenarios where EVs need to be charged quickly and efficiently to meet the demands of busy individuals, travelers, commercial operators, and public transportation services.
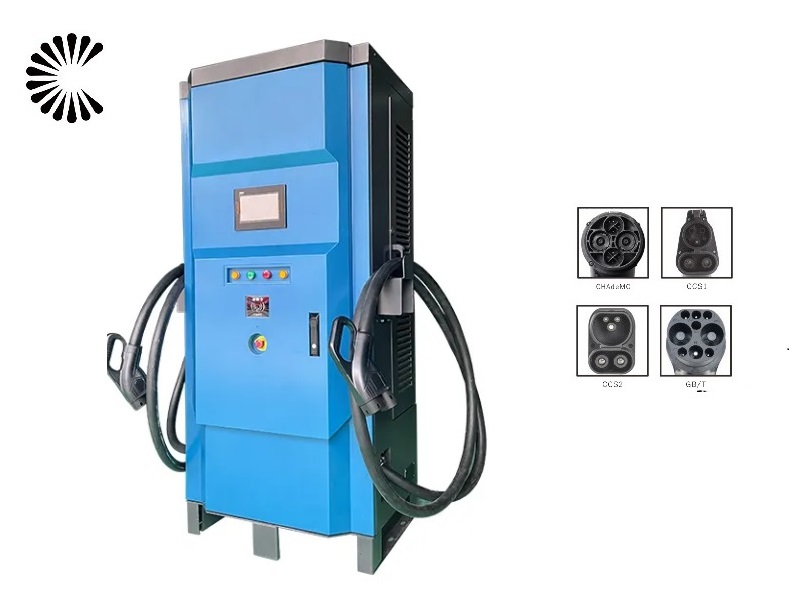
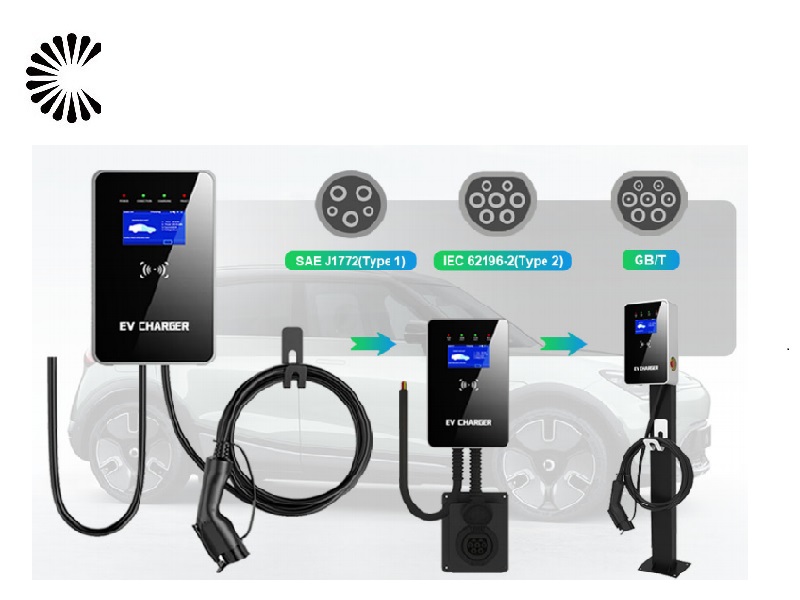
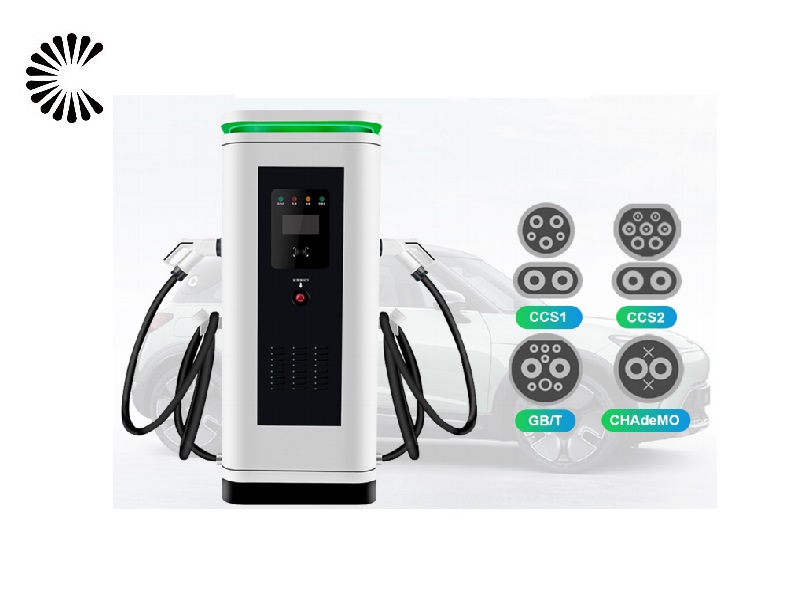
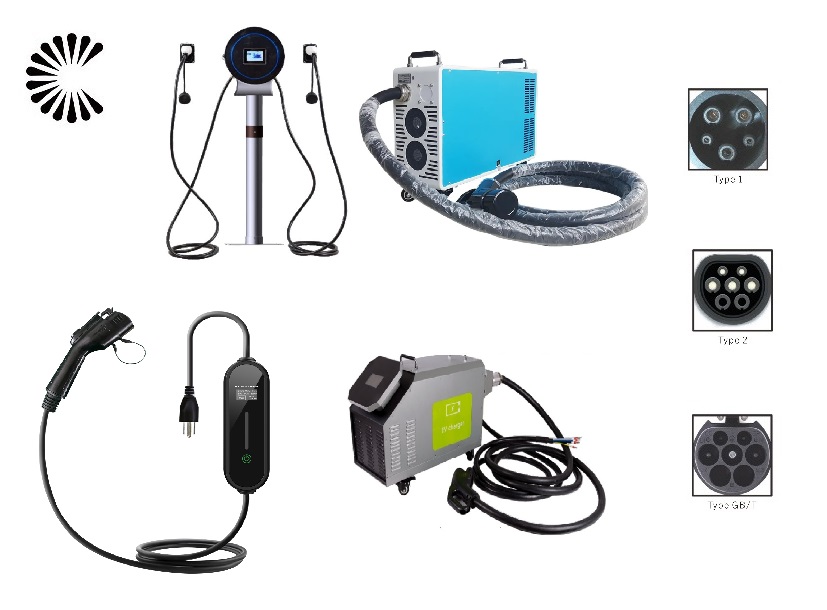
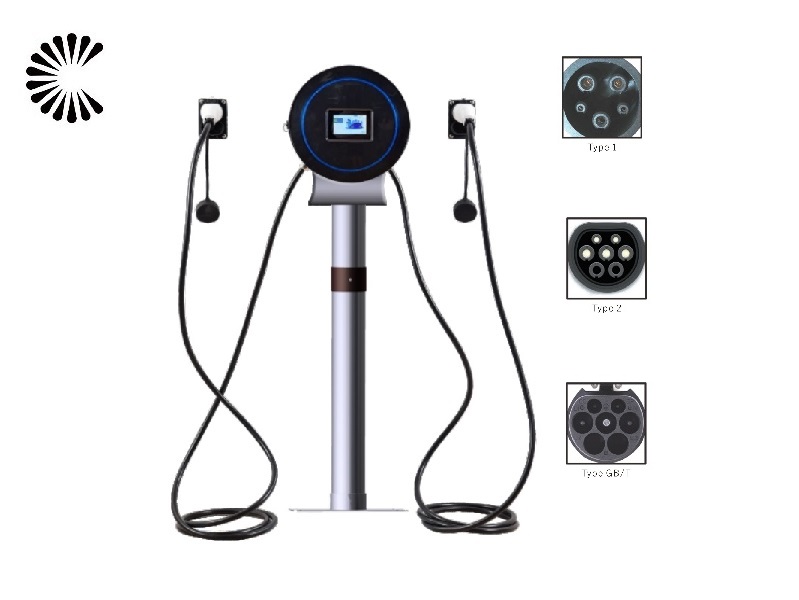
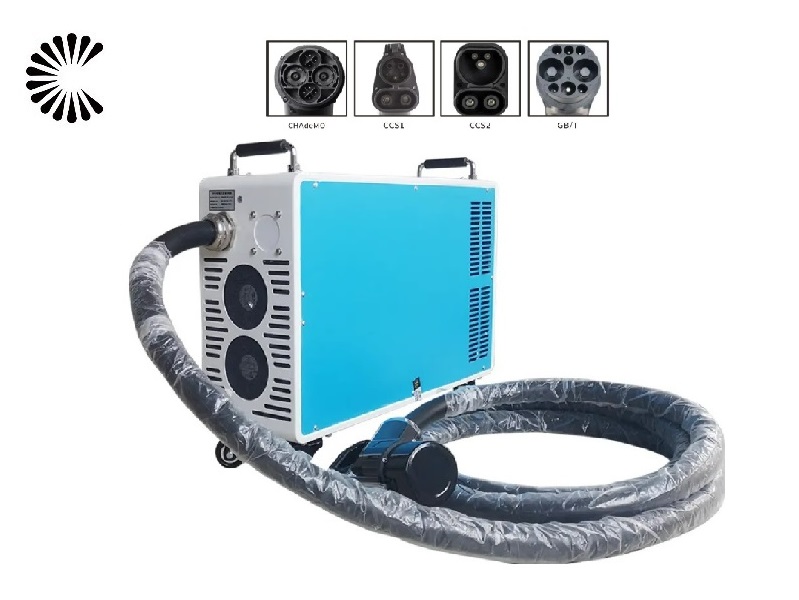
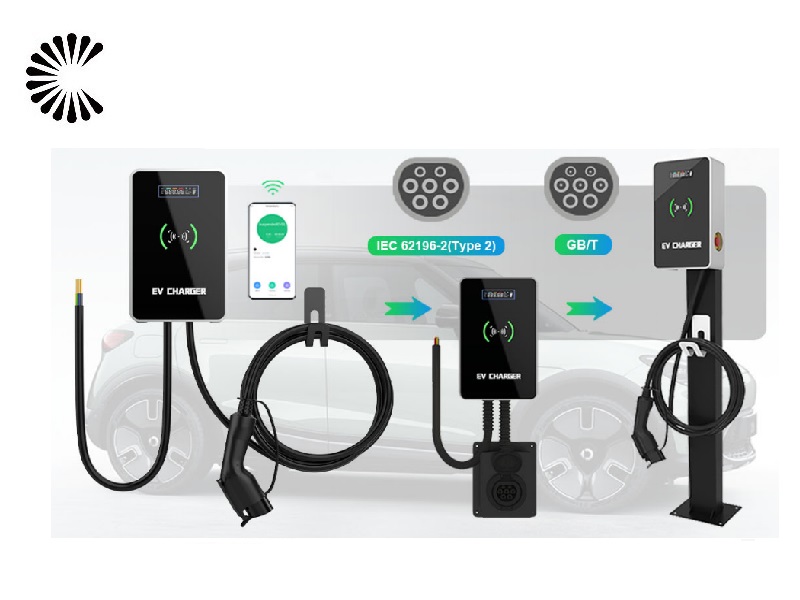
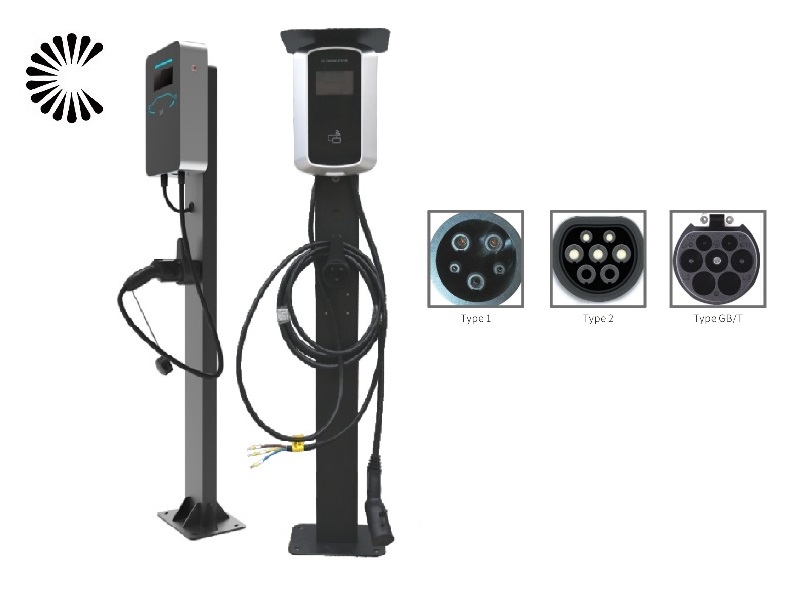
It is appplicable for all kinds of charing protocols, Suitable for all kinds of new energy vehicles on the market,Applicable to a variety of electric vehicles, electric buses,Forklift,golf cartsightseeing cartractor, etc.
| CHAdeMO | Nissan leaf&NV200, KIA soul, CITRONEN C-Zero%Bendingo, Peu geot On, Mitsubishi l-Mev&outlander, Geely TX electric Taxi,Zero Motorcycles, Tesla Mode S(need adapter) |
| CCS | BMW i3,VW e-golf&e-up, Jaguar ipace, Tesla model 3, Hyundai ioniq&kona, Audi e-tron, OPEL ampere e, Chevrolet spark, Geely TX electric Taxi,Ford focus, Renault new Zoe |
| GB/T | BYD, BAIC,Chery, Geely, Aion S, MG, Xiao Peng, JAC, Zotype etc. |
EV Charger Wholesale Manufacturer In China
Charging an Electric Vehicle (EV) involves refilling the energy stored in the EV’s battery. This is done by connecting the EV to a charging station or charger. ChargersGO is the manufacturer and wholesaler for EV Charger. Please feel free to contact with us.